Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-156
High Risk Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Chronic Total Occlusion of Left Circumflex Artery Involving Bifurcation Lesions With Severe Calcification and Tortuosity. How We Succeeded.
By Kei Takahashi, Koshi Matsuo
Presenter
Kei Takahashi
Authors
Kei Takahashi1, Koshi Matsuo1
Affiliation
Yao Tokushukai General Hospital, Japan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-156
Coronary - High-Risk Intervention (Diabetes, Heart Failure, Renal Failure, Shock, etc)
High Risk Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Chronic Total Occlusion of Left Circumflex Artery Involving Bifurcation Lesions With Severe Calcification and Tortuosity. How We Succeeded.
Kei Takahashi1, Koshi Matsuo1
Yao Tokushukai General Hospital, Japan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
An 84-year-old female was brought in with a chief complaint of shortness of breath. She had a history of hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and chronic kidney disease. On arrival, her vital signs were stable. Bilateral wheezing sounds and apical holosystolic murmur were heard. Chest x-ray showed cardiomegaly, pulmonary congestion, and pleural effusion. She was diagnosed with acute heart failure with reduced ejection fraction based on ischemic cardiomyopathy and she was hospitalized.
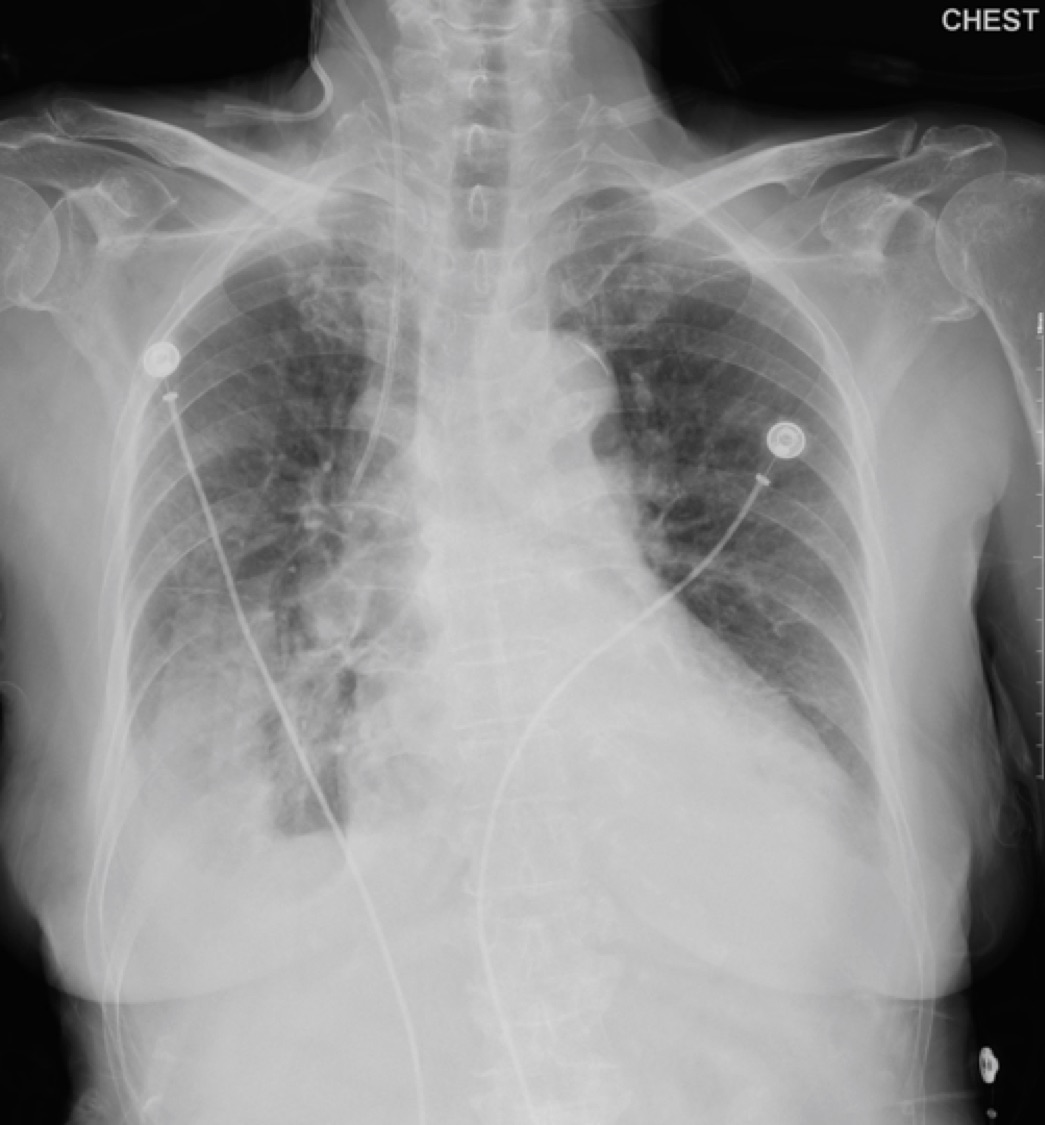

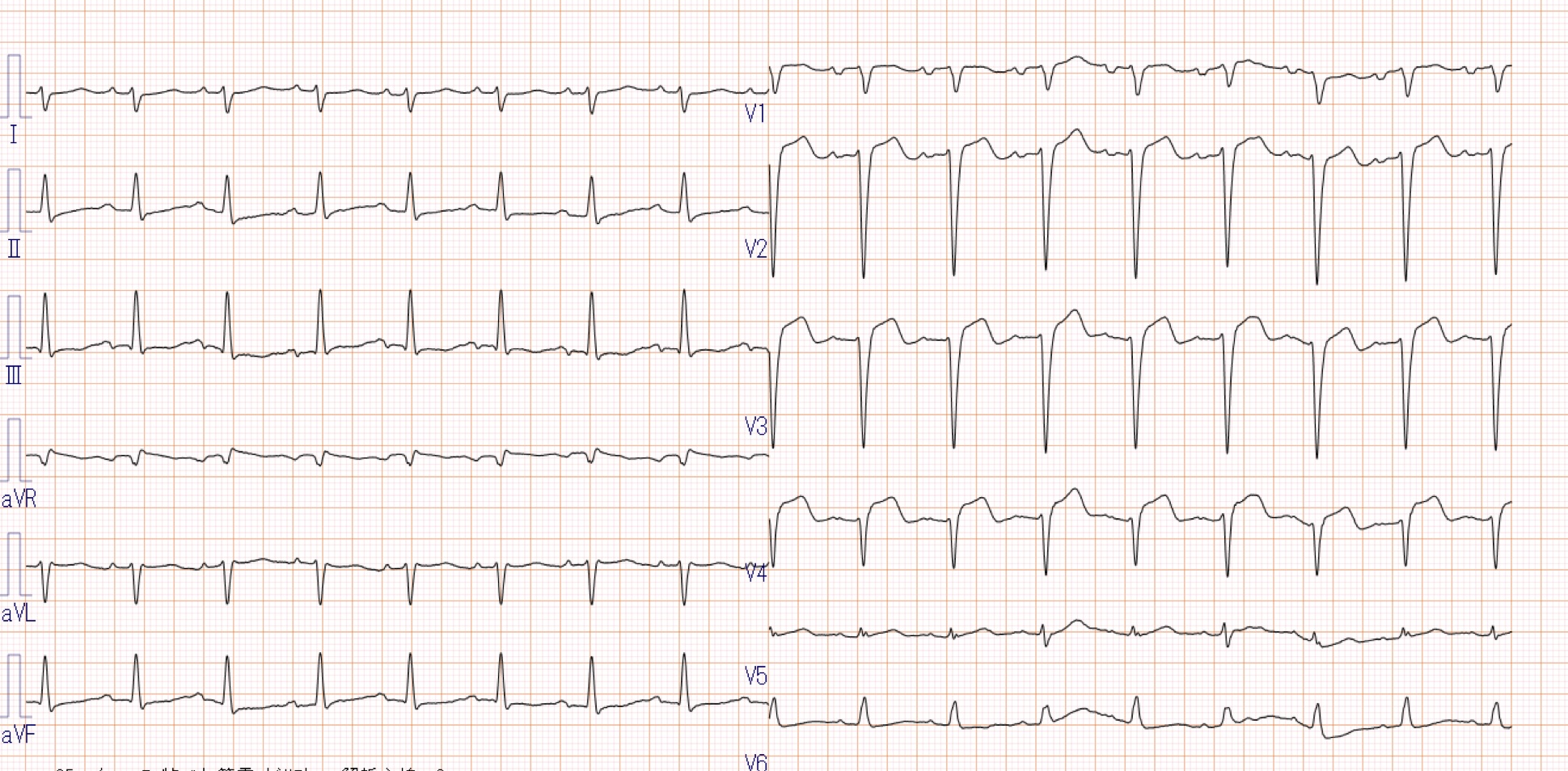
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
An electrocardiogram demonstrated sinus rhythm with poor R progression. A point-of-care ultrasound examination demonstrated reduced ejection fraction and diffusely decreased wall motion with moderate mitral valve regurgitation. Laboratory investigations showed elevated brain natriuretic peptide, 1660 pg/ml, and troponin I, 4.31 ng/ml. Since her hemodynamics became unstable and ongoing cardiogenic shock was observed, we decided to perform emergent percutaneous coronary intervention.

