Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-019
Mechanical Clot Buster for SVG STEMI
By Jonathan Gabriel Sung
Presenter
Jonathan Gabriel Sung
Authors
Jonathan Gabriel Sung1
Affiliation
Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong, China1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-019
Coronary - Adjunctive Procedures (Thrombectomy, Atherectomy, Special Balloons)
Mechanical Clot Buster for SVG STEMI
Jonathan Gabriel Sung1
Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong, China1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
We report a case of 63-year-old gentleman with history of smoking, hypertension, hyperlipidemia who had CABG (SVG to dRCA, SVG to OM1 and LIMA to mLAD) for TVD with ACS in 2010. He underwent PCI to native LCx in 2019 for refractory angina despite optimal medical therapy. He presented this time with persistent chest pain for 2 hours. He remained hemodynamically stable on admission.
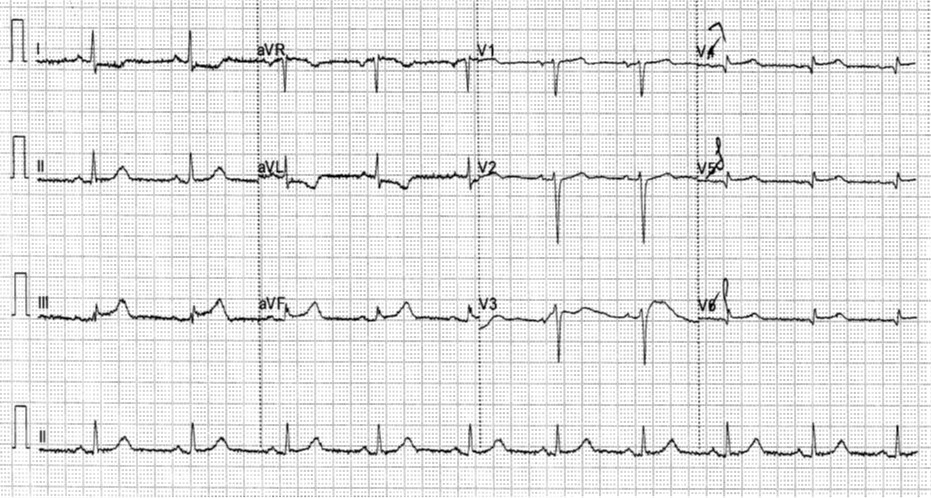

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
ECG showed ST elevation over inferior leads with RV involvement.Echocardiogram showed normal LV systolic function and hypokinesis over inferior region with unremarkable valves and no pericardial effusion.