Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-101
A Tricky Case Report: Staged Intervention for Double Ostial Lesions
By Tung-Lin Tsui, Shih-Chi Liu
Presenter
Tung-Lin Tsui
Authors
Tung-Lin Tsui1, Shih-Chi Liu2
Affiliation
Camillians Saint Mary's Hospital Luodong, Taiwan1, Fu Jen Catholic University Hospital, Taiwan2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-101
Coronary - Complex PCI - Multi-Vessel Disease
A Tricky Case Report: Staged Intervention for Double Ostial Lesions
Tung-Lin Tsui1, Shih-Chi Liu2
Camillians Saint Mary's Hospital Luodong, Taiwan1, Fu Jen Catholic University Hospital, Taiwan2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
This 71-year-old female patient who has history ofESRD, DM, duodenal ulcers, gout, dyslipidemia, unstable angina, and ischemia heart disease. Previous coronary angiography showed left main coronary artery disease with critical stenotic lesions over the ostial area of both left circumflex artery and right coronary artery. The EKG showed normal sinus rhythm.
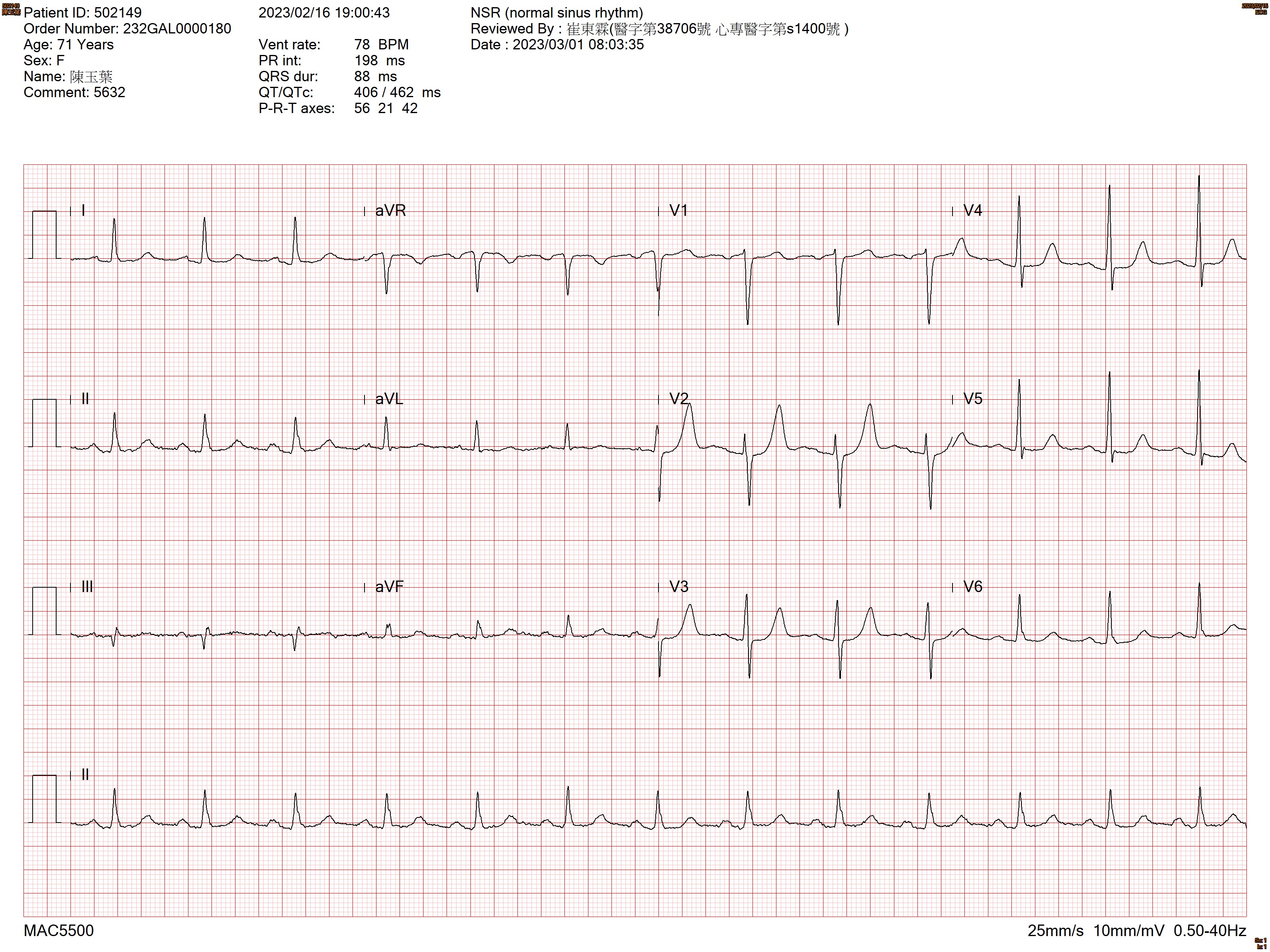

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
The Tl-201 myocardial perfusion SPECT scintiphotos: Severe IHD & myocardial ischemia in basal 1/2 inferior& basal 1/2 inferolateral (severereduction of uptake) and apical (definitely abnormal) walls of LV was demonstrated.
