Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-058
A-IVUS Guided CTO Case Report: What Is Next Step for 3 CTOs?
By Kuo-Ming Yang, Feng Yu Kuo
Presenter
Kuo-Ming Yang
Authors
Kuo-Ming Yang1, Feng Yu Kuo1
Affiliation
Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-058
Coronary - Complex PCI - CTO
A-IVUS Guided CTO Case Report: What Is Next Step for 3 CTOs?
Kuo-Ming Yang1, Feng Yu Kuo1
Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
This is a 67-year-old female with a past medical history of hypertension, stable angina and dyslipidemia, who presented with intermittent chest tightness and cold sweating for several months. Coronary angiography was provided in a local hospital and triple vessel disease with CTO on the ostium part of the left anterior descending artery was diagnosed. Due to CAGB refusal, she went to our hospital for PCI management. No abnormal physical examination was not on her.

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Regarding the relevant tests, the ECG and CXR showed no specific abnormalities. The blood tests including full blood account, liver function and renal function were all normal.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
The cardiac catheterization for angiography was done after the initial clinical assessment. The result showed 3 major parts of chronic total obstruction lesions in the ostium part of the left anterior descending artery (LAD), the posterolateral branch part of the right coronary artery (RCA), and the distal part of the left circumflex artery. Moreover, a 70-80% stenosis was also diagnosed in the proximal part of RCA.


