Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-164
To Treat or Not to Treat, for Those With Discordance Between Resting Full-Cycle Ratio and Fractional Flow Reserve, That Is a Question
By Da-Wei Chang, Wei-Che Tsai, Shu Meng Cheng
Presenter
Da-Wei Chang
Authors
Da-Wei Chang1, Wei-Che Tsai1, Shu Meng Cheng1
Affiliation
Tri-Service General Hospital, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-164
Coronary - Imaging & Physiology - FFR
To Treat or Not to Treat, for Those With Discordance Between Resting Full-Cycle Ratio and Fractional Flow Reserve, That Is a Question
Da-Wei Chang1, Wei-Che Tsai1, Shu Meng Cheng1
Tri-Service General Hospital, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
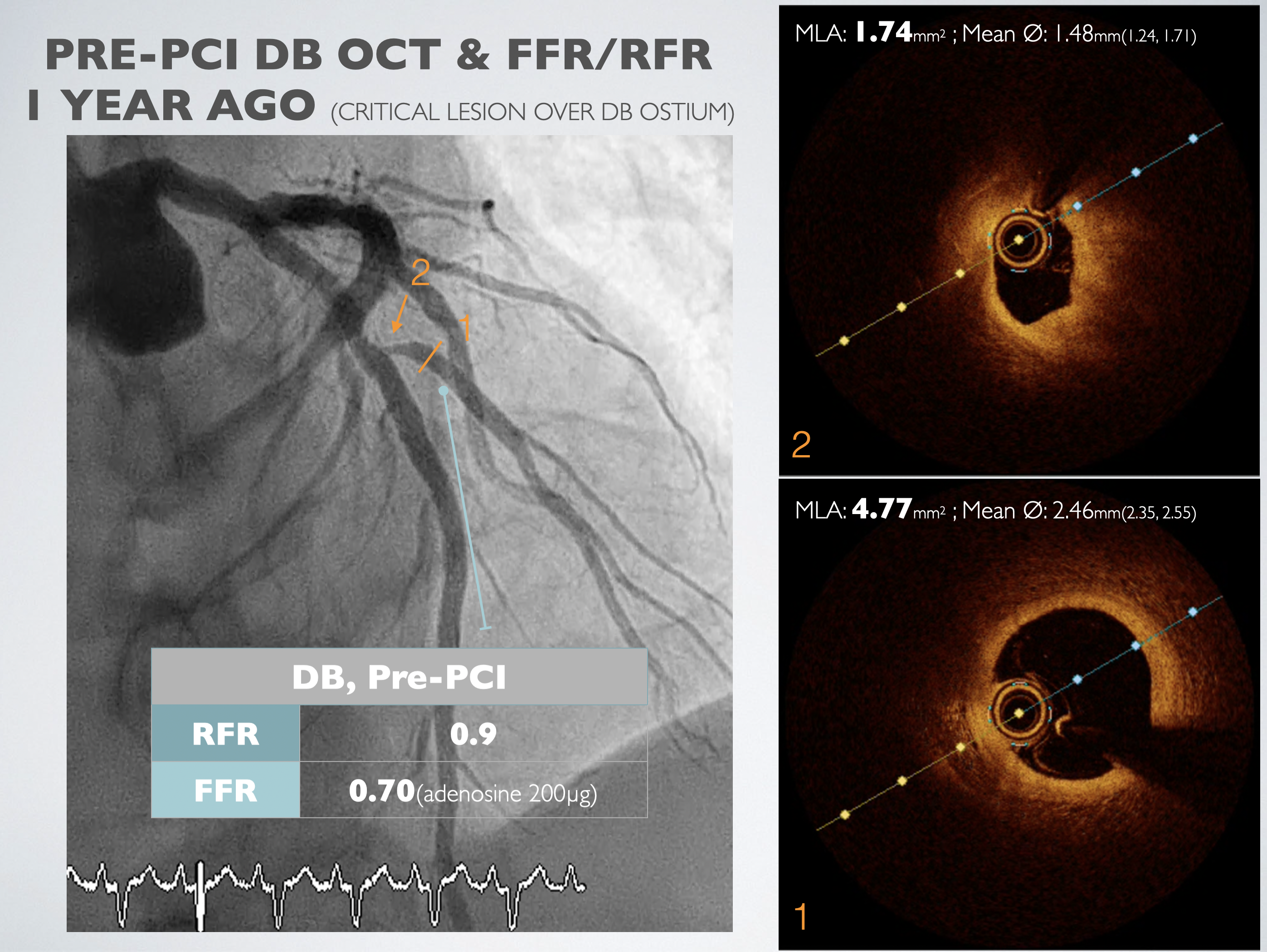