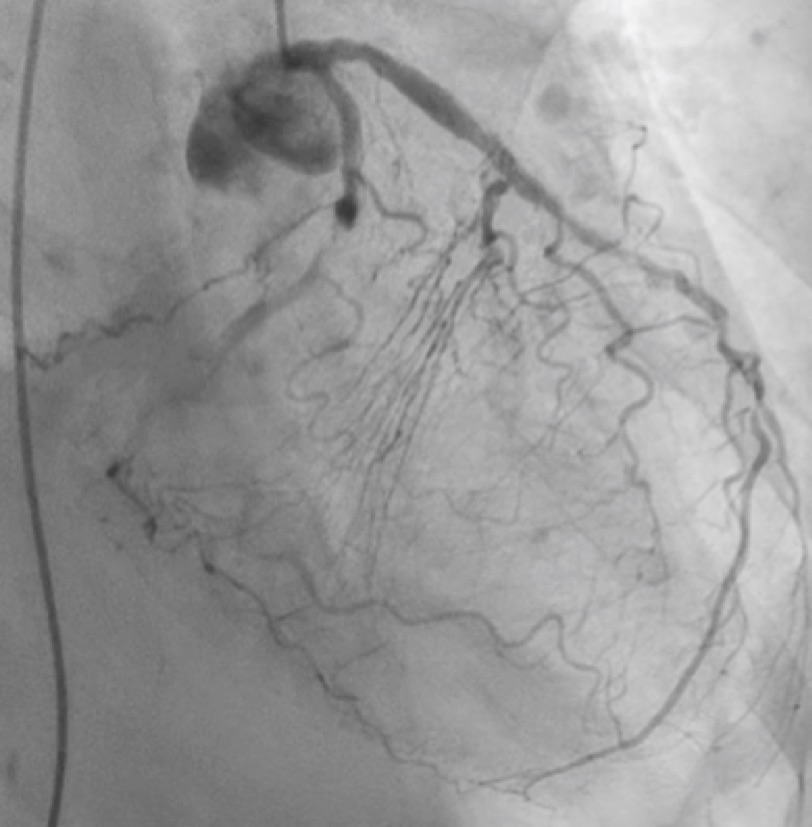
Relevant Catheterization Findings
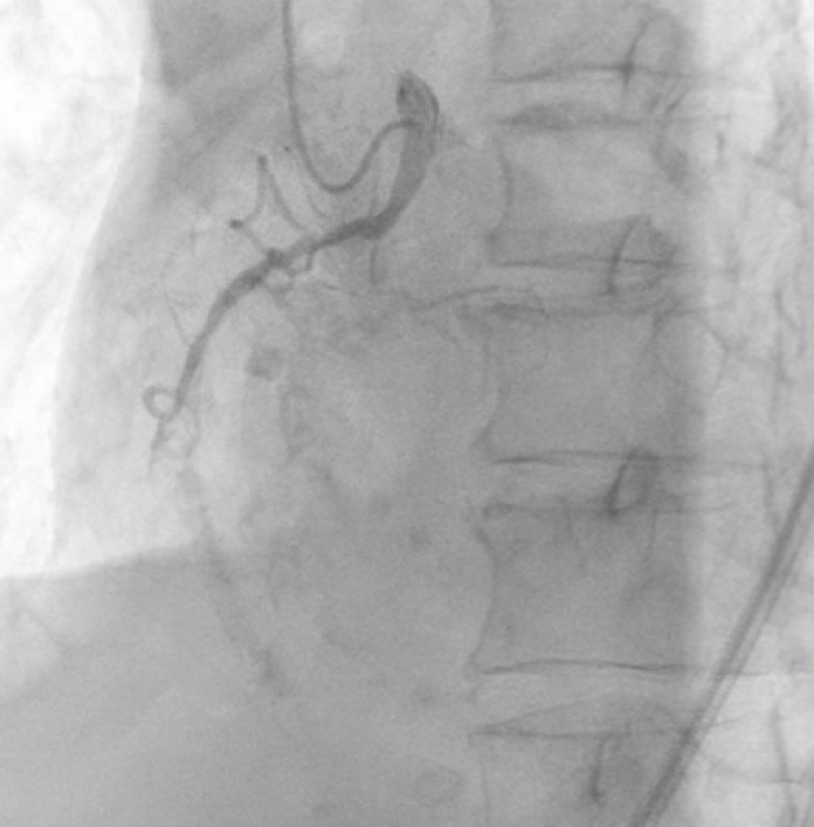
Coronary angiography revealed chronic total occlusion (CTO) of the left circumflex artery (LCX) and the right coronary artery (RCA) with a severe stenosis lesion of the left anterior descending artery (LAD). In particular, the CTO of LCX revealed severe calcification and tortuosity.
