Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-195
Unveiling the Overlooked: Subclavian Steal Syndrome as an Underrecognized Neurovascular Culprit
By Hanestya Oky Hermawan, Putu Dwipa Krisna Devi, Primasitha Maharany Harsoyo, Mohammad Budiarto, J. Nugroho Eko Putranto
Presenter
Putu Dwipa Krisna Devi
Authors
Hanestya Oky Hermawan1, Putu Dwipa Krisna Devi2, Primasitha Maharany Harsoyo1, Mohammad Budiarto3, J. Nugroho Eko Putranto4
Affiliation
General Regional Academic Hospital Dr. Soetomo, Universitas Airlangga, Indonesia1, Universitas Airlangga, Indonesia2, Mitra keluarga waru, Indonesia3, Dr. Soetomo General Hospital, Indonesia4,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-195
Endovascular - Other Endovascular Intervention
Unveiling the Overlooked: Subclavian Steal Syndrome as an Underrecognized Neurovascular Culprit
Hanestya Oky Hermawan1, Putu Dwipa Krisna Devi2, Primasitha Maharany Harsoyo1, Mohammad Budiarto3, J. Nugroho Eko Putranto4
General Regional Academic Hospital Dr. Soetomo, Universitas Airlangga, Indonesia1, Universitas Airlangga, Indonesia2, Mitra keluarga waru, Indonesia3, Dr. Soetomo General Hospital, Indonesia4,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 72-year-old female presented with left arm claudication and declining memory retention for five months. There was a systolic blood pressure difference of 51 mmHg between the right and left arms. Physical examination of the head and neck revealed a bruit upon auscultation in the left supraclavicular area. The chest X-ray image depicts a normal shape and size of the heart with an evidence of aortosclerosis.

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
From duplex ultrasonography (DUS), the right vertebral artery exhibited normal flow in the antegrade direction, whereas retrograde flow was observed in the left vertebral artery (Figure 1). Doppler ultrasound results also indicated a monophasic Doppler curve morphology in the axillary, brachial, ulnar, and radial arteries of the left arm, without evidence of plaque or thrombus along these arteries (Figure 2).




Relevant Catheterization Findings
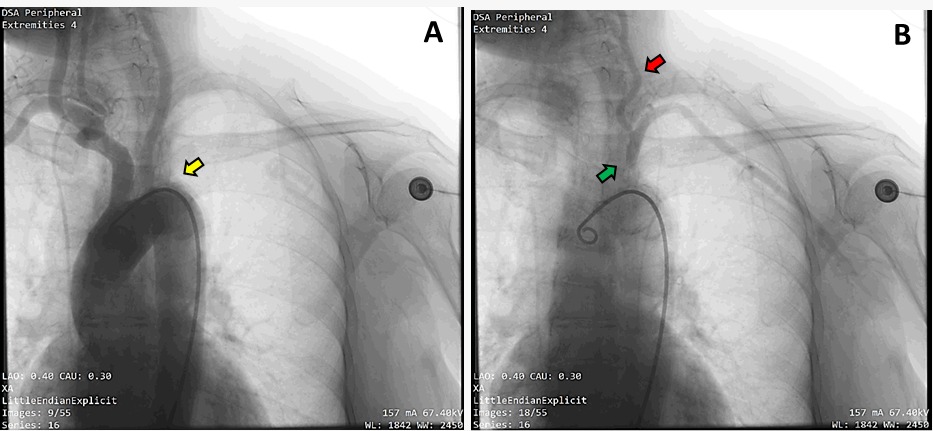
Aortography revealed the absence of contrast flow toward the left subclavian artery. Additionally, there was evidence of retrograde flow from the left vertebral artery to the left subclavian artery on delayed imaging (Figure3).

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Aortography in the region of the ascending aorta was conducted using an auto-injector. Aortography revealed the absence of contrast flow toward the left subclavian artery and an evidence of retrograde flow from the left vertebral artery to the left subclavian artery on delayed imaging (Figure 4a). These findings indicated total occlusion at the ostial of the left subclavian artery, confirming the presence of subclavian steal phenomenon. A 6Fsheath was employed for access in the left radial artery. The guiding catheter 3.5 6F successfully reached the left subclavian artery retrogradely. A guidewire was used to penetrate the lesion (Figure 4b). After successful lesion penetration, pre-dilatation was performed using a semi-compliant balloon measuring 3.0 x 20 mm with dilations of 6/3, 6/7, 6/8, 6/7, 6/8, 6/9, followed by a balloon measuring6.0 x 40 mm with dilations of 6/120; 6/120 (Figure 4c). A vascular stent measuring 7.0 x 29 mm was successfully deployed along the ostium to the proximal of the left subclavian artery, with stent balloon dilations of12/23 and post-dilations of 14/10 (Figure 4d). Post-stent angiography evaluation demonstrated good flow in the left subclavian artery, left vertebral artery, and left internal mammary artery (Figure 4e).


Case Summary
SSS may present with neurological and vascular symptoms, often diagnosed incidentally in asymptomatic patients. Endovascular treatment, such as percutaneous transluminal angioplasty(PTA), is the treatment of choice, presenting a high success rate, minimal complications, and a low mortality rate. This technique offers greater long-term permeability when revascularization is indicated due to symptoms of vertebrobasilar ischemia than when it is indicated due to upper limb ischemia. This case underscores the potential reversibility of neurological symptoms in SSS through PTA, emphasizing its high success rate and marked clinical improvement.

