Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-101
Lymph Node Exosomes Delivery Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Regulating PTEN-PI3K/Akt Pathway Mediated Myocardiocyte Apoptosis
By Shuaihua Qiao, Baochuan Wu, Rong Gu
Presenter
Shuaihua Qiao
Authors
Shuaihua Qiao1, Baochuan Wu2, Rong Gu2
Affiliation
Kings College London, United Kingdom1, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, China2
View Study Report
TCTAP A-101
Pharmacotherapy (Innovation)
Lymph Node Exosomes Delivery Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Regulating PTEN-PI3K/Akt Pathway Mediated Myocardiocyte Apoptosis
Shuaihua Qiao1, Baochuan Wu2, Rong Gu2
Kings College London, United Kingdom1, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, China2
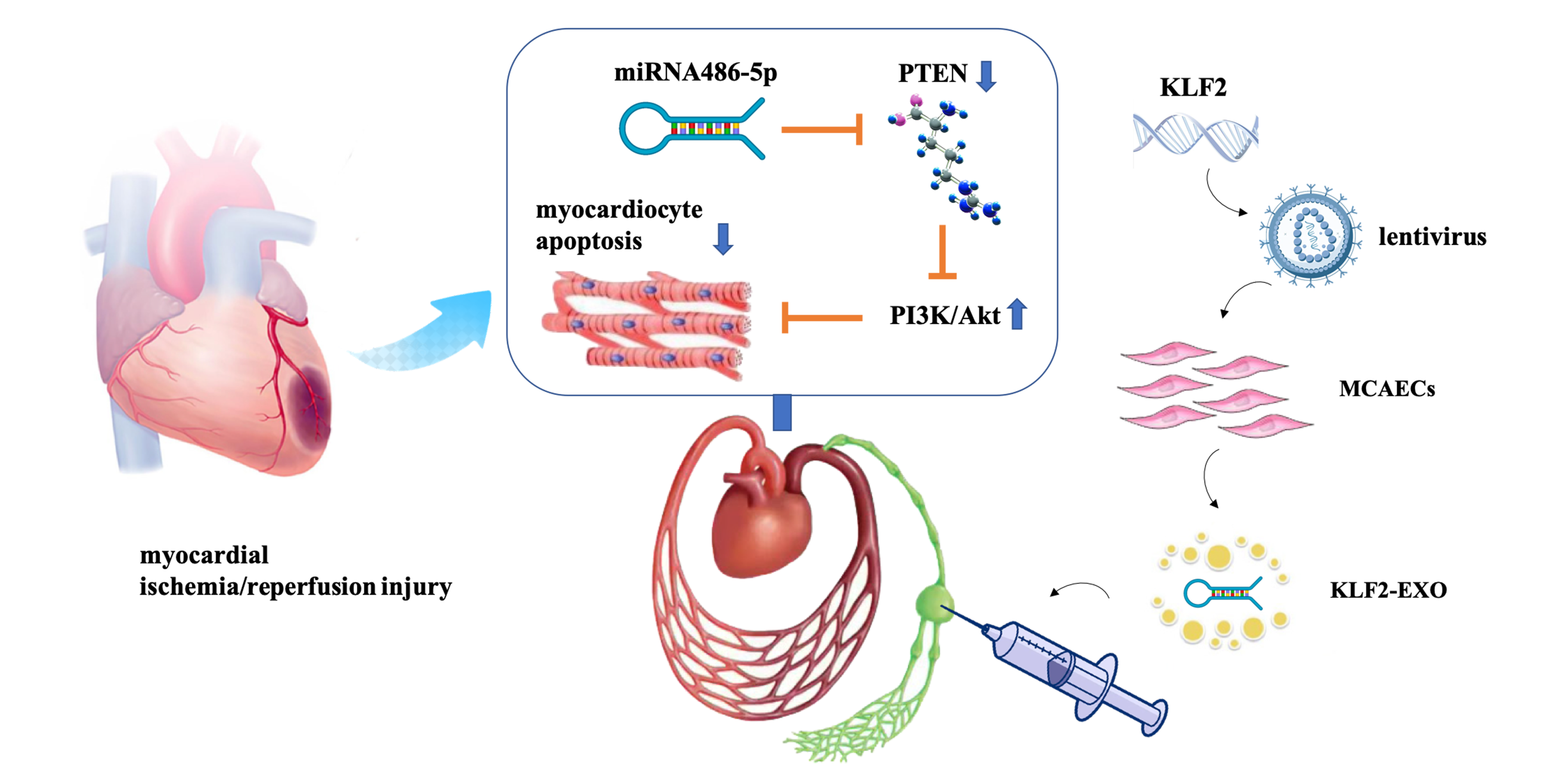
Background
The ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury followed acute myocardial infarction induces an excessive myocardiocyte apoptosis. Exosomes from KLF2-overexpressing endothelial cells (KLF2-EXO) dampened I/R injury effects in previous studies. The intra lymph node drainage pathway provides the heart with an alternative method for studying the therapeutic effects of exosomes. In the study, we would explore the role of intra lymph node injection of KLF2-EXO in myocardial I/R process.
Methods
The mouse coronary endothelial cells (MCAECs) were isolated from mouse coronary endothelium according to the previous protocol, and recombinant lentivirus vector assembled with KLF2 were transfected into MCAECs. Exosomes were isolated from the KLF2-overexpressing endothelial cells supernatant via gradient centrifugation and identified with particle size analyser, transmission electron microscopy and western blotting. The mice were applied to ischemia and reperfusion operation, and KLF2-EXO was administrated through intra inguinal lymph node injection. We conducted echocardiography to evaluate heart function, Evans blue/TTC staining and Masson trichrome staining to assess infarct size and fibrosis area. We labelled exosomes with CM-DiL and immunofluorescence staining revealed transfer and location of KLF2-EXO. MicroRNA microarray and bioinformatics analysis were applied to explore potent mediator, and then prediction of target genes and dual-luciferase reporter assay were used to confirm downstream pathway.
Results
MCAECs were isolated successfully from the mouse coronary endothelium of C57BL/6 mice, and exosomes as KLF2-EXO were isolated from KLF2-transduced MCAECs. Intra inguinal lymph node injection of KLF2-EXO attenuated myocardial I/R injury, including improved cardiac function, reducing infarct area and alleviating fibrosis. Further experiments revealed KLF2-EXO could be transported into heart and inhibited myocardiocyte apoptosis after I/R injury. MicroRNA-sequencing of KLF2-EXO implicated that miRNA-486-5p (miR-486-5p) was a potent candidate mediator that inhibited myocardiocyte apoptosis, and the miR-486-5p antagomir reversed the effect. Further bioinformatics analysis and confirmation experiments revealed PTEN functioned as a downstream target and the PTEN- PI3K/Akt pathway participated in the regulation of myocardiocyte apoptosis.
Conclusion
Our data demonstrated that intra lymph node injection of KLF2-EXO attenuated myocardial I/R injury in mice via delivering miR-486-5p to target PTEN- PI3K/Akt pathway, which restrained myocardiocyte apoptosis. KLF2-EXO could be an alternative therapy for myocardial I/R injury.