Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-022
Coronary Artery Dissection and Hematoma Formation After Intravascular Lithotripsy for Severe Coronary Artery Calcification
By Nao Yasuda, Takuma Tsuda
Presenter
Nao Yasuda
Authors
Nao Yasuda1, Takuma Tsuda1
Affiliation
Nagoya Ekisaikai Hospital, Japan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-022
Coronary - Adjunctive Procedures (Thrombectomy, Atherectomy, Special Balloons)
Coronary Artery Dissection and Hematoma Formation After Intravascular Lithotripsy for Severe Coronary Artery Calcification
Nao Yasuda1, Takuma Tsuda1
Nagoya Ekisaikai Hospital, Japan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
Case was 60’s-y-o-female with hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and prior cerebral infarction. Preoperative echocardiography showed inferior wall hypokinesis and thinning and also revealed deteriorated EF (=45.9%) with moderate MR. Therefore, coronary angiography was planned. Pre-angiography ECG, chest X-ray and lab tests were normal.



Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Myocardial scintigraphy showed inferior and apical ischemia.


Relevant Catheterization Findings
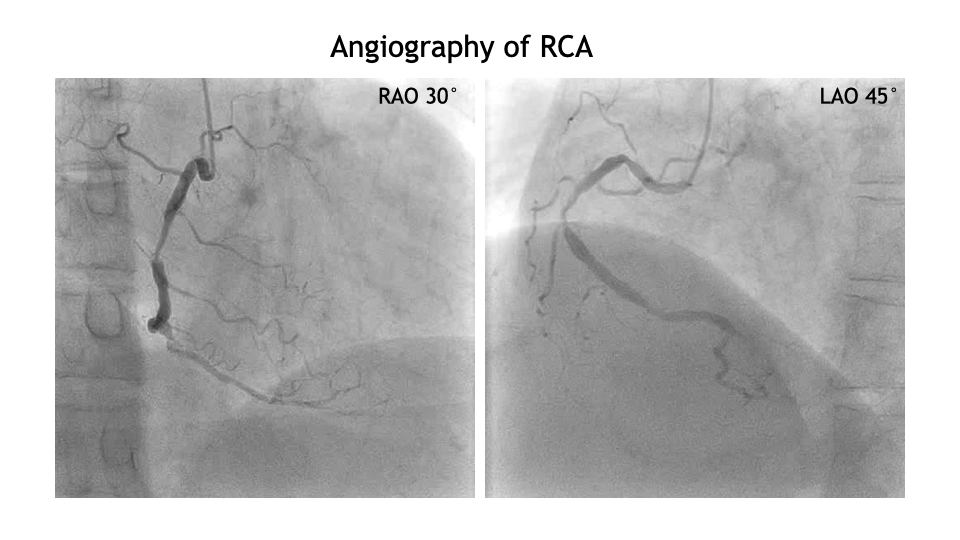
Angiography revealed 75-90% stenosis of RCA #2 segment and 100% stenosis (CTO) of #4AV. LCA showed 75% stenosis of #7 segment, 100% stenosis (CTO) of #15, and 90% stenosis of OM branch.



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
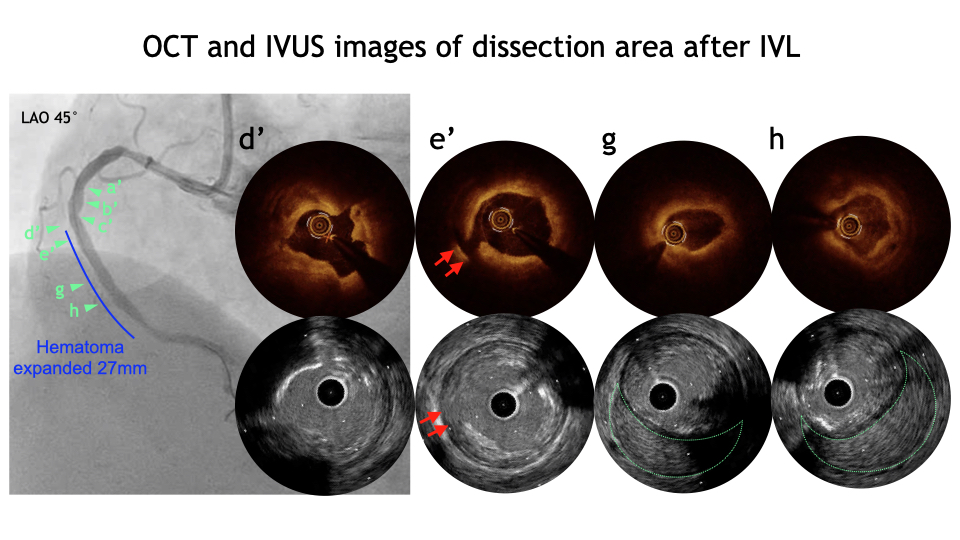
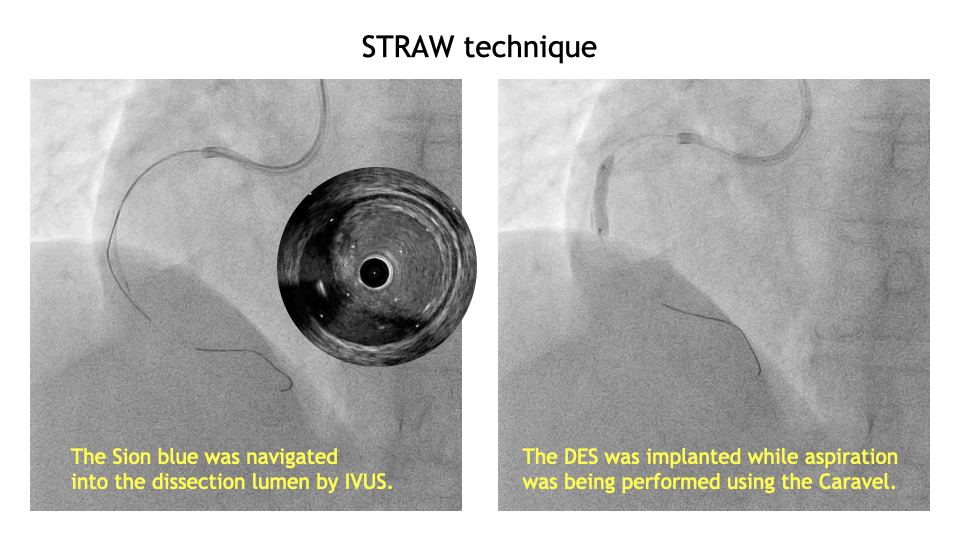
PCI was performed for RCA #2 lesion. OCT showed circumferential calcification with thickness ≥500μm and length ≥5mm. SHOCKWAVE was performed with a 3.0mm balloon, 10 shots for 8 cycles. After re-evaluation by OCT, SHOCKWAVE was sized up to use a 3.5mm balloon, with 10 shots for 8 cycles. OCT only suspected hematoma at the distal RCA.IVUS clearly identify a large hematoma extending into the distal RCA. The Sion blue was navigated into the dissection lumen by IVUS guidance with a tip detection method. The Caravel was navigated to aspirate the hematoma with STRAW technique. After IVUS showed decrease in the hematoma, additional aspiration was performed during DES implantation. No further hematoma expansion was observed after stenting, and the procedure was finalized.




Case Summary
Although severe coronary dissection is a rare complication of IVL, we experienced extensive dissection and hematoma formation after IVL for severe calcification, which could be managed by STRAW technique. Careful evaluation of imaging modalities could also be helpful.

