Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-016
Navigating the Complex Coronaries in Acute Myocardial Infarction
By Mohd Tawfeq Mohd Noor, Yuen Han Lim, Faten Aqilah Aris, Rowina Lynne Murray, Jassie Teo
Presenter
Mohd Tawfeq Mohd Noor
Authors
Mohd Tawfeq Mohd Noor1, Yuen Han Lim1, Faten Aqilah Aris1, Rowina Lynne Murray1, Jassie Teo1
Affiliation
National Heart Institute, Malaysia1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-016
Coronary - ACS/AMI
Navigating the Complex Coronaries in Acute Myocardial Infarction
Mohd Tawfeq Mohd Noor1, Yuen Han Lim1, Faten Aqilah Aris1, Rowina Lynne Murray1, Jassie Teo1
National Heart Institute, Malaysia1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 50-year-old man, known case of hypertension and dyslipidemia presented with chest pain for 5 hours prior to presentation. Blood pressure was 80/50, heart rate 65 upon arrival. Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed ST elevation over the inferior leads. He was treated as acute inferior myocardial infarction in cardiogenic shock and was subjected for primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Unfortunately patient had episode of ventricular fibrillation at emergency department.


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Patient was resuscitated for 10 minutes before primary percutaneous coronary intervention started. Echocardiography showed ejection fraction of 35%.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiogram was done via right femoral artery revealed acute total occlusion of distal right coronary artery with tight bifurcation stenosis at distal left main, ostial to proximal left anterior descending and left circumflex arteries.


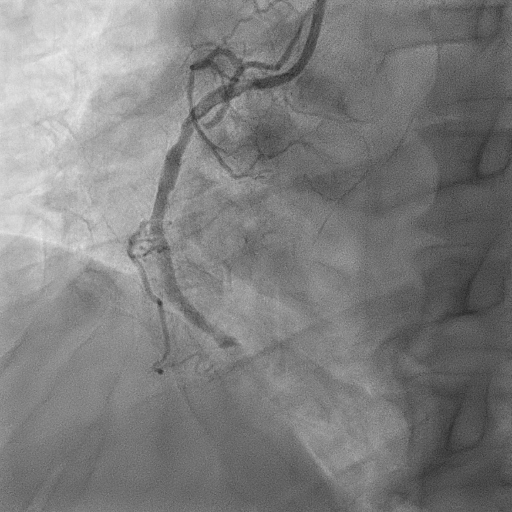



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Patient had another episode of ventricular fibrillation while transferred to the invasive catheterization laboratory. Intra-aortic balloon pump was inserted via left femoral artery.
JR 3.5-6French was used as guiding catheter. Runthrough floppy wire was wired to distal right coronary artery. Thrombus aspiration was done using Export catheter. Multiple red thrombus aspirated. He had to be resuscitated throughout the procedure as asystole.
Intracoronary Tirofiban given due to heavy thrombus burden. Able to restore the coronary flow.
Repeated shot taken noted ulcerated plaque at distal segment. Stenosis distal to the ulcerated plaque was prepared predilated with semi compliant balloon 2.0, 20 mm at nominal pressure. Xience stent 3.0, 18 mm was deployed at distal segment.
Patient hemodynamic required two inotropic supports, he was on invasive mechanical ventilation and was transferred to critical care unit.
Patient was able to be weaned off from mechanical ventilation and hemodynamic support gradually. He opted for high risk percutaneous coronary intervention for left main, left anterior descending and left circumflex bifurcation lesion Medina 1,1,1. The procedure was done one week after the index procedure.
Upfront two-stent bifurcation stenting was done with imaging guidance. Double kissing crush technique were used with stents Megatron 3.5, 28 mm, Synergy 2.5, 48 mm and Synergy 2.75, 20mm were deployed. Patient was stable and discharged home the day after.