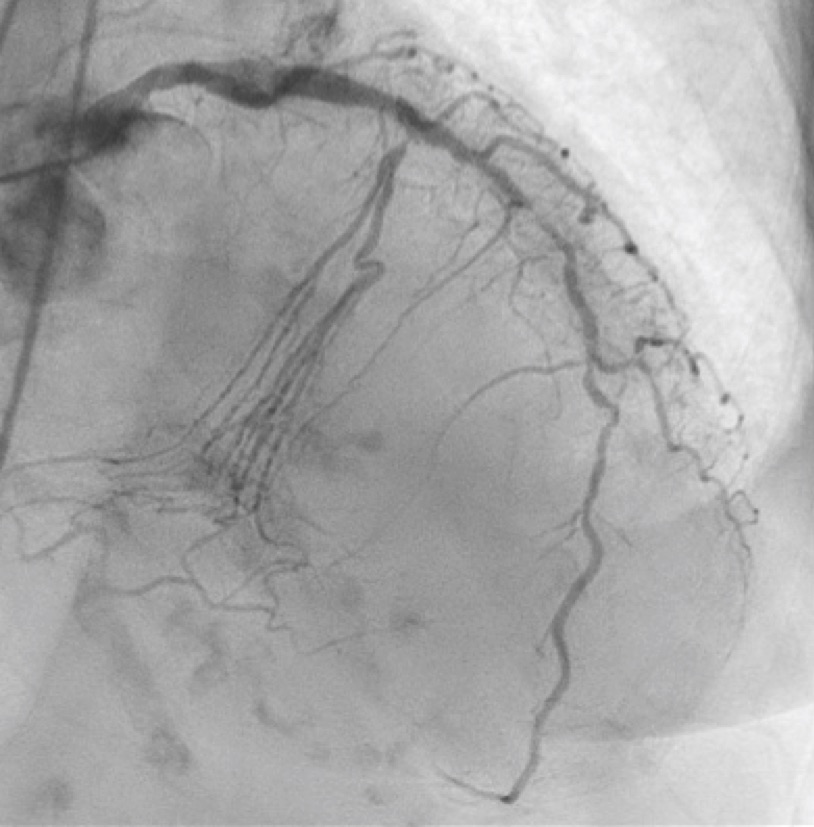



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
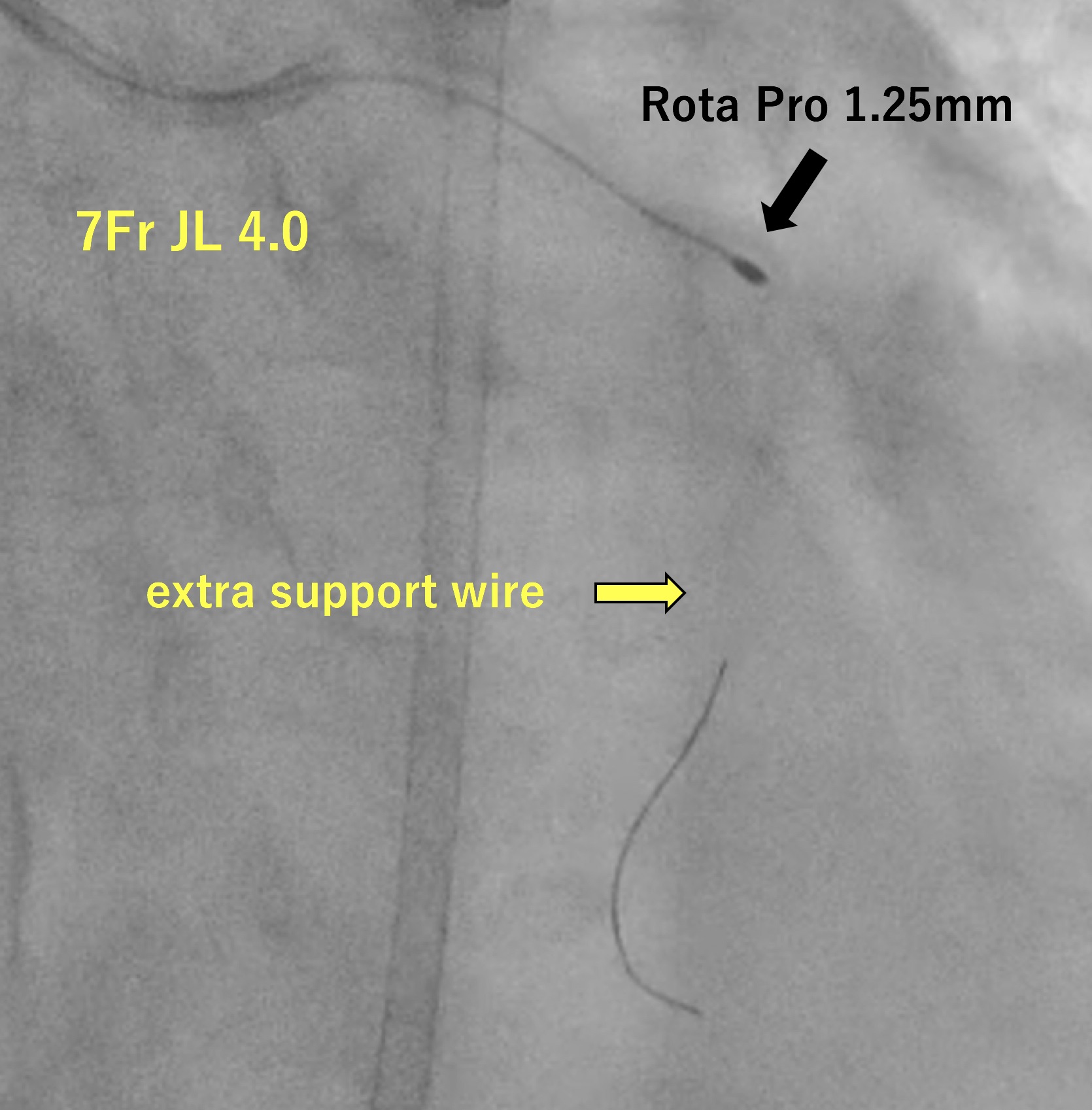
We performed PCI for LCX just after PCI for RCA was done successfully. A 7-Fr JL 4.0 guiding catheter was engaged in LCA. We used a workhorse guidewire (GW) SION Blue to reach chronic total occlusion (CTO) entry supported with a microcatheter (MC) Corsair Pro. We exchanged SION Blue with a flexible tip GW XT-R in an attempt to track the microchannel but failed. Even though a flexible micro-cone tip GW Gaia Next 1 couldn’t penetrate the severely calcified lesion, we expected a hydrophilic GW Gladius EX to pass through the lesion. Although it didn’t head for the main branch, it could pass through the proximal lesion of the CTO and reach the small side branch. However, Corsair Pro didn’t pass through the lesion. Then, we chose a dual-lumen MC SASUKE and inserted Gaia Next 1 from the side lumen to penetrate the CTO of the main branch. Gaia Next 1 could penetrate the cap and reach the distal true lumen of the main branch. Then, MC Zizai passed the lesion after dilatation with a semi-compliant balloon. We exchanged Gaia Next 1 with a rota-extra support wire and performed rotational atherectomy (RA). Since RA with 1.25 mm rota-burr was inadequate to gain enough lumen area, we performed additional RA with 1.5 mm rota-burr. We dilated the lesion with non-compliant and semi-compliant balloon before a drug-coated balloon dilatation. The final angiogram showed an acceptable result. As a result, she recovered from cardiogenic shock after PCI for LAD and she was discharged.