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiogram findings:- left main: normal- LAD: pLAD CTO- LCx: diffuse disease with TIMI III flow- RCA: pRCA CTO- LIMA to LAD: patent- SVG to LCx: patent- SVG to dRCA: total occlusion with significant thrombus burden
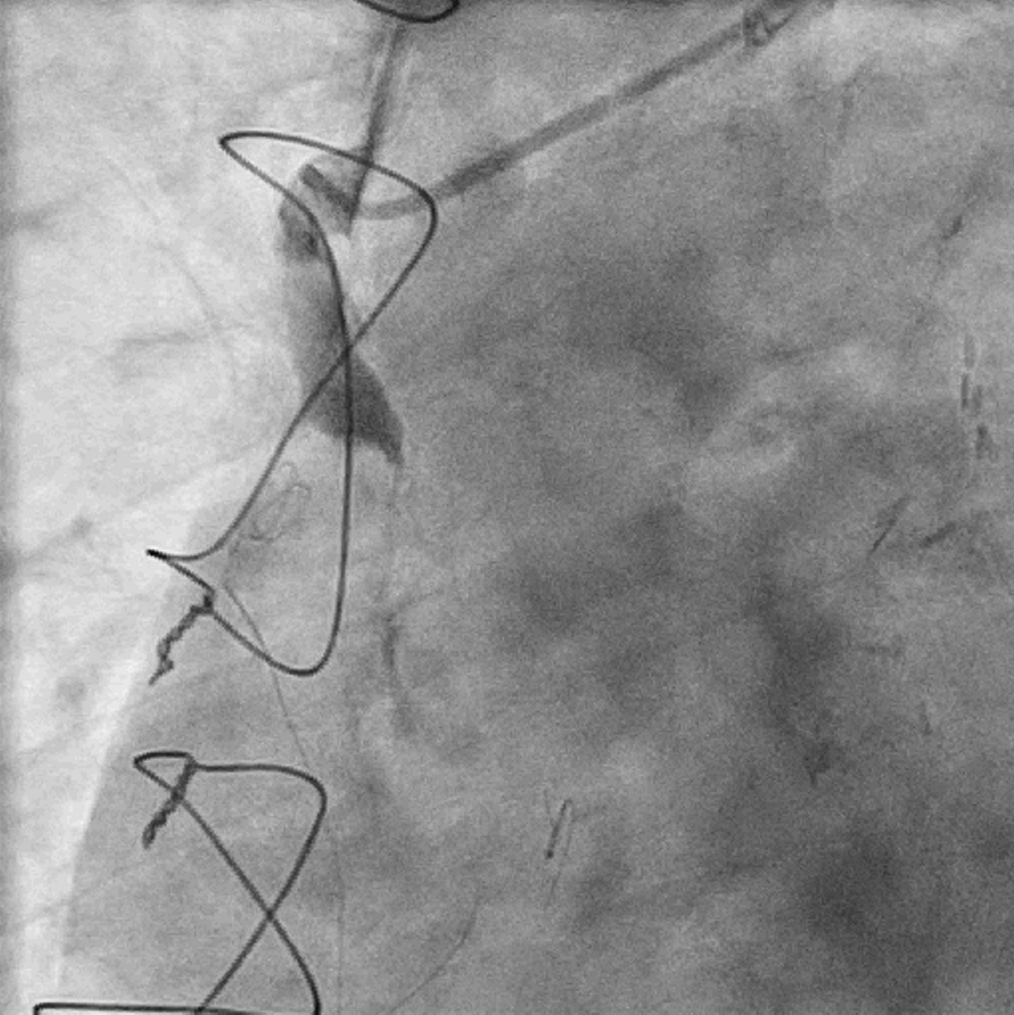



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
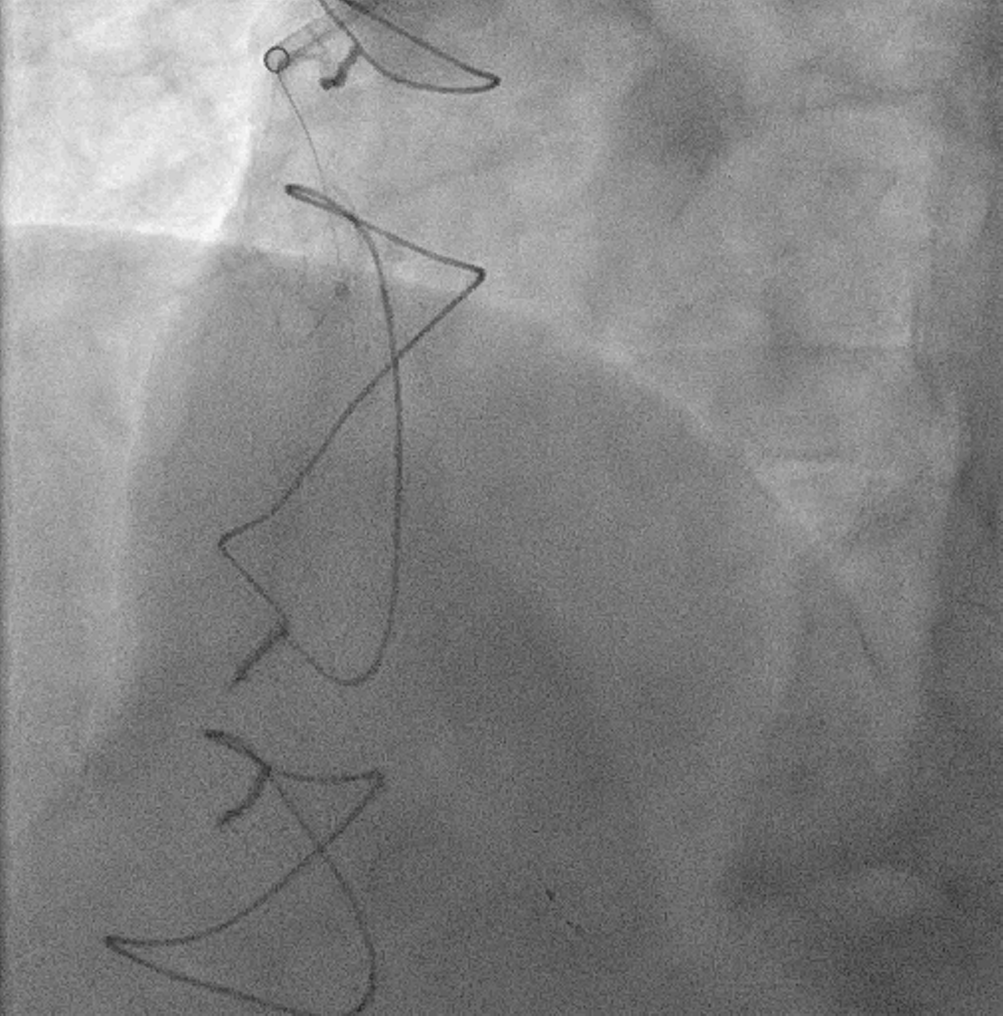
7Fr RFA access was established at the beginning of the procedure and JR4 7Fr guide catheter was engaged at SVG-dRCA. Systemic heparin was given up front and ACT was monitored throughout the case. Runthrough NS was threaded past the SVG and placed in dRCA. Flow improved after Dottering with a compliant balloon 2.0 mm x 15 mm. Spider FX was then inserted and exchanged out with the Runthrough NS for distal protection. Mechanical thrombectomy was performed with Penumbra Indigo System CAT RX with 7 runs of clot aspiration. The entire system including the guide catheter and manifold was cautiously aspirated and flushed to clear off any residual clots. Final angiogram showed significant reduction in thrombus load and TIMI III flow restored. In view of satisfactory flow and high risk of stent thrombosis, no stent was deployed before the end of the procedure. Patient was put on Aspirin, Ticagrelor and subcutaneous enoxaparin after returning to the CCU.