A 54-year-old male with history of hyperlipidemia, DM, and AMI with cardiogenic shock s/p ECMO and PCI with stents deployed at P/3 LAD and P/3 LCX. Heart failure symptoms persisted after the procedure. Follow up CAG showed total occlusion of LAD in-stent area. DEB to the CTO lesion and a DES to M/3 LAD de novo lesion were done, as well as POBA to DB ostial lesion. Months later, CAG showed a borderline lesion of DB ostium. FFR=0.7, and improved to 0.72 after POBA. CAG follow up for the DB lesion.


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
LAB: Hb: 15.1, BUN/Cr: 20/0.9ECG: Sinus rhythm, heart rate 73bpm, RBBB and LPFB pattern, Q waves over lead II/III/aVF.Echocardiography: Generalized hypokinesia of LV with EF 20-25%. AFib during the exam with E/E’med 15.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
MCA: Luminal irregularity and patent;LAD: Luminal irregularity, calcification, and slight intimal hyperplasia in the proximal stent (BMS) and middle stent (DES); discrete 70% stenosis at the ostium of main DB; TIMI 3 flow;LCX: Luminal irregularity and ectasia; intimal hyperplasia in the proximal stent; TIMI 2-3 flow; segmental 70-80% stenosis



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
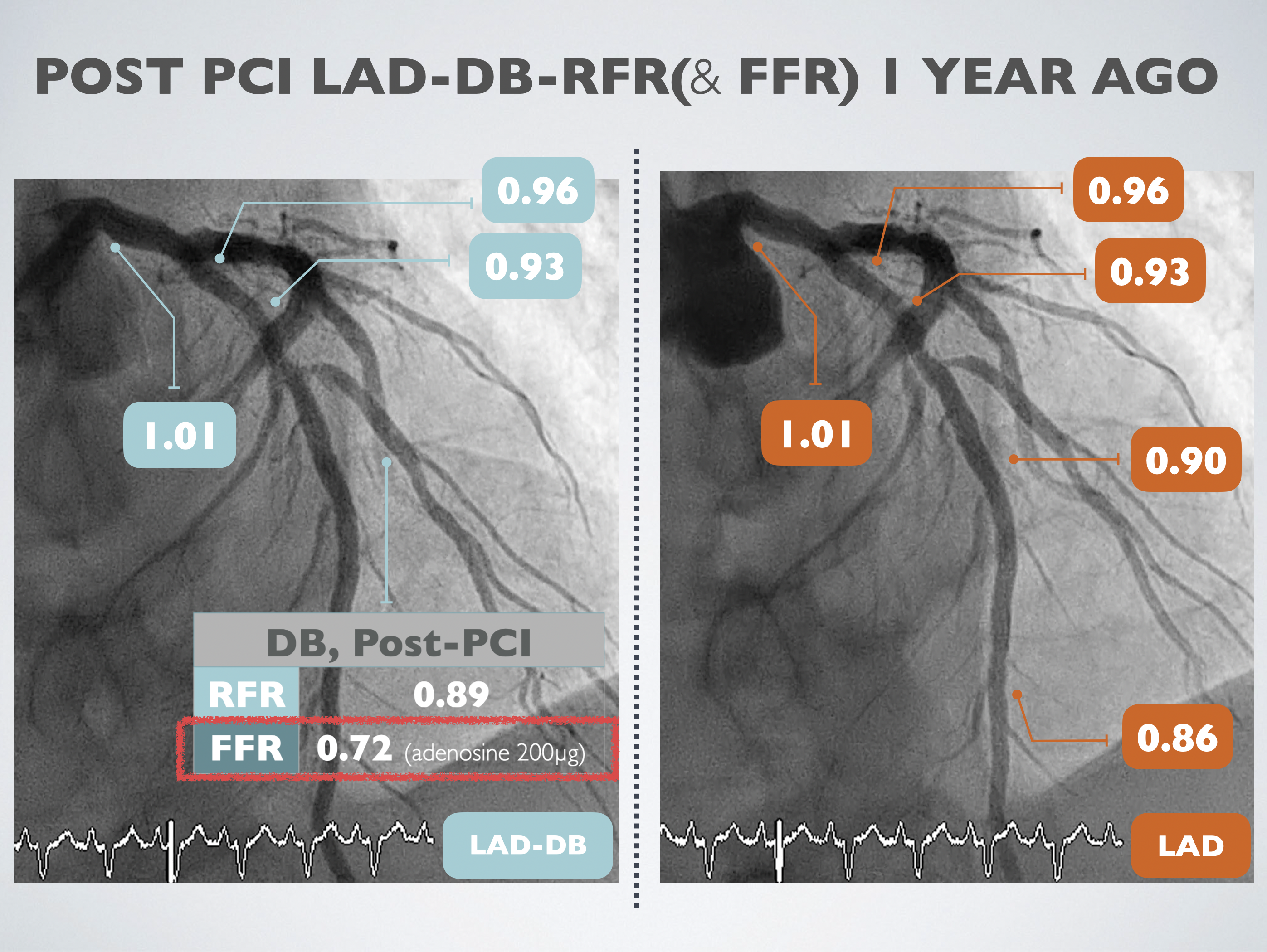
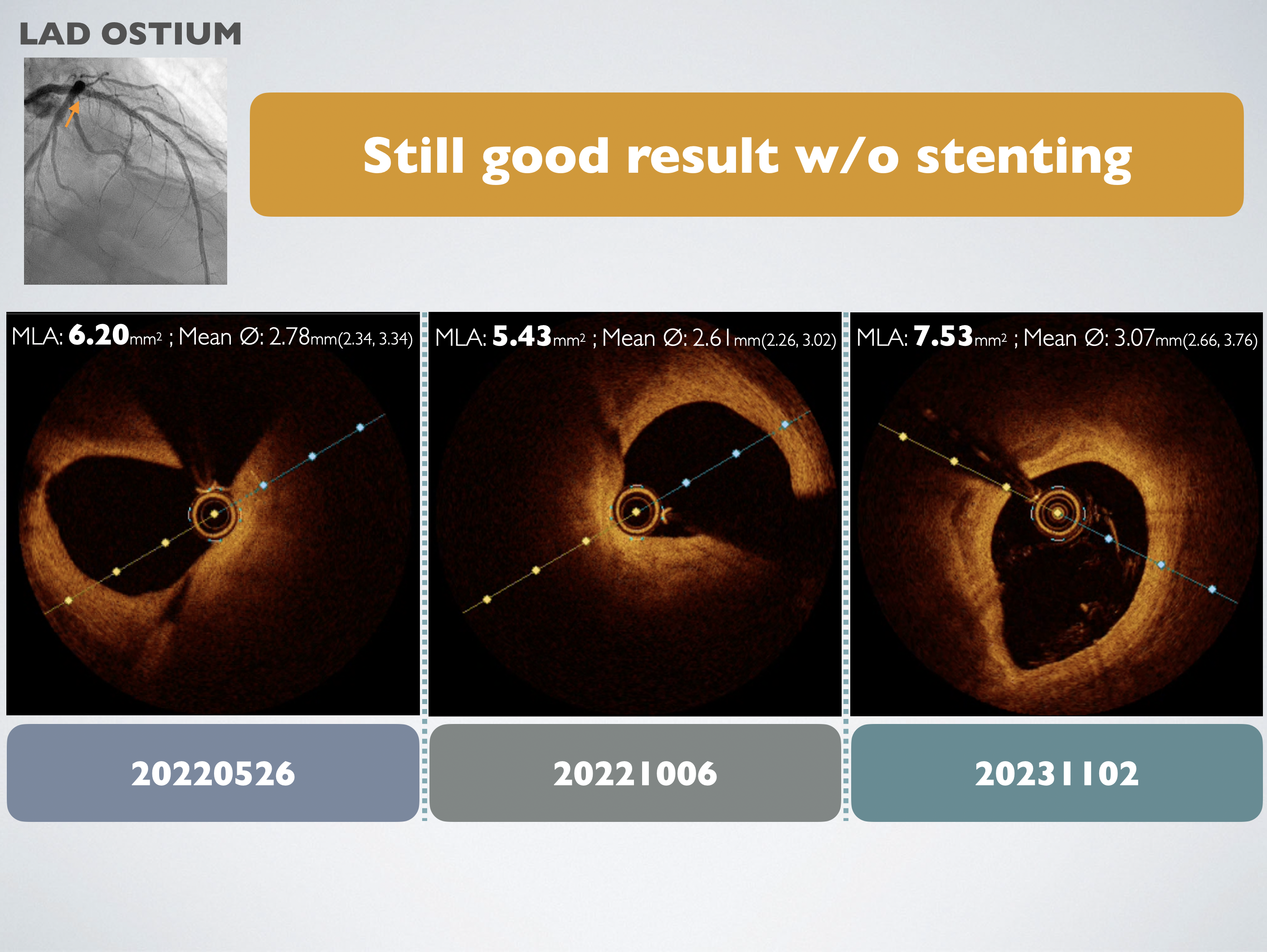
Left heart catheterization was carried out using the right distal radial artery approach. We utilized an EBU3.5 6Fr guiding catheter to access the LMCA, and a SION wire was threaded to the distal LAD. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) was conducted through manipulated contrast injection, unveiling the patency of the previously totally occluded stent at the proximal LAD with complete endothelialization. The minimum in-stent area was measured at 3.99 mm². Subsequently, OCT was performed at the DB ostium, revealing a minimum in-stent area of 2.25 mm² at the proximal DB and 3.57 mm² at the DB ostium.Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) was recorded at the distal LAD post 200mcg adenosine injection, demonstrating a value of 0.80. Simultaneously, the Resting Full-cycle Ratio (RFR) showed a value of 0.86. The catheter was then pulled back, and FFR was recorded at the distal stent edge, LAD-DB bifurcation, proximal stent edge, and LM ostium, yielding results of 0.91, 0.91, 0.93, and 1.0, respectively.Following this, the pressure wire was advanced to the distal DB. After injecting 200mcg of adenosine, FFR revealed a value of 0.79, and RFR showed 0.87. Considering the previous FFR result of 0.72, an improvement in the condition was noted, leading to the decision to conclude the procedure.