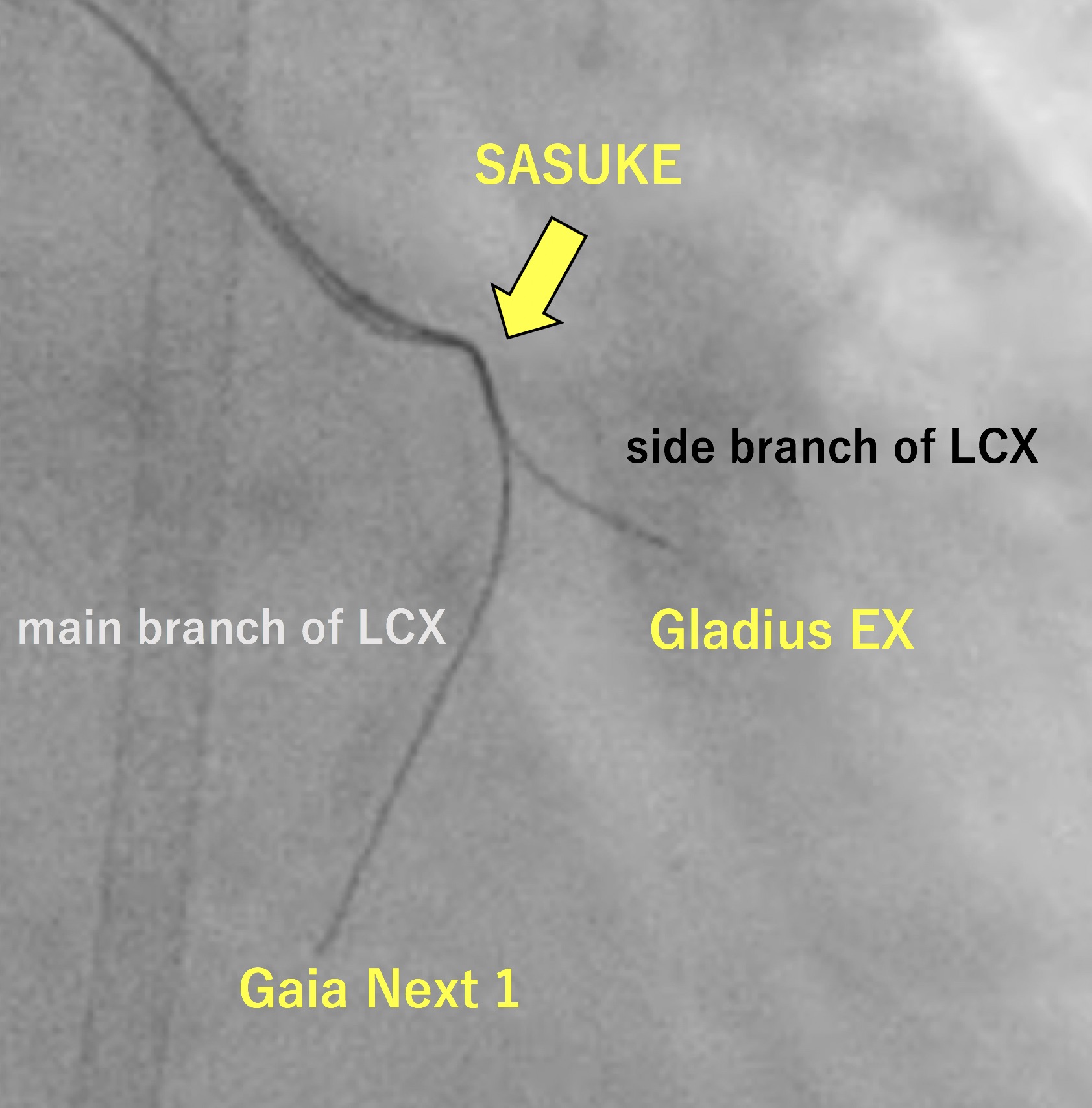



Case Summary
Gladius EX and SASUKE played an important role in the severe calcification and tortuosity. Gladius EX with high torque response and lubricity demonstrated a good performance to follow the calcification. Once Gladius EX reaches the side branch, SASUKE with lubricity and durability of the coating might give us a chance to aim the main branch by wiring from the side lumen. Gaia Next 1 with high torque ability and penetration efficacy also helped us succeed in reaching the distal true lumen of the main branch. Rota floppy wire is often used in the calcified lesion. However, in our case, we used extra support wire because it was more effective in stabilizing the atherectomy device.

