Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-128
Iatrogenic Aorto-Coronary Dissection During CTO PCI Right Coronary Artery in Post-CABG Patient
By Vimean Sey, Doni Firman, Amir Aziz Alkatiri, Arwin Saleh Mangkuanom, Nanda Iryuza
Presenter
Vimean Sey
Authors
Vimean Sey1, Doni Firman2, Amir Aziz Alkatiri2, Arwin Saleh Mangkuanom2, Nanda Iryuza2
Affiliation
Cambodia China Friendship Preah Kossamak Hospital, Cambodia1, National Cardiovascular Center Harapan Kita, Indonesia2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-128
Coronary - Complication Management
Iatrogenic Aorto-Coronary Dissection During CTO PCI Right Coronary Artery in Post-CABG Patient
Vimean Sey1, Doni Firman2, Amir Aziz Alkatiri2, Arwin Saleh Mangkuanom2, Nanda Iryuza2
Cambodia China Friendship Preah Kossamak Hospital, Cambodia1, National Cardiovascular Center Harapan Kita, Indonesia2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 62-year-old male with a past medical history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, ischemic heart disease had a previous CABG for distal left main disease and two vessel diseases, with LIMA to LAD, SVG to OM, and LCX in December 2020. He’s been presented to the emergency department due to progressively worsening angina and dyspnea on exertion. He had been hospitalized multiple times for the past 3 months due to the same reason, despite optimal medical treatment.
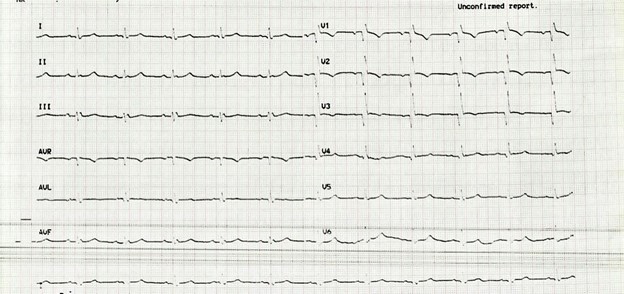

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
An electrocardiogram revealed a complete RBBB pattern. An echocardiogram showed global left ventricular systolic function is reduced with an ejection fraction of 49%. Cardiac biomarker - Troponin I kit test was negative at presentation. The rest of the laboratory parameters were within normal limits.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
A coronary angiogram revealed distal left main disease, chronic total occlusion (CTO) of the proximal left anterior descending (LAD), non-dominant left circumflex (LCX) with diffuse disease in the distal, and dominant right coronary artery (RCA) with diffuse disease in the proximal and chronic total occlusion (CTO) in the distal. Patent LIMA to LAD, SVG to OM, and SVG to LCX. Based on these findings and after a heart team and patient discussion, right coronary artery intervention was planned.


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
A 7-F Judkins Right was selected. Sion Blue wire was passed to the right marginal artery to provide more support. Fielder XT-A wire with back-up support by a Fine-cross micro-catheter cannot cross the lesion. We changed the guiding catheter to Amplatz Left 1-7 F and escalated the wire to Gaia Second, and successfully crossed the lesion. We pre-dilated with a 1.5 x 15 mm semi-compliant balloon and then with 3.0 x 15 mm non-compliant Scoring balloon. A 3.0 x 38 mm drug eluting stent (DES) could not crossed the lesion even after multiple dilatations with non-compliant Scoring balloon. With Guide Liner deep engaged into right coronary artery, stent could be delivered. A test injection for stent placement showed spiral dissection and intra-mural hematoma from mid right coronary artery up to the crux with contrast extravasation on the aortic root. First, a 3.0 x 38 mm drug eluting stent (DES) was deployed at the mid to distal segment of RCA to stop dissection goes further to distal part. A 3.0 x 15 mm Cutting balloon was inflated multiple times from mid to proximal right coronary artery to fenestrate the sub-intima hematoma. Another 3.5 x 38 mm stent was deployed from the ostium to proximal segment of the right coronary artery to close the dissection entry site. Final angiographic shoot revealed good stent optimization with TIMI 3 flow without visible contrast trapping. The patient was discharged after 72 hours of the procedure without any complications.
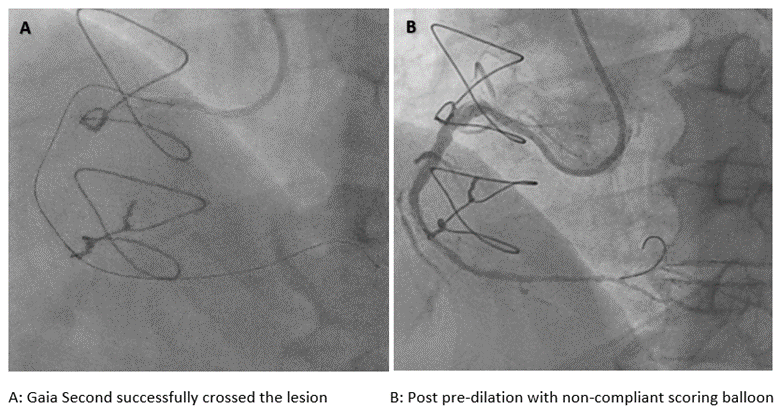
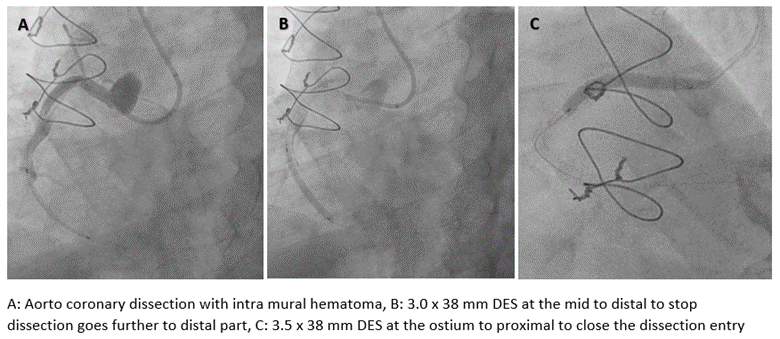
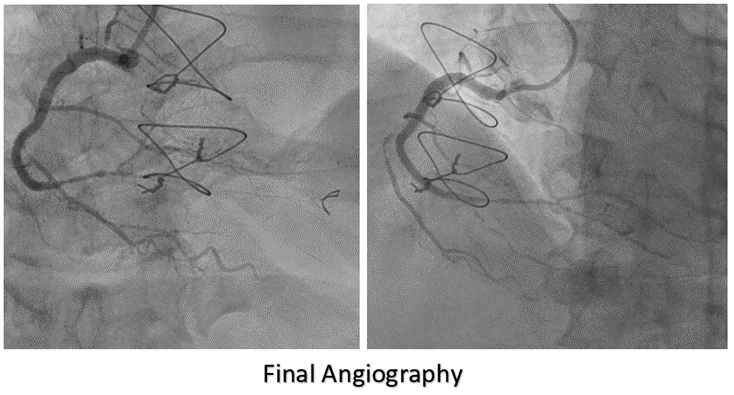



Case Summary
Iatrogenic dissection of the right coronary artery and its extension to the aortic root and eventually to the ascending aorta is a rare but potential complication that must be taken into account while performing both diagnostic procedures and PCIs, especially in patients with chronic total occlusions. The mechanism and causes can vary with the catheter itself, contrast injection, guide wire injury, guide extensions, balloons, and stents. Stent implantation to seal the flap in the ostial right coronary artery is the most common management strategy and has the highest success rate.