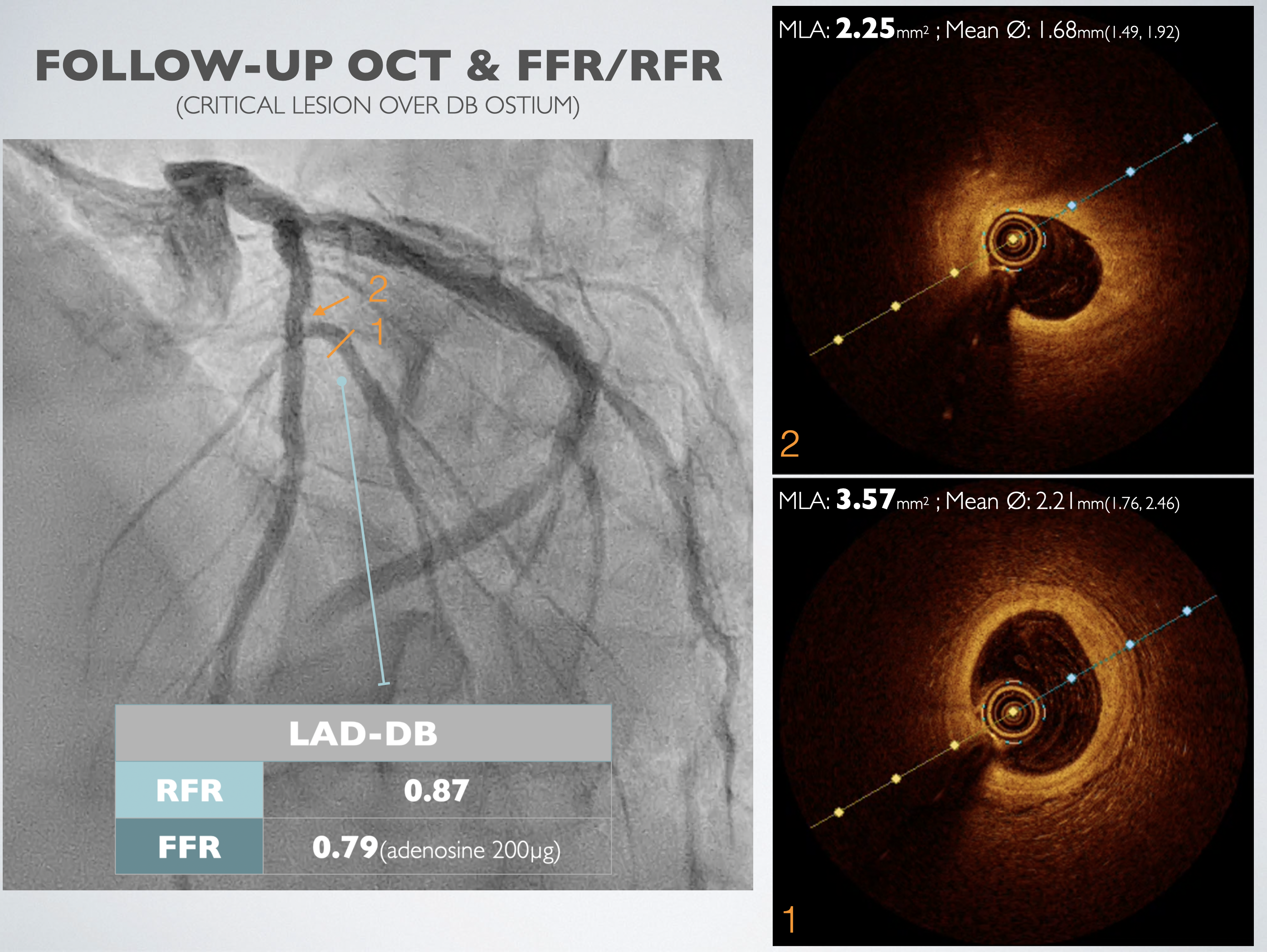
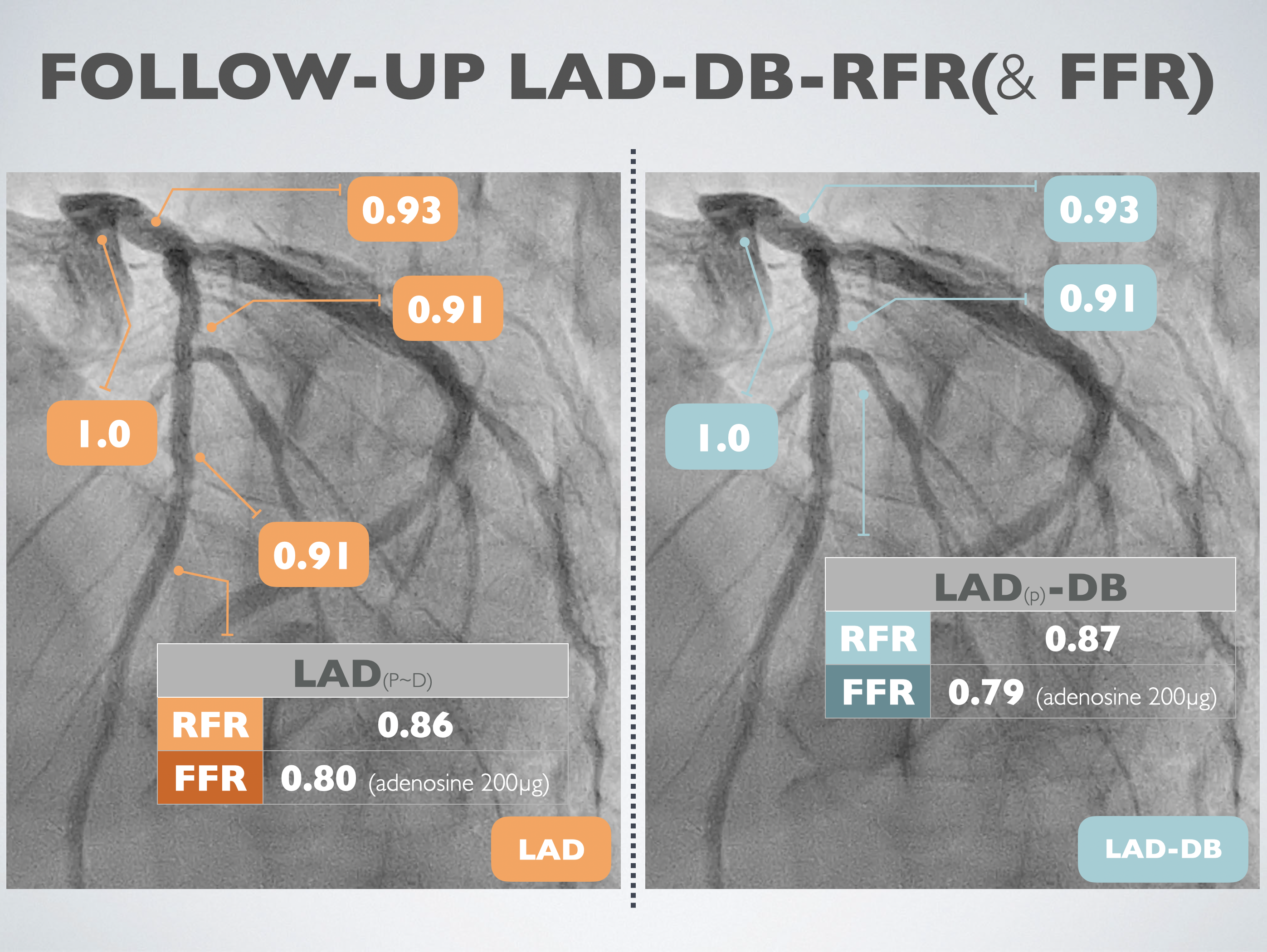



Case Summary
Firstly, the follow-up OCT suggested that blood flow in CTO vessels and microvascular function does not normalize immediately after treatment but improves over time. Possible reasons include microvascular resistance, positive remodeling, and vascular wall hibernation. Secondly, based on OCT evidence, we assert that despite discrepancies between FFR and NHPR, FFR remains the standard and is more reliable. Previous studies reported that insulin-treated diabetes mellitus was a predictor of negative FFR and positive iFR/RFR discrepancy, and there is no association between an increased risk of vessel-oriented composite outcomes and discordance of FFR/RFR after two years.

