Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-148
Case Report: Successful Revascularization of de Novo Chronic Total Occlusion Lesion With Drug Coating Balloon
By Wee Pang Ng, Jin Kiang Cheng, Jian Hao Sim, Richard Chay Shien Long, Wen Sheng Wong, Azrina Abdul Kadir, Gurudevan Mahadevan, Kim Fong Ng
Presenter
Wee Pang Ng
Authors
Wee Pang Ng1, Jin Kiang Cheng2, Jian Hao Sim1, Richard Chay Shien Long3, Wen Sheng Wong1, Azrina Abdul Kadir1, Gurudevan Mahadevan1, Kim Fong Ng1
Affiliation
Sultanah Aminah Hospital, Malaysia1, Hospital Sultanah Aminah, Malaysia2, Sultanah Aminah Hospital,, Malaysia3,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-148
Coronary - DES/BRS/DCB
Case Report: Successful Revascularization of de Novo Chronic Total Occlusion Lesion With Drug Coating Balloon
Wee Pang Ng1, Jin Kiang Cheng2, Jian Hao Sim1, Richard Chay Shien Long3, Wen Sheng Wong1, Azrina Abdul Kadir1, Gurudevan Mahadevan1, Kim Fong Ng1
Sultanah Aminah Hospital, Malaysia1, Hospital Sultanah Aminah, Malaysia2, Sultanah Aminah Hospital,, Malaysia3,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 51-year-old Chinese man with no prior history of medical illness, active smoker for 20 pack years, presented with new onset of chest pain for 3 days. He complained of central chest pain, heaviness in nature with pain score 4/10 on arrival. Vital signs were stable, BP 102/68 mmHg, HR 64 bpm, SpO2 100% on room air. Lungs were clear, heart sound normal with no murmur. A 12-lead ECG showed sinus rhythm with widespread ST-segment depression over lead I, II, III, aVF, V3-V6 with ST elevation over aVR.
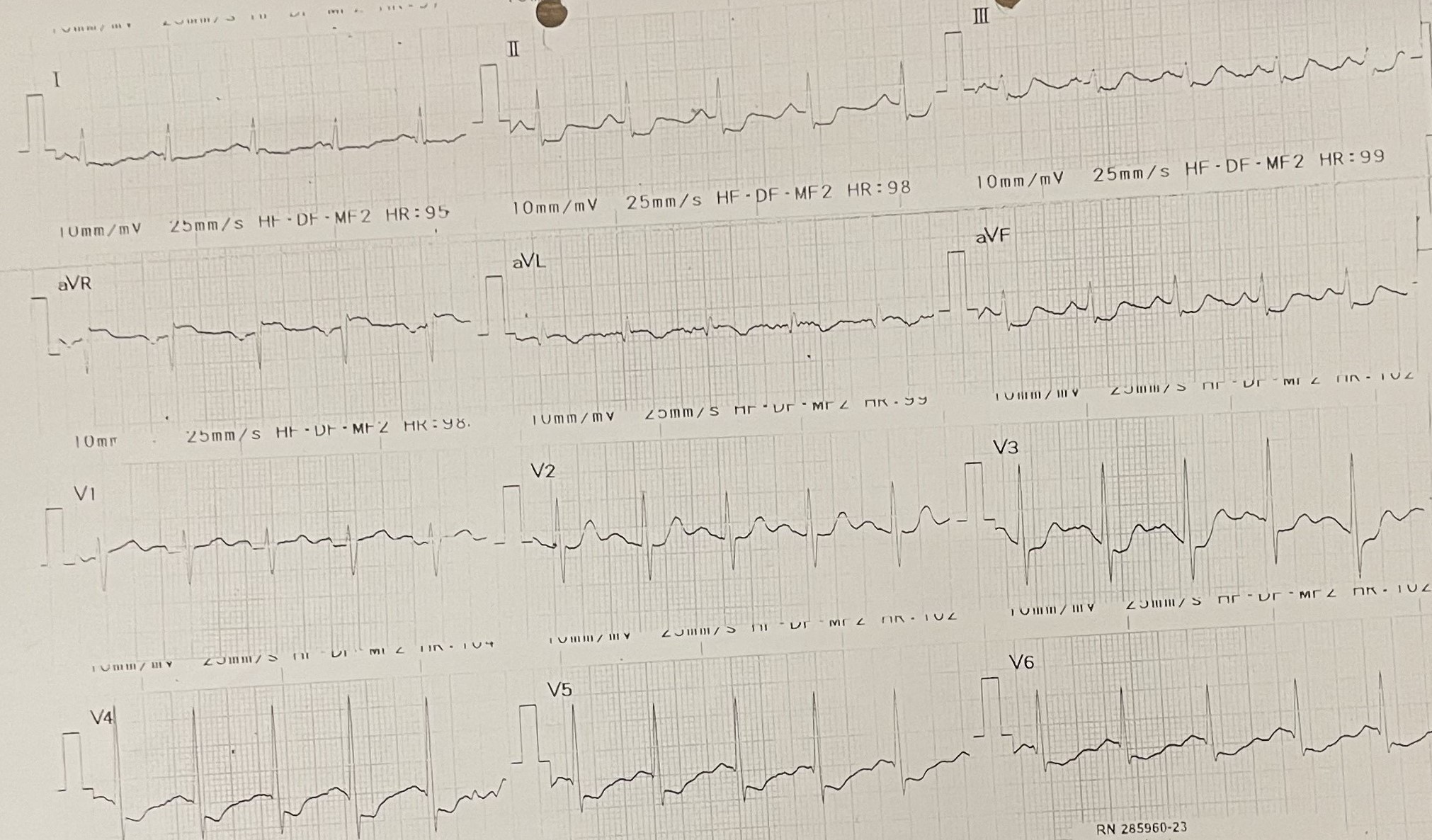

