Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-102
Beyond Oncocardiology: Shaping and Redefining the Role of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Among Patients With Cancer
By Wei-Syun Hu
Presenter
Wei-Syun Hu
Authors
Wei-Syun Hu1
Affiliation
China Medical University Hospital, Taiwan1
View Study Report
TCTAP A-102
Pharmacotherapy (Innovation)
Beyond Oncocardiology: Shaping and Redefining the Role of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Among Patients With Cancer
Wei-Syun Hu1
China Medical University Hospital, Taiwan1
Background
Cancerpatients have high incidence of comorbid diabetes mellitus (DM). Once twoillnesses coexist; the situation would become very complicated, and the mortalityrate would rise in a relatively geometrically progressive manner. Given the recent clinical trials andadjustments in heart failure guidelines, favoring a more prominent role of sodium-glucosecotransporter-2 inhibitor (SGLT2I), studies into the efficacy and safety of SGLT2I indifferent populations are of great interest. Indeed, SGLT2I has gained disseminated role in recentadvancement in pharmacologic intervention for medical care beyond initial role asanti-diabetic agent.
Methods
Using Taiwan’s National Health Insurance ResearchDatabase to analyze the prognosis of cancer patients with coexisting DM,comparing those receiving SGLT2I with those who do not. After index-yearand matching (age, sex, some comorbidities and medications), the authors obtaintwo groups of 20,339 patients.
Results
The cancer patients withDM for SGLT2I users were at a lower incidences of all-causedeath than the non- SGLT2I cohort (5.05vs. 8.39 per 100 person-years), corresponding to adjusted HR values of 0.64 (95% CI= 0.60-0.68).
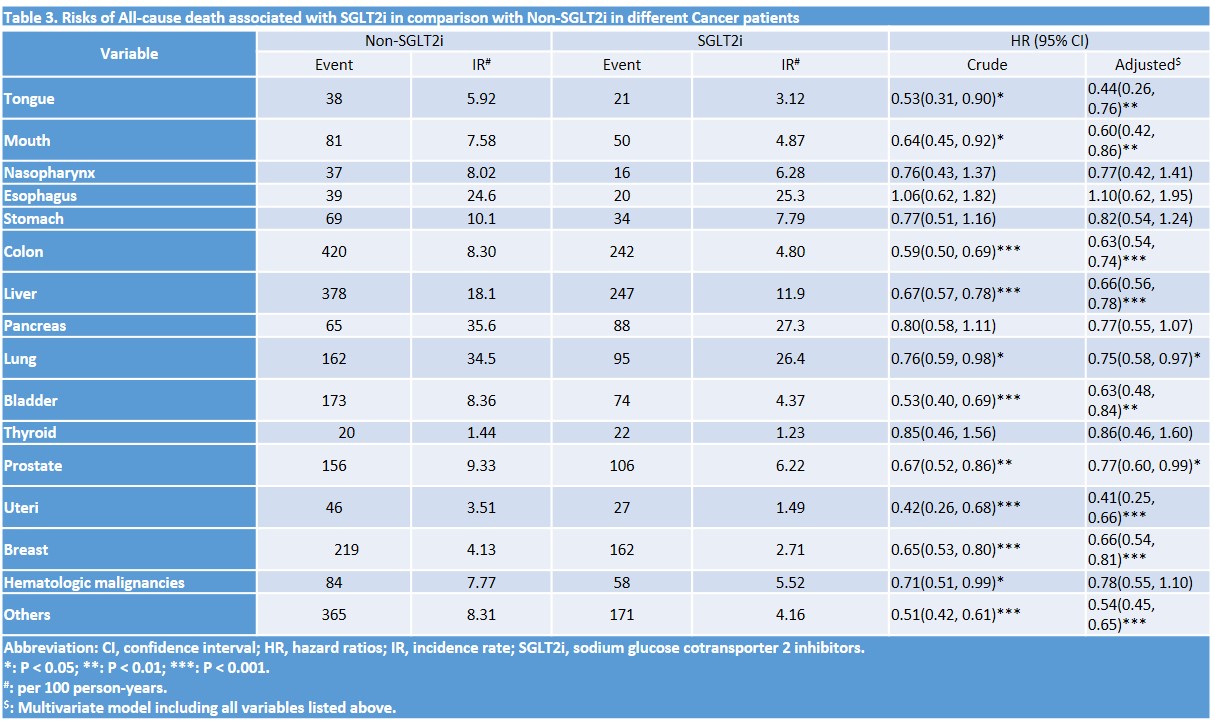

Conclusion
The majorfinding is that after performing Kaplan Meier analysis, SGLT2I users had a lower risk of all cause death,especially for those younger age. Interesting, uteri cancers tend to have ahigher protective risk reduction for death. Strengths of this study include theexamination of a clinically important outcome and a large sample size thatallows for the estimation of precise treatment effects. The concept is originaland important to the literature. Given thelargely number of patients in each group (20,339), the study is powered,especially considering the limited differences in baseline characteristicsbetween 2 groups.