The first coronary intervention: DES x 1 for LMCA to distal LAD and DES x 1 for ostium to proximal LCX.


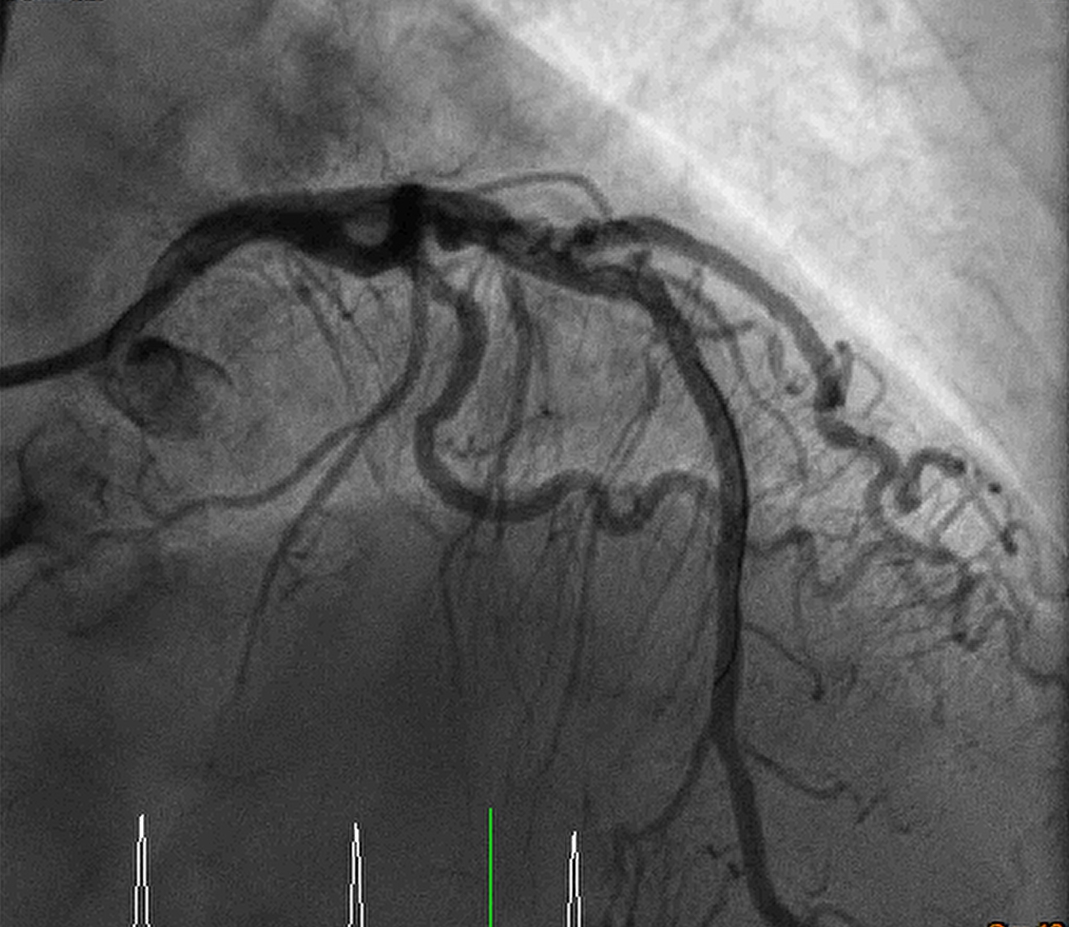
The first coronary intervention: DES x 1 for LMCA to distal LAD and DES x 1 for ostium to proximal LCX.