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Creatine kinase level was elevated (753 u/L), renal function profile and serum electrolytes were within normal. Chest x-ray showed normal heart size with clear lung field. A transthoracic echocardiogram showed LVEF 50-55% with hypokinesia over inferolateral segment, normal chamber size. He was diagnosed with Non ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI) and underwent selective in-hospital coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) during the admission.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiogram showed dominant RCA with findings of two vessel disease.Left main stem- normalLAD- proximal 20-30% mild stenosisLCX- mid chronic total occlusion 100%, collaterals from distal LAD to OM branch seenRCA- dominant, mid 99% stenosis

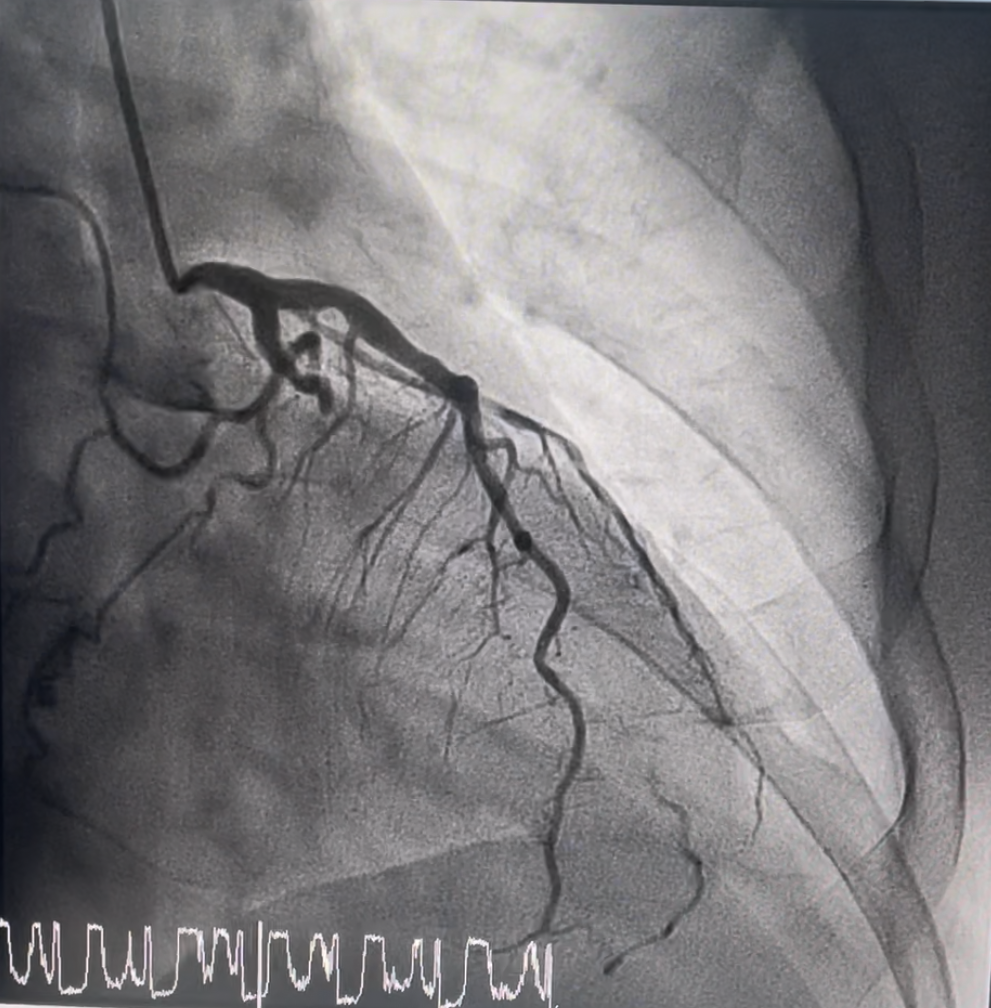




Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was performed via transradial approach with 6 Fr sheath. Right coronary system was engaged with JR 4.0 6 Fr guiding catheter, RCA was wired down with Sion Blue wire till distal RCA. Mid RCA lesion site was predilated with NC Balloon 3.0x 15 mm, up to 24 atm, subsequently was stented with drug-eluting stent (DES)- Combo Plus 3.5x 38mm + Combo Plus 3.5x 13 mm. Good result was obtained, TIMI 3 flow.Then we proceed with PCI to CTO mid LCX. Left coronary system was engaged using EBU 3.0 6 Fr guiding catheter. CTO lesion was successfully crossed with Sion Blue wire till distal LCX. Lesion was prepared with Ryurei Balloon 2.0x 15 mm, up to 22 atm. Subsequently, Sirolimus DCB (Selution SLR 2.5x 40mm) was deployed at mid LCX, inflated up to 8 atm for 60 seconds. Good result was obtained, TIMI 3 flow, residual stenosis 20%, no dissection seen. He was angina free and discharged well the next day. We performed a re-look coronary angiogram after 3 months, which showed good positive remodeling with no restenosis over LCX. Patient remained asymptomatic.
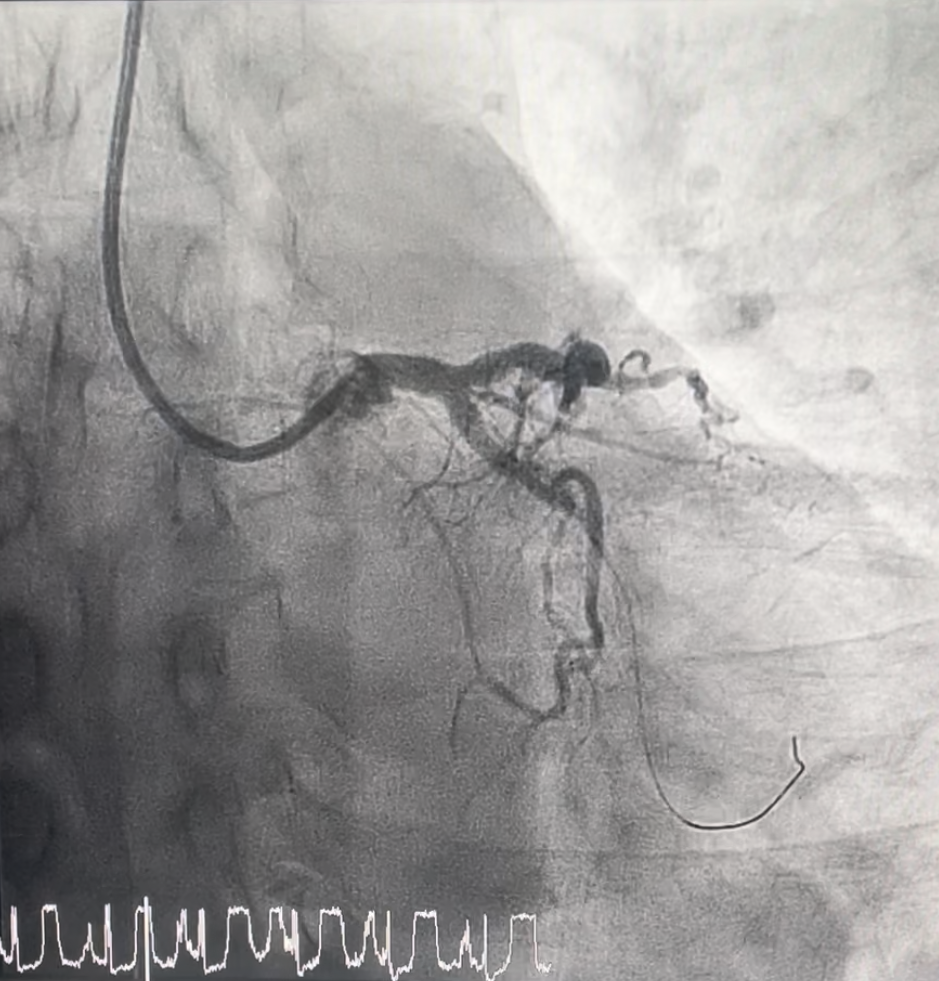
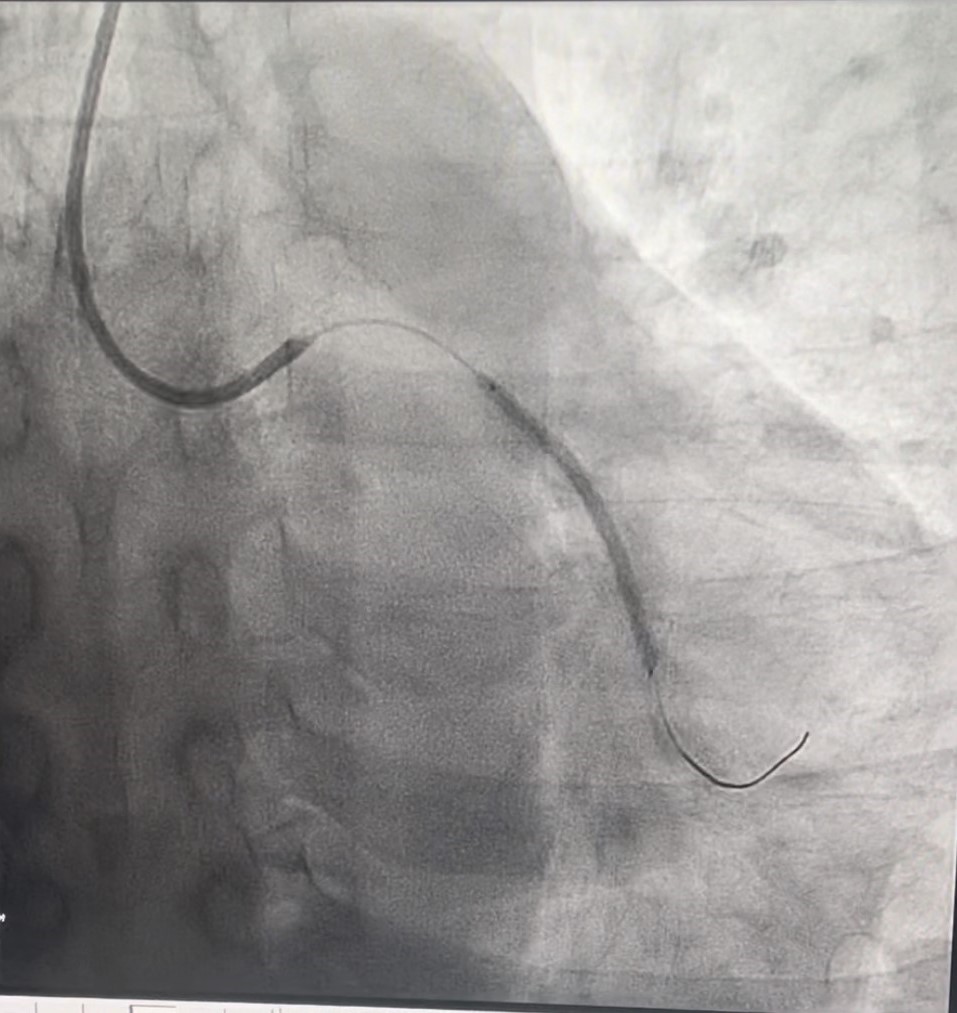
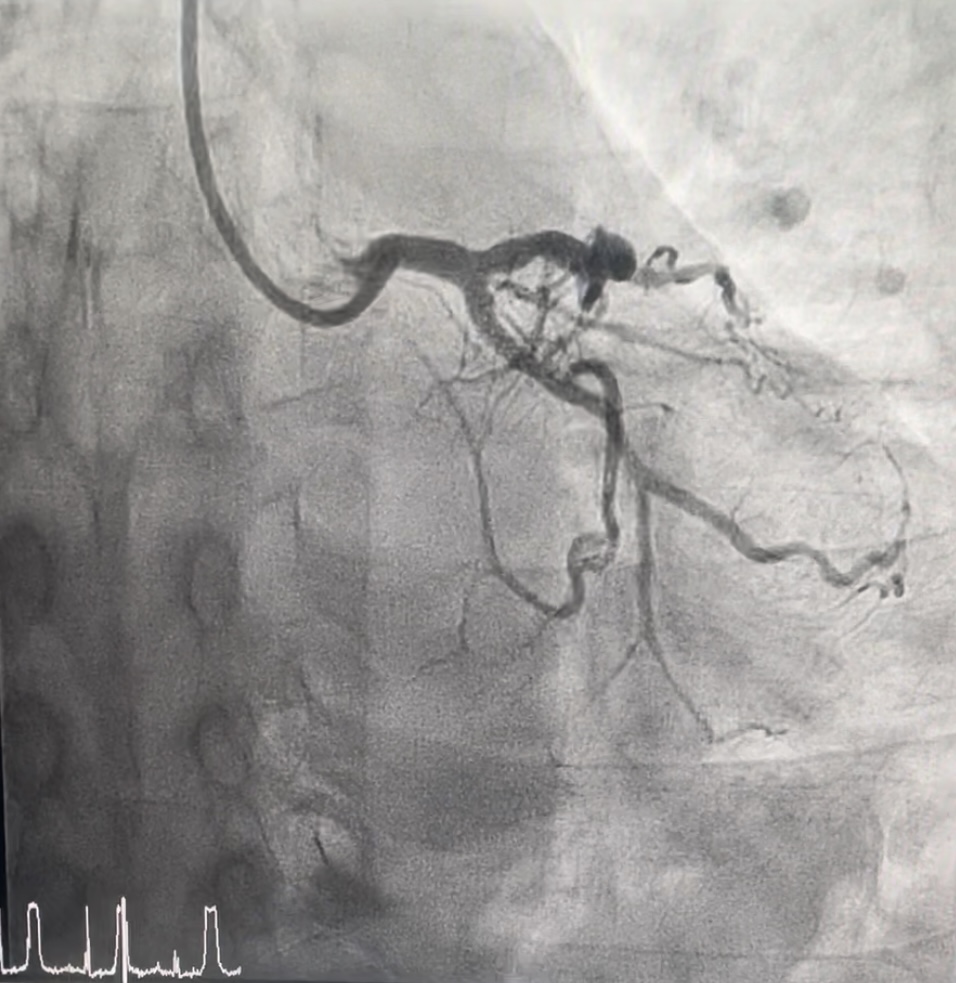



Case Summary
This case showed good result on revascularization of de novo chronic total occlusion (CTO) lesion with drug coating balloon (DCB) only treatment. DCB has now been widely used for small vessel lesion (< 3.0 mm) and in-stent restenosis (ISR), however studies on DCB only treatment for CTO lesion are scarce. CTO lesions have higher risk of in-stent restenosis and stent thrombosis, which remains a challenge in interventional cardiology. The rationale of “stentless” strategy using DCB could potentially offer a solution. More clinical studies on DCB only treatment to CTO lesions are encouraged.