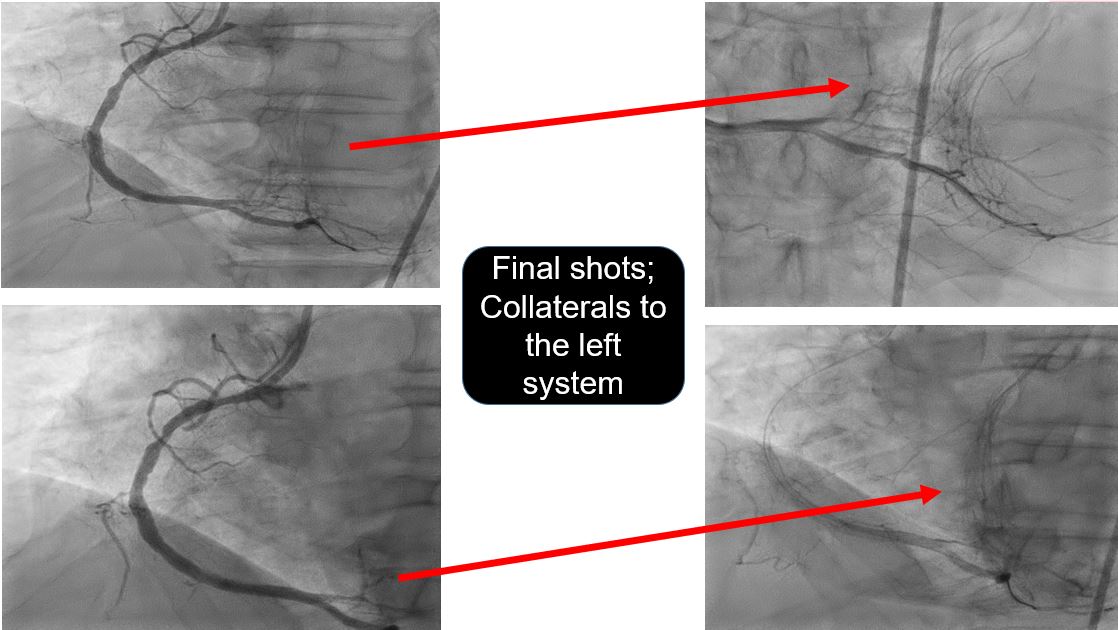
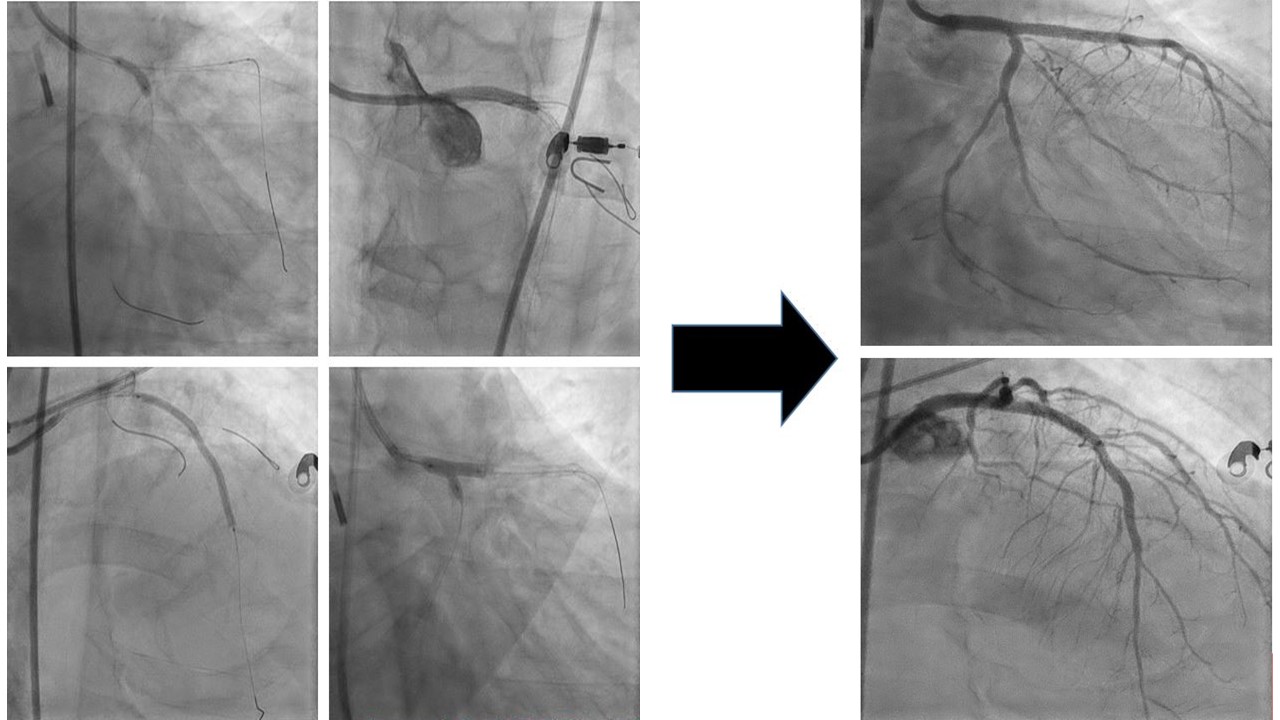
Case Summary
This patient presented with acute inferior myocardial infarction in cardiogenic shock, with total occlusion of his right coronary artery and severe critical lesion of the bifurcation left main, left anterior descending and left circumflex arteries. Patient with heavy thrombus burden has increased risk of no-reflow, microvascular obstruction and distal embolization. The decision for immediate or delayed stenting depending on clinical judgment and case to case basis. Immediate coronary intervention for non-infarct related arteries in cardiogenic shock was not done in this case considering the complexity of the lesion and long duration of cardiac arrest.