Relevant Catheterization Findings
1. PTCA for LAD lesion: Fielder FC wire to distal LAD. After 2.5x15 balloon dilatation, a DES (Biomime Morph 3.0-2.5x60) over distal LM to distal LAD. OS-P LAD instent area was dilated with NC 3.0x15. TIMI 3 flow was found over LAD. 2. PTCA for LCX lesion: Floppy wire with 1.0x5 balloon was wired to distal LCX. The OS-P LCX lesion was dialated with 2.75x20 balloon, and then DES 3.0x19 (Biomime) over OS-P LCX, final kissing balloon with 3.0x15 balloon over LAD and 2.75x20 balloon over LCX was done.
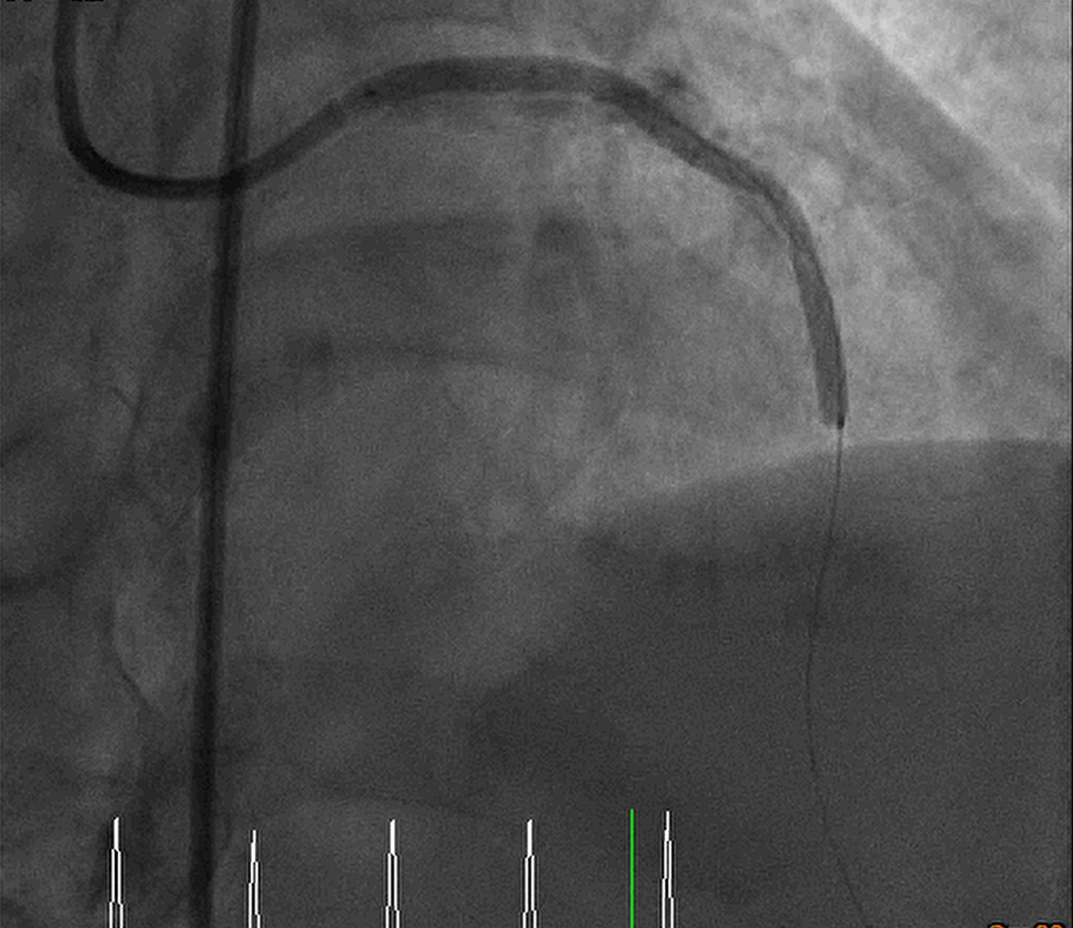
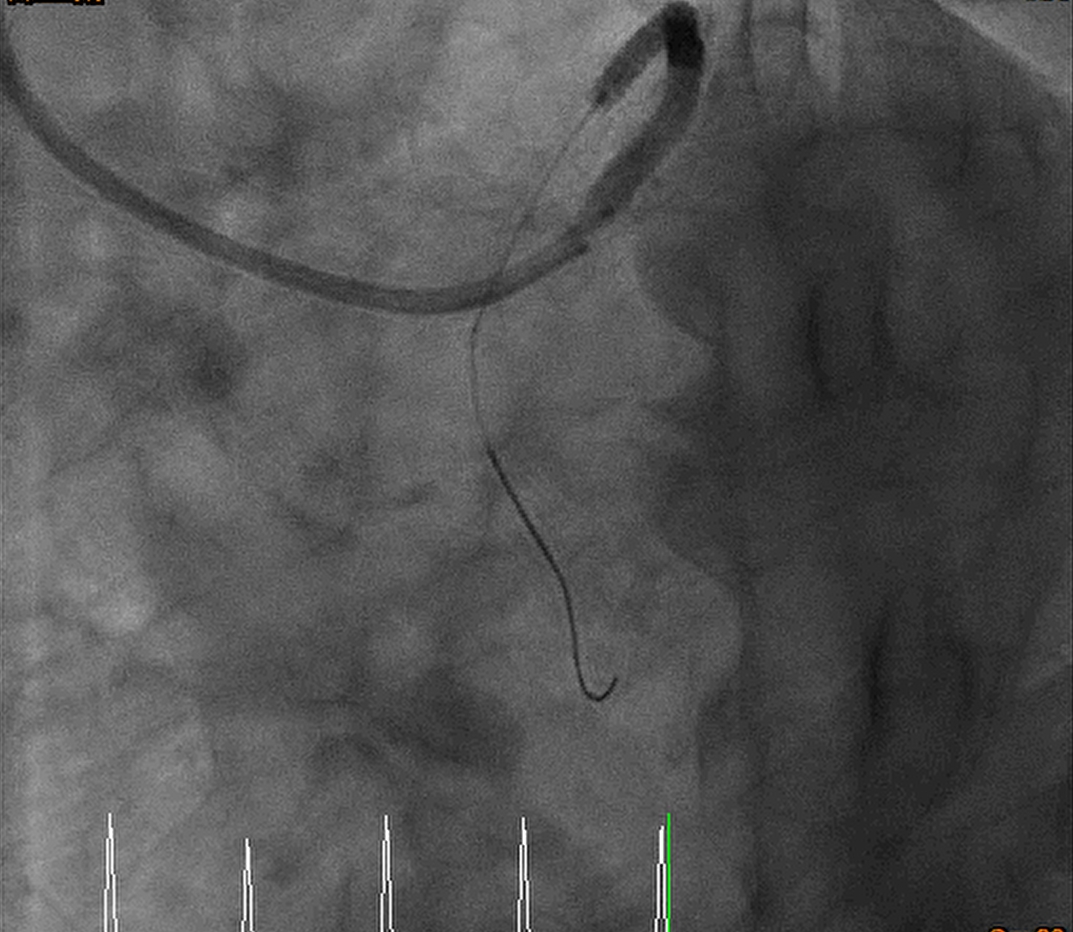
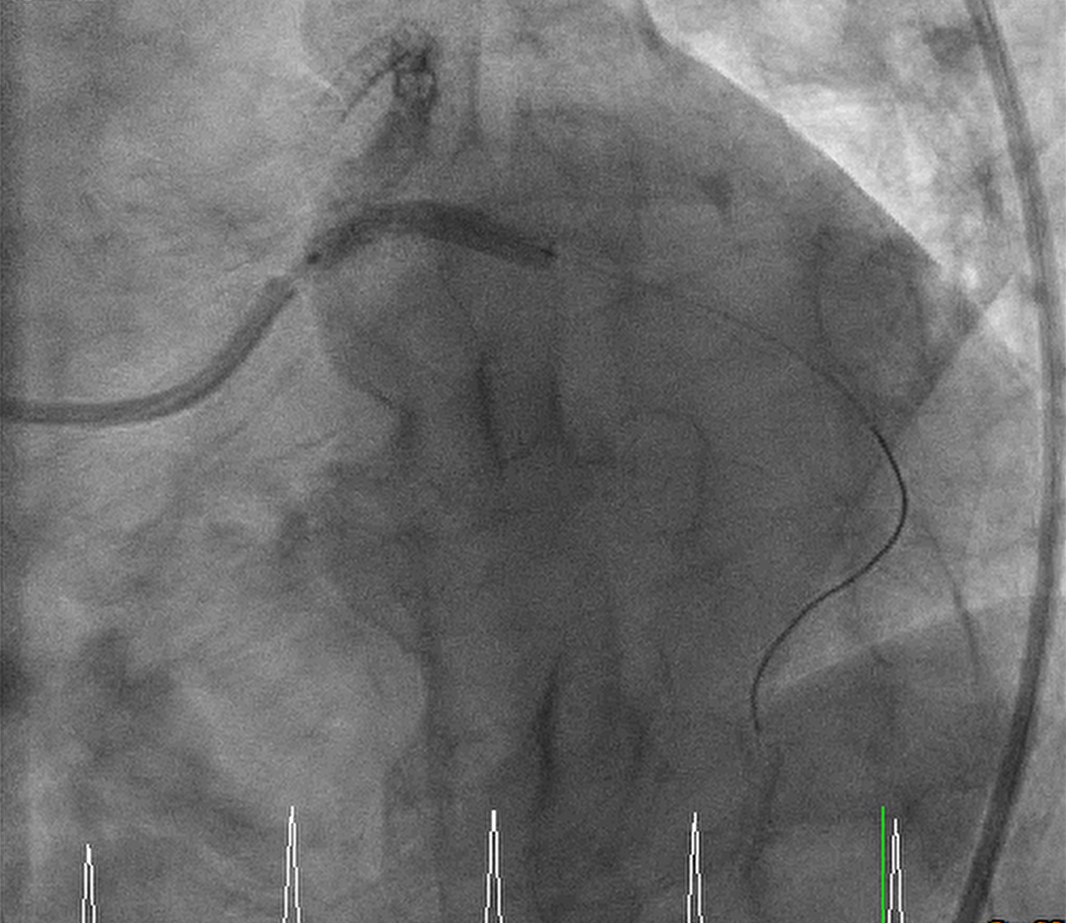



