Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-200
Successful Thrombectomy Using Myocardial Biopsy Forceps in Subacute Limb Ischemia
By Eiji Miyauchi
Presenter
Eiji Miyauchi
Authors
Eiji Miyauchi1
Affiliation
Kagoshima City Hospital, Japan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-200
Endovascular - Thrombus Removal Devices and Techniques
Successful Thrombectomy Using Myocardial Biopsy Forceps in Subacute Limb Ischemia
Eiji Miyauchi1
Kagoshima City Hospital, Japan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 68-year-old male with sudden pain in his left lower limb was referred to our clinic for further evaluation and treatment. He had a history of surgical thrombectomy and superficial femoral artery-posterior tibial artery bypass for acute limb ischemia on his right leg. Although there were no motor or sensory impairments in the left lower leg, his foot appeared cyanotic and felt cold. Arterial pulses could not be palpated below the knee, the left ABI (Ankle-Brachial Index) was unmeasurable.


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Contrast-enhanced CT revealed a thrombus in the proximal portion of the left superficial femoral artery (SFA), complete thrombotic occlusion from the middle part of the SFA to the proximal portion of the popliteal artery (POPA), and residual thrombi even from the middle part of POPA to the tibioperoneal trunk (TPT) (Figure 1). It was diagnosed as acute lower limb arterial occlusion (Category I).
Relevant Catheterization Findings
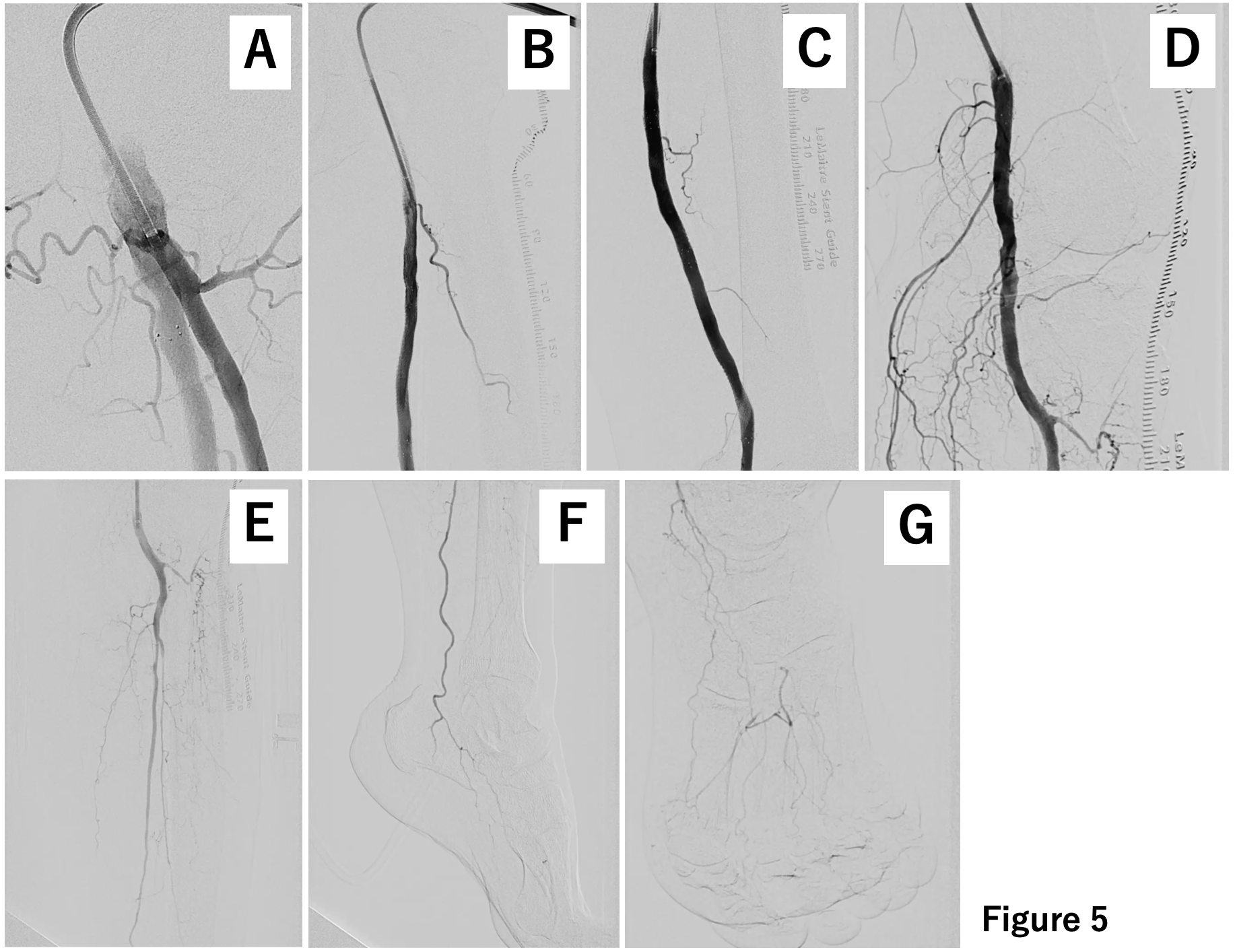
On the 5th day of hospitalization, an endovascular treatment (EVT) was performed. As well as contrast-enhanced CT, initial angiography revealed complete thrombotic occlusion from the middle part of the SFA to the proximal portion of the POPA, and residual thrombi even from the middle part of POPA to the TPT.