Patient was brought back to the catheterization laboratory 3 days later. Repeated angiogram showed patent SVG-dRCA with minimal residual thrombus and excellent flow. He was put on lifelong oral anticoagulation upon discharge.

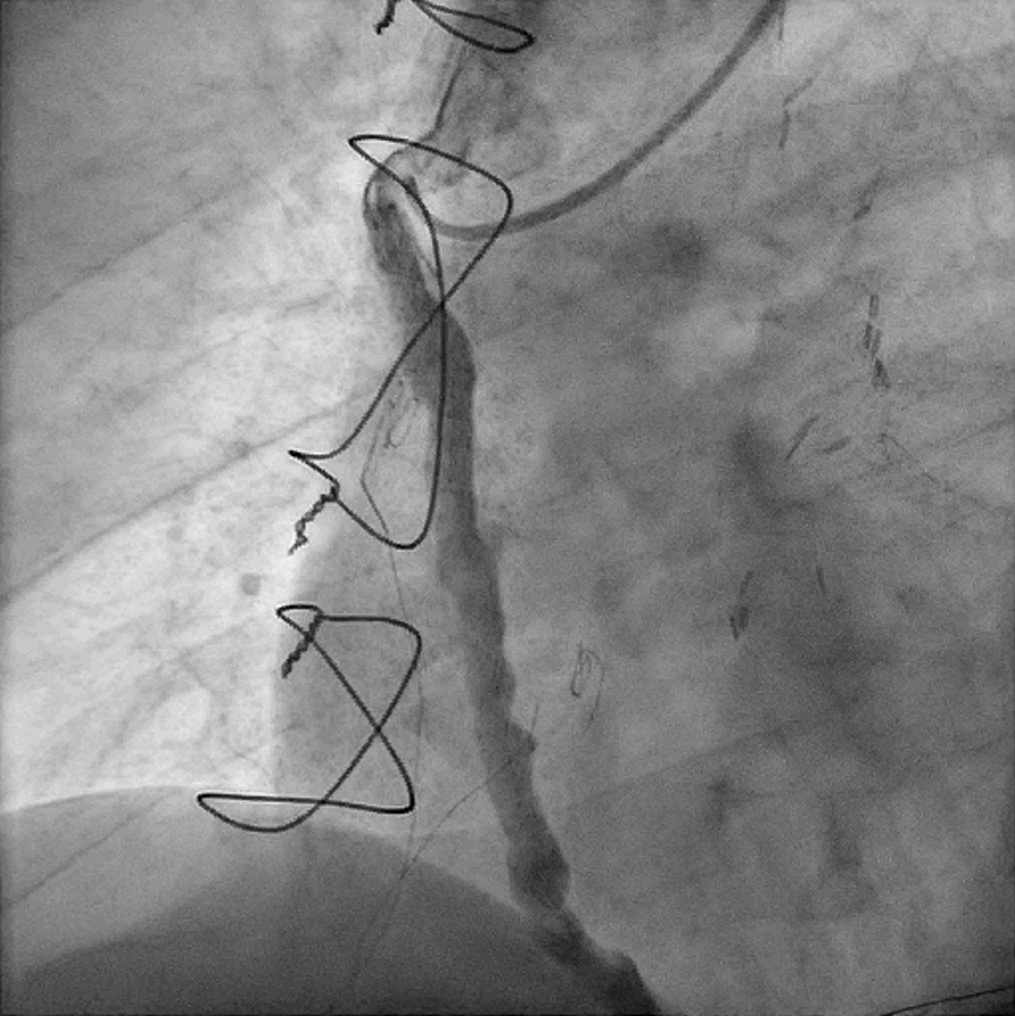
Patient was brought back to the catheterization laboratory 3 days later. Repeated angiogram showed patent SVG-dRCA with minimal residual thrombus and excellent flow. He was put on lifelong oral anticoagulation upon discharge.



Case Summary
This case illustrates the use of mechanical coronary thrombectomy in an occluded SVG with excessive thrombus load. Alternative options include the administration of intravenous or intracoronary glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor, intracoronary fibrinolytics (e.g. alteplase), balloon angioplasty and catheter-based thrombus aspiration. However, these options are either associated with high risk of bleeding or no-reflow. Penumbra Indigo System CAT RX could provide effective thrombus clearance by maintaining sustained mechanical aspiration. The decision to not use any stenting was based on the excellent angiographic result achieved and anticipated high risk of stent thrombosis in this ectatic SVG.