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Via left radial artery and righ femoral artery approach, PTCA for RCA OS-P functional CTO lesion was done step by step:
Guiding catheter: Retrograde: EBU 3.5 7F Antegrade: 1._SCR 3.5 6F_ 2._SAL 1.0 7F_ PTCA wire: 1._ASAHI Sion_ 2._Floppy_ 3._Fielder FC_ 4._ROTA wire_ 1. Transradial approach was arranged initially, antegrade approach was done but difficult guiding catheter approach and difficult retrograde approach was found, so we arranged the transfemoral approach. 2. Difficult retrograde approach was found even if finecross plus Fielder FC, and then we tried antegrade approach. 3. Via Finecross support, Asahi Sion was wired to distal RCA and Predilatation with 1.0x5 balloon but 2.0x15 balloon cannot pass the OS-P RCA lesion. 4. The Tornus 2.1Fr catheter was delivered and pass the OS-P RCA stenotic lesion and then dilated with 2.0x15 and 2.5x15 balloon. 5. Residual stenosis was still noted with heavty calcification, so 2.75x13 NSE scoring balloon was delivered and dilated with 6-12 bars. 6. Balloon dilatation with NCB 3.5x15 and then DES 3.5x19 over OS-P RCA, and post dilatation with NCB 3.5x10 with 24 bars 7. Final result was good, the flow was TIMI 3 Final diagnosis: CAD with UA s/p coronary intervention with Tornus catheter, balloon dilatation, and scoring balloon dilatation for OS-P RCA functional CTO lesion, and stenting with DES x 1 successfully.

