Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-038
Short Term Outcomes of Drug Coated Balloons (DCB) in Percutaneous Coronary Interventions: A Single Centre Experience
By Raja Ramesh Nukavarapu, Ramesh Babu Pothineni
Presenter
Raja Ramesh Nukavarapu
Authors
Raja Ramesh Nukavarapu1, Ramesh Babu Pothineni1
Affiliation
Aster Ramesh Hospitals, India1
View Study Report
TCTAP A-038
DES/BRS/DCB
Short Term Outcomes of Drug Coated Balloons (DCB) in Percutaneous Coronary Interventions: A Single Centre Experience
Raja Ramesh Nukavarapu1, Ramesh Babu Pothineni1
Aster Ramesh Hospitals, India1
Background
Drug-eluting stents (DES) have revolutionized coronary interventions, but their limitations, particularly in-stent restenosis (ISR) and stent thrombosis, remain significant concerns. To address these challenges, drug-coated balloons (DCBs) have emerged as a promising alternative strategy. While DCBs have established efficacy in treating ISR, their role in de novo lesions remains uncertain. The current prospective, single-center observational study aims to evaluate the safety and efficacy of DCB in various lesion subsets, including de novo lesions, to expand the understanding of its clinical applications. The primary objectives of this study are:
Methods
Study Design and Population
Results
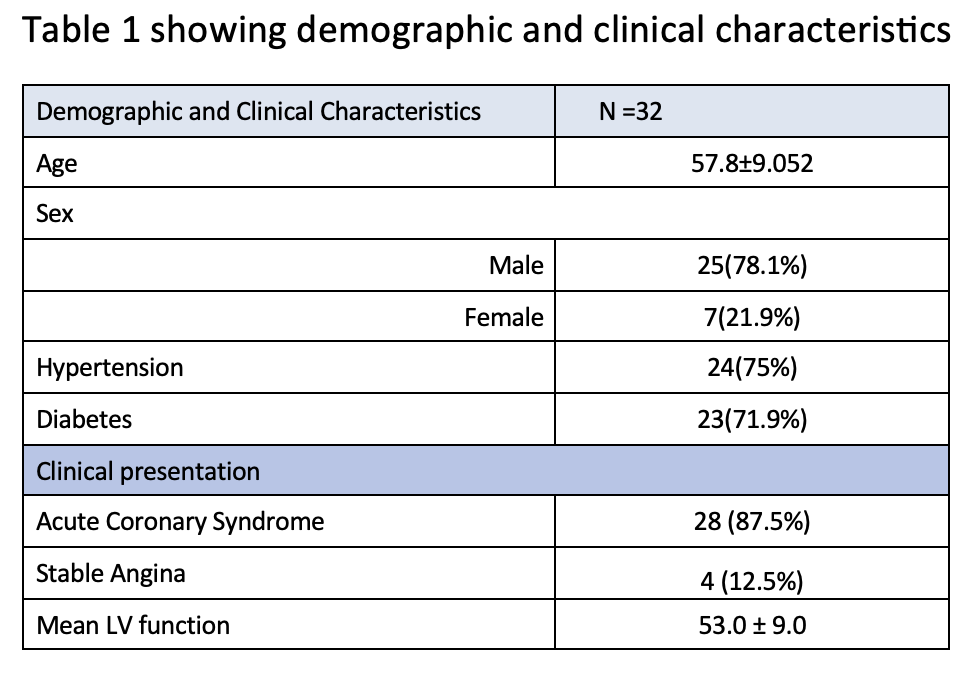
During the study period, a total of 36 lesions were treated with drug-coated balloons (DCB) in 32 patients. The mean age of the patients was 57.8 ± 9.05 years, with 25 (78.1%) males and 7 (21.9%) females. Hypertension was present in 24 (75%) patients, and diabetes was present in 23 (71.9%) patients.
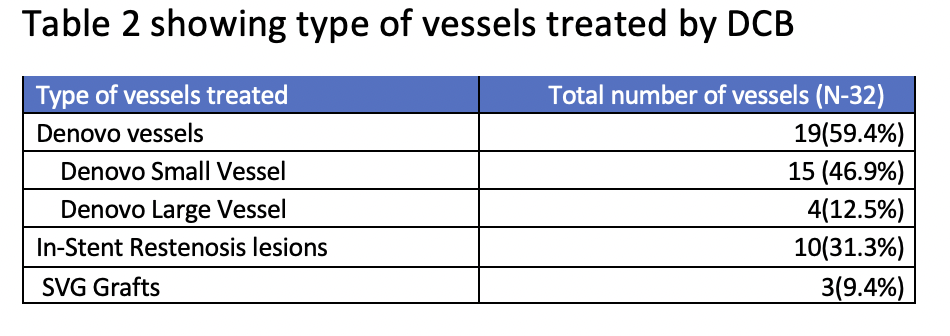
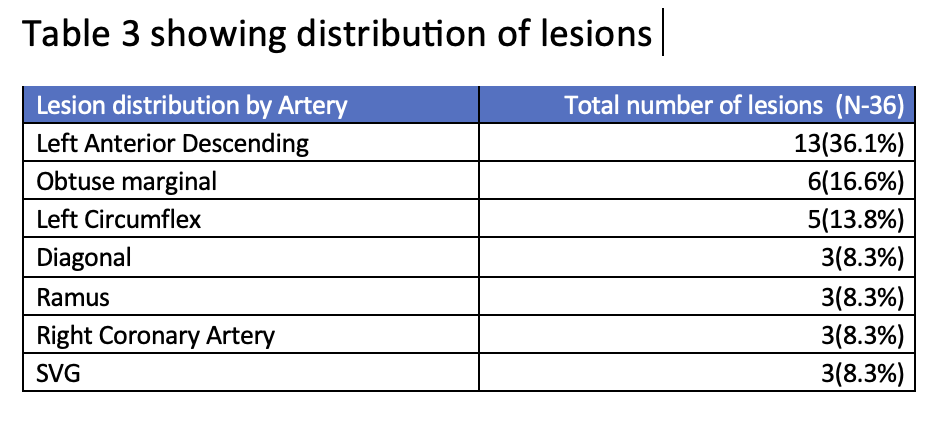



Conclusion
This prospective, single-center observational study demonstrates the efficacy and safety of drug-coated balloons (DCB) in various lesion subsets, including in-stent restenosis (ISR), denovo vessels (both small and large), and patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) and chronic stable angina.