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
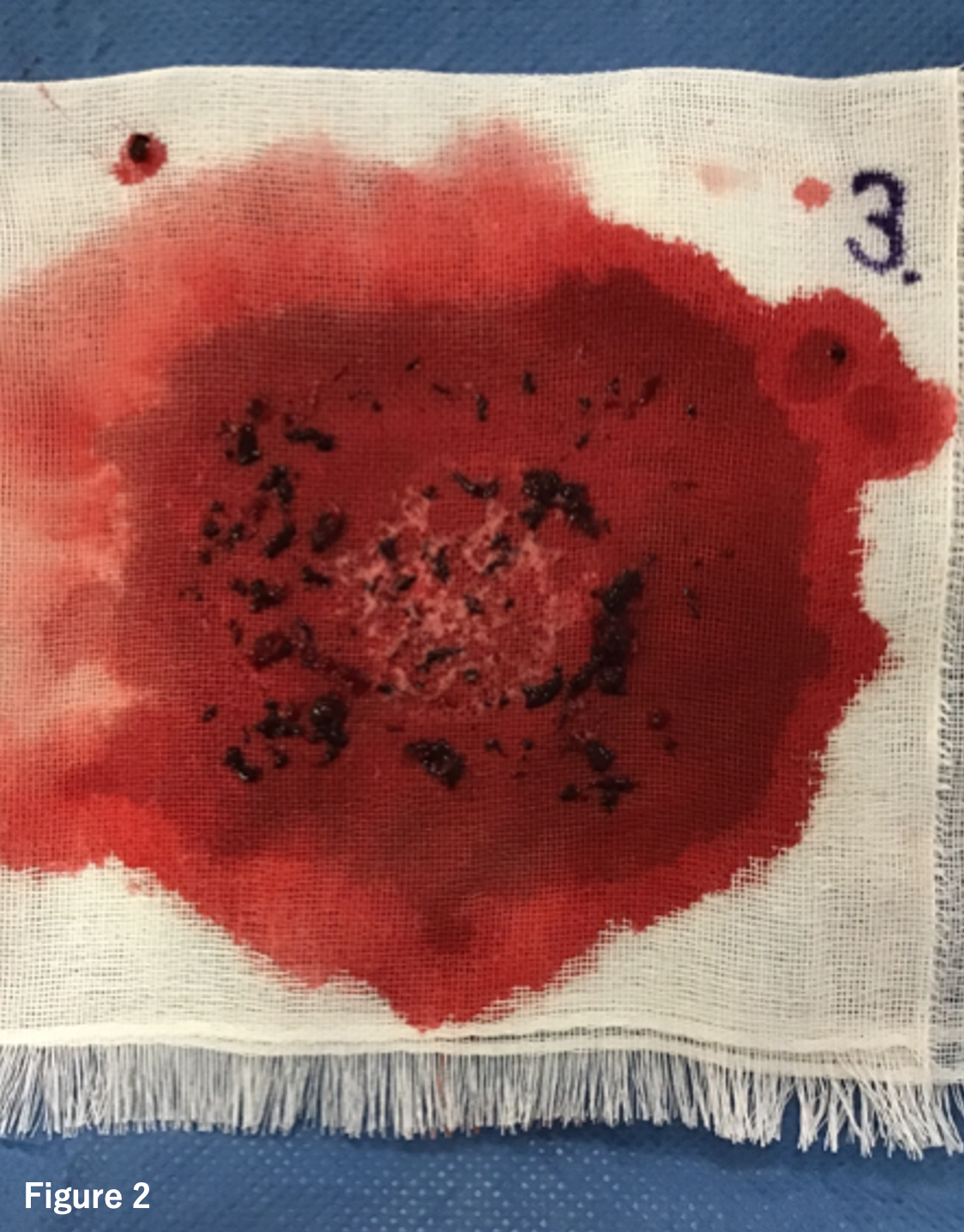
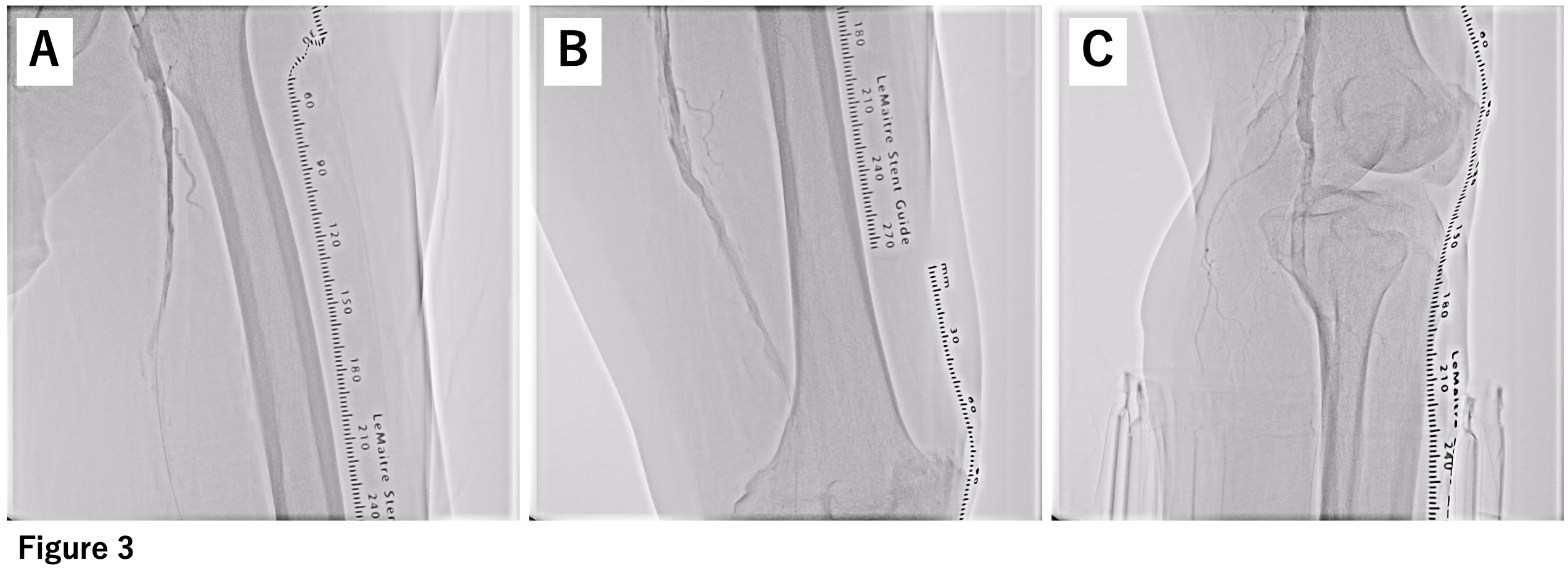
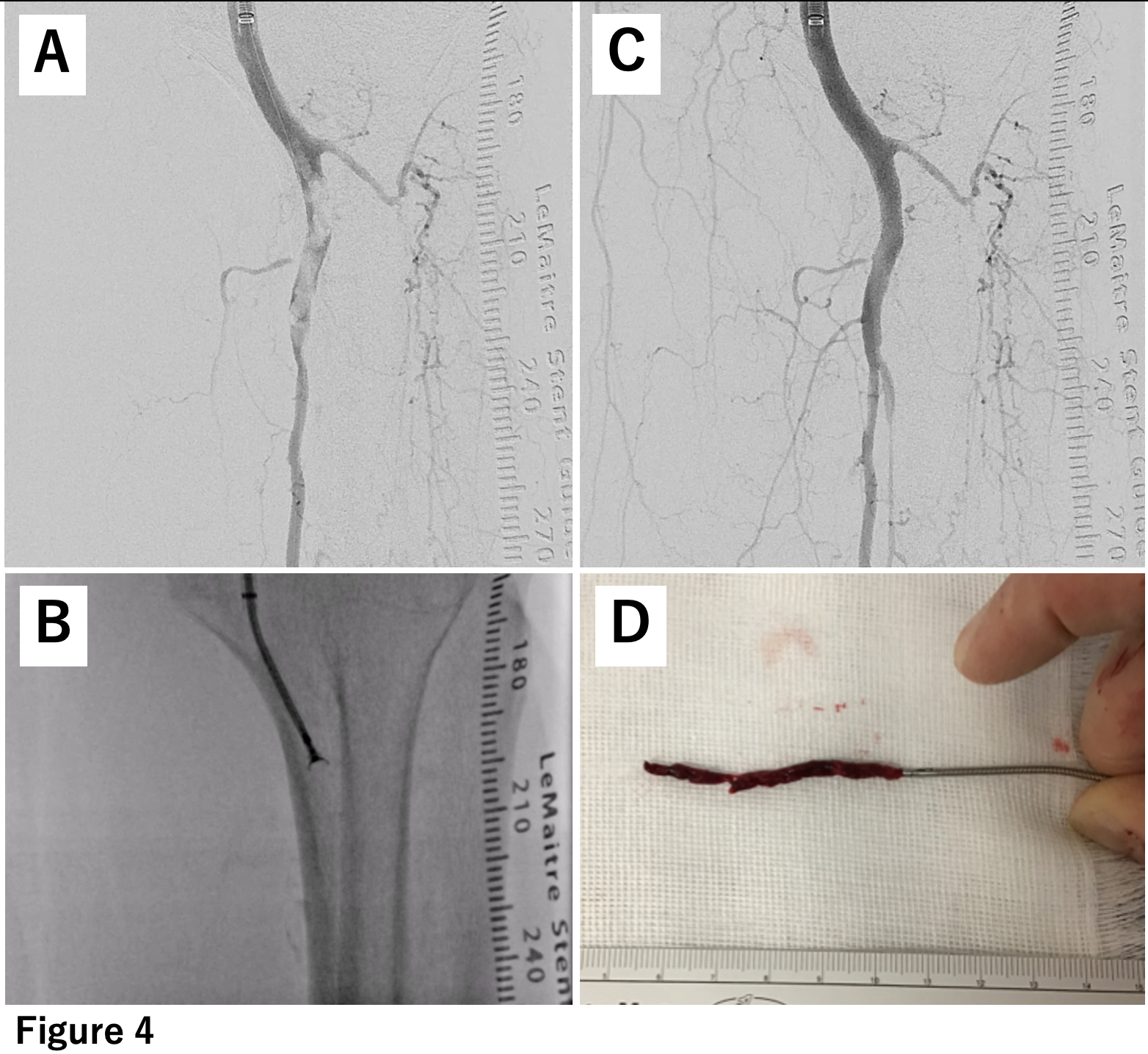
A 7-french guiding sheath was inserted retrogradely from the left common femoral artery, and aspiration was attempted using a 6-french aspiration catheter. Although a small amount of red thrombus was removed (Figure 2), angiography revealed severe stenosis and slow flow remained (Figure 3). Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) revealed a significant amount of thrombus with slightly increased brightness from the proximal part of the superficial femoral artery (SFA) to the tibiofibular trunk (TPT). Therefore, the thrombus within the SFA was sealed using a bare nitinol stent. Attempts were made to move the thrombus from POPA to TPT using a Fogarty catheter repeatedly, however, some residual thrombus that couldn't be completely sealed dispersed into the TPT (Figure 4).



Case Summary
The use of biopsy forceps may be an alternative method for ALI cases when an aspiration catheter and balloon angioplasty do not work sufficiently. Thrombectomy using biopsy forceps is a feasible technique for removal of an arterial thrombus.