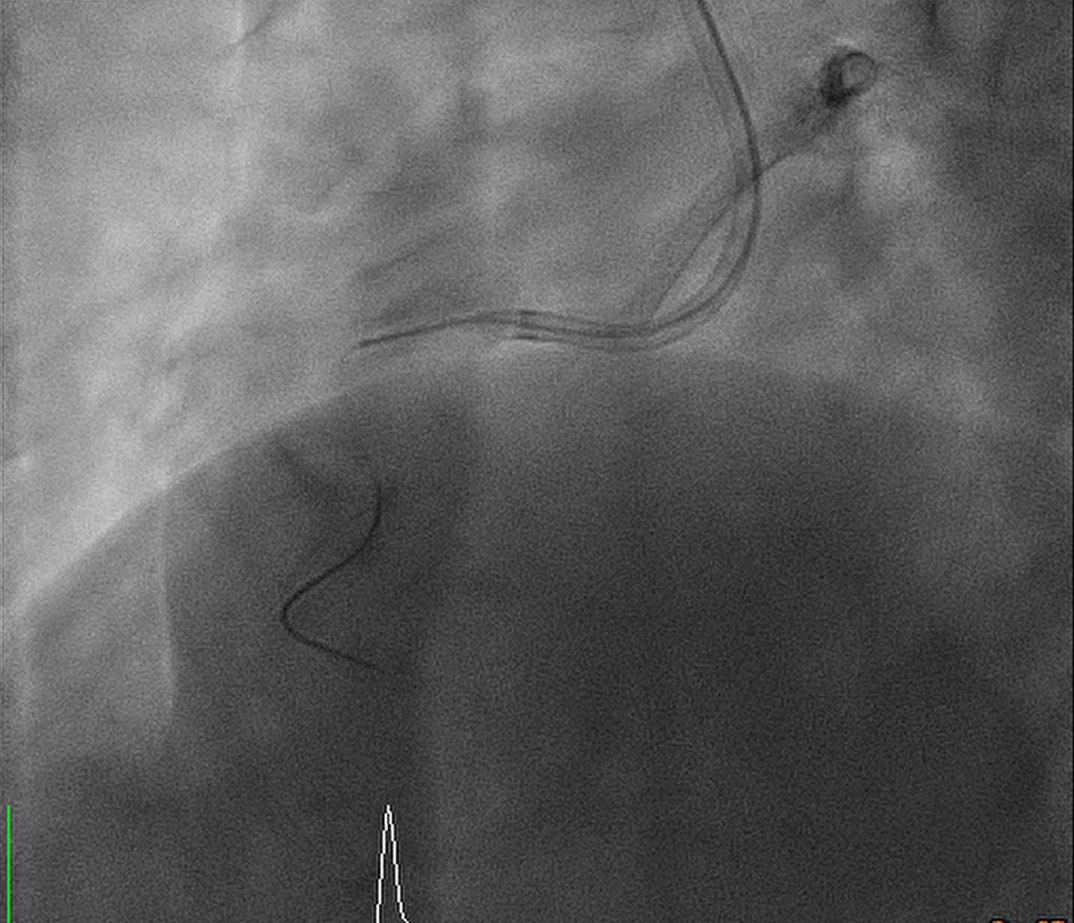
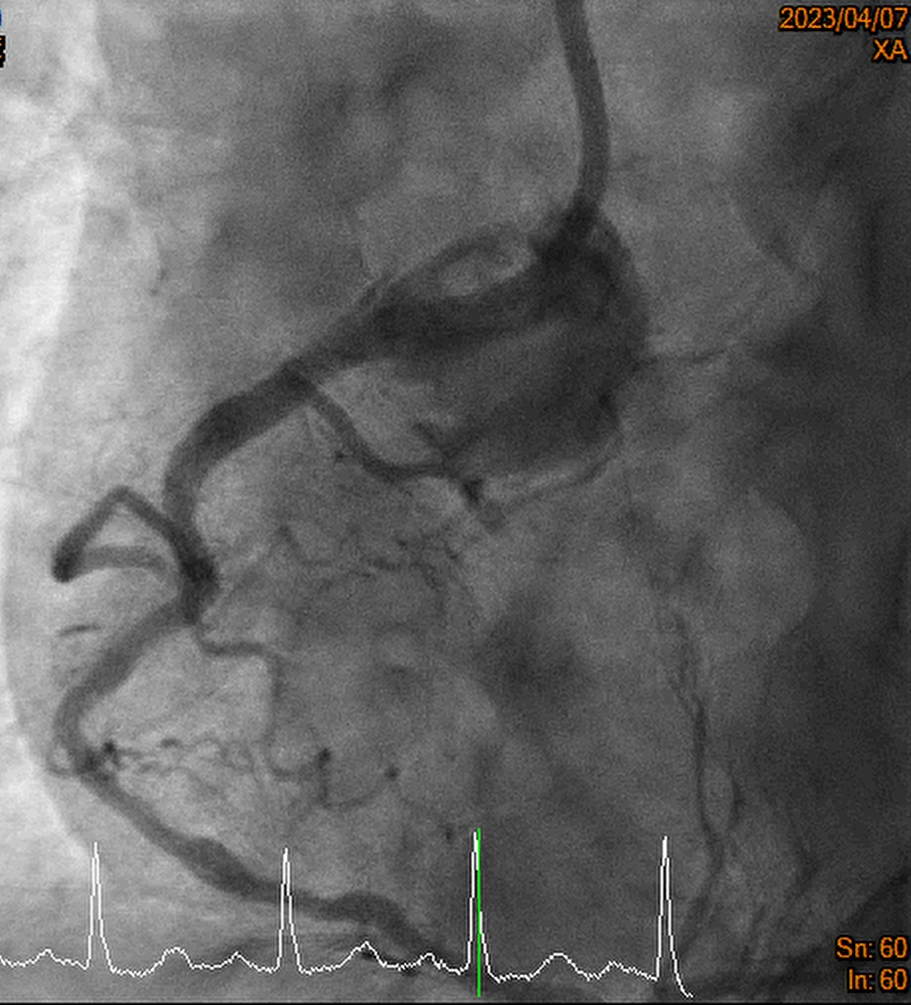
Guiding catheter: Retrograde: EBU 3.5 7F Antegrade: 1._SCR 3.5 6F_ 2._SAL 1.0 7F_ PTCA wire: 1._ASAHI Sion_ 2._Floppy_ 3._Fielder FC_ 4._ROTA wire_ 1. Transradial approach was arranged initially, antegrade approach was done but difficult guiding catheter approach and difficult retrograde approach was found, so we arranged the transfemoral approach. 2. Difficult retrograde approach was found even if finecross plus Fielder FC, and then we tried antegrade approach. 3. Via Finecross support, Asahi Sion was wired to distal RCA and Predilatation with 1.0x5 balloon but 2.0x15 balloon cannot pass the OS-P RCA lesion. 4. The Tornus 2.1Fr catheter was delivered and pass the OS-P RCA stenotic lesion and then dilated with 2.0x15 and 2.5x15 balloon. 5. Residual stenosis was still noted with heavty calcification, so 2.75x13 NSE scoring balloon was delivered and dilated with 6-12 bars. 6. Balloon dilatation with NCB 3.5x15 and then DES 3.5x19 over OS-P RCA, and post dilatation with NCB 3.5x10 with 24 bars 7. Final result was good, the flow was TIMI 3 Final diagnosis: CAD with UA s/p coronary intervention with Tornus catheter, balloon dilatation, and scoring balloon dilatation for OS-P RCA functional CTO lesion, and stenting with DES x 1 successfully.



Case Summary
1. The treatment of coronary CTO remains a challenge for the interventional cardiologist. Failure of balloon angioplasty is second more common cause of an unsuccessful procedure. The Tornus microcatheter was designed specifically for the treatment of “nondilatable” CTO, and it is safe and feasible in CTO lesions in whom balloon angioplasty has been unsuccessful. 2. For better prepare for stenting over hevy calcified lesion, angioplasty with dilatation by scoring balloon and non-compliance balloon is a reasonable choice. Otherwiser, ROTA is another choice but the risk of bradycardia should be considered.3. For OS-P functional CTO with visible channel, antegrade approach should be better choice.