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
The lesion in the proximal part of RCA was managed successfully first. Then the CTO lesion in the ostium part of LAD was chosen for revascularization. The Runthrough wire was placed into the intermediate artery through 7F EBU guiding catheter. Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) was used to check the possible access from the ostium of LAD. The Conquest Pro wire, whose tip was shaped, with a microcatheter was placed near the access to penetrate the lesion. The Gaia 3rd wire was shifted to penetrate the lesion continuously after a short, penetrated tunnel in the lesion was formed by the Conquest Pro wire. During the penetration, a few difficulties occurred such as breaking the tip of the Gaia 3rd wire and false lumen access. The lesion of CTO was penetrated successfully afterwards. Then the lumen by the wire was checked to confirm all lumen was true lumen by IVUS after it was dilated by small balloons. The lesions in the proximal and distal parts of LAD, and in the ostium part of the diagonal artery were noted afterwards. After wiring into the diagonal artery, a 3.0 x 30 mm Drug-eluting stent (DES) stent was deployed in the LAD-O to -P with the jailed balloon technique. Post-dilation in LAD-P was provided afterwards. Then pre-dilation for the lesion in the distal part of LAD was provided by a 2.5 x 10 mm balloon and a 2.5 x 13 DES was deployed there. IVUS was used to check the stents in LAD were expanded well afterwards.
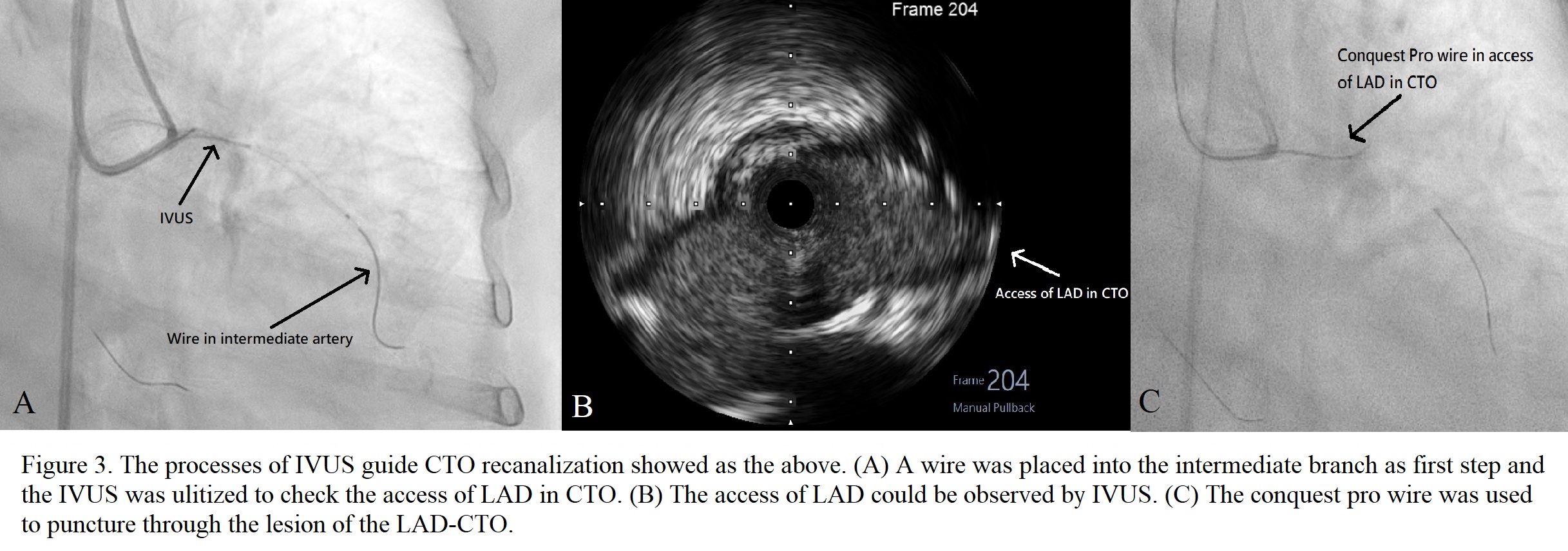
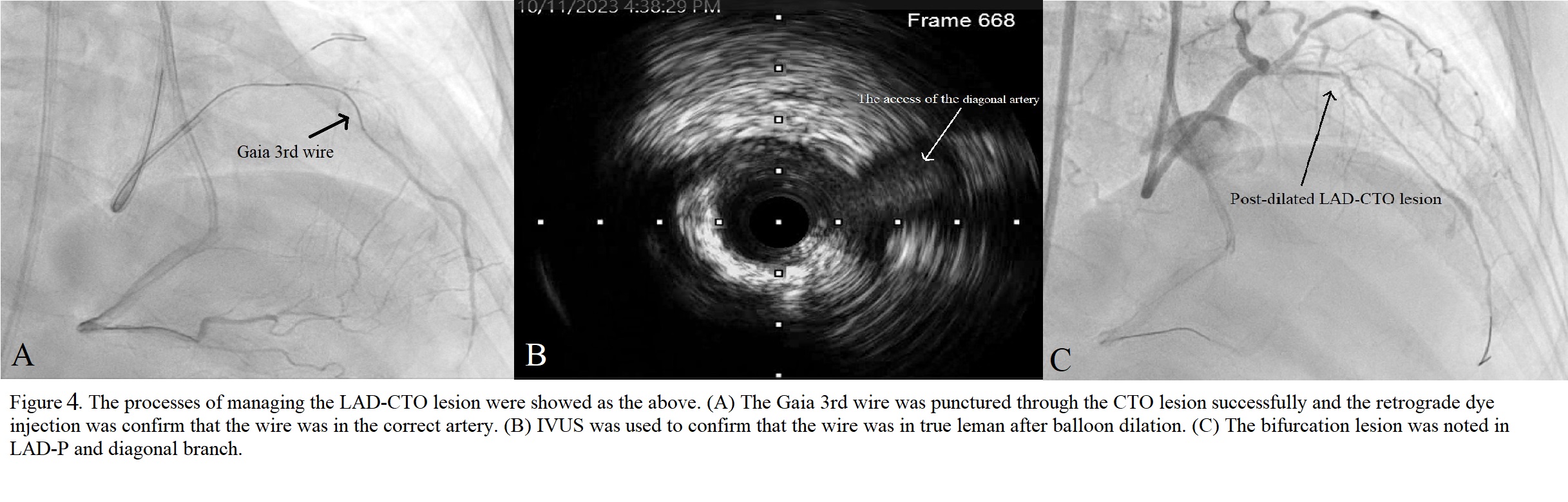
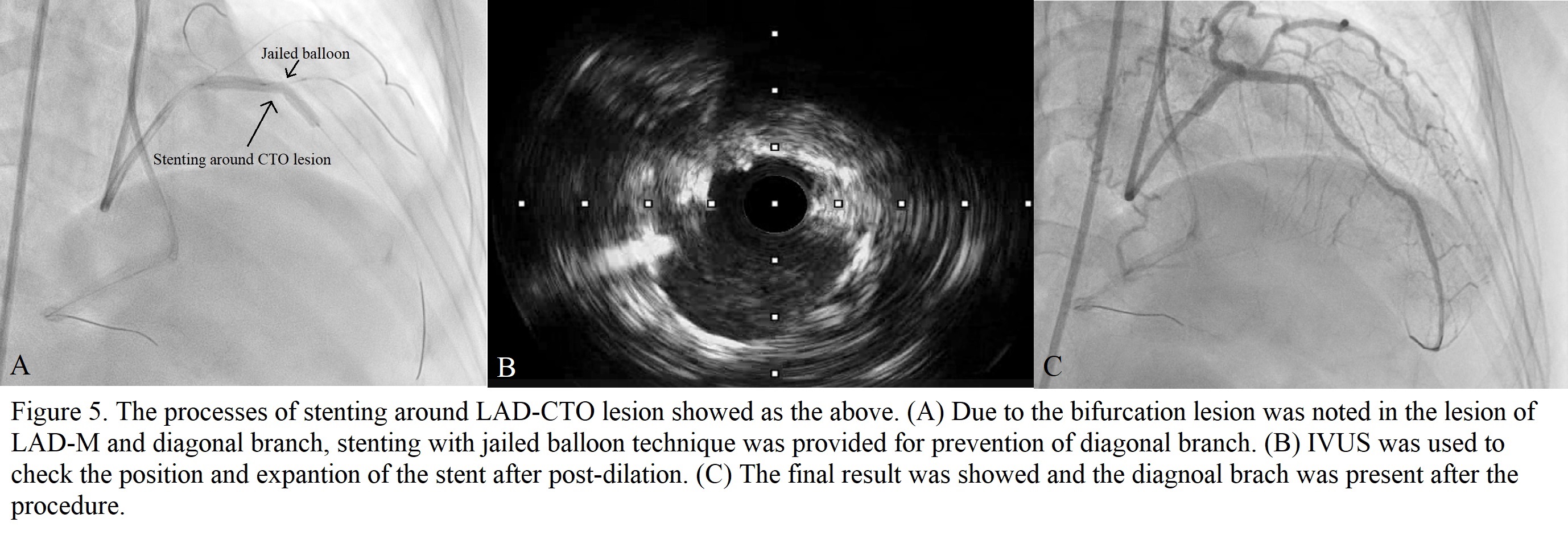



Case Summary
How to provide the largest benefit on patients with CTOs is important. Several points need to be considered. First, it is critical to set a plan for CTO management. In this case, the patient may receive the best outcome after opening the CTO in LAD. Second, IVUS-guide CTO recanalization can provide possible benefits such as reduced cardiac death, and complication rates. Thus, IVUS-guide PCI was utilized to reduce the possible complications. Finally, jailed balloon technique (JBT) is superior to jailed wire technique (JWT) in reducing side branch (SB) occlusion in patients with high V-RESOLVE scores. Thus, the JBT was chosen to prevent the risk of SB occlusion. The best outcome is our goal.

