Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2024. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-009
Obesity Paradox in ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction Outcomes in a Philippine Tertiary Center
By Anna Francesca Abarquez, Richard Henry Tiongco, Jaime Alfonso Aherrera
Presenter
Anna Francesca Abarquez
Authors
Anna Francesca Abarquez1, Richard Henry Tiongco2, Jaime Alfonso Aherrera2
Affiliation
The Medical City, Philippines1, Philippine General Hospital, Philippines2
View Study Report
TCTAP A-009
ACS/AMI
Obesity Paradox in ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction Outcomes in a Philippine Tertiary Center
Anna Francesca Abarquez1, Richard Henry Tiongco2, Jaime Alfonso Aherrera2
The Medical City, Philippines1, Philippine General Hospital, Philippines2
Background
Cardiovascular disease remains to be the number one leading cause of morbidity and mortality locally, estimated to cause one in five deaths in the Philippines. Obesity, has become the leading metabolic disease in the world with the World Health Organization (WHO) referring to it as a global epidemic. However, when Obesity and CAD coexist, data from several epidemiologic studies have found that individuals with obesity present more favorable prognosis compared to individuals who are normal or underweight, hence the term Obesity Paradox.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study conducted at the University of the Philippines -Philippine General Hospital. The charts and angiographic clips of patients diagnosed with ST-Elevation Acute Myocardial Infarction who underwent coronary angiogram+/-percutaneous coronary intervention from March 1, 2020- March 30 2022 at the UP-PGH were reviewed.
Results
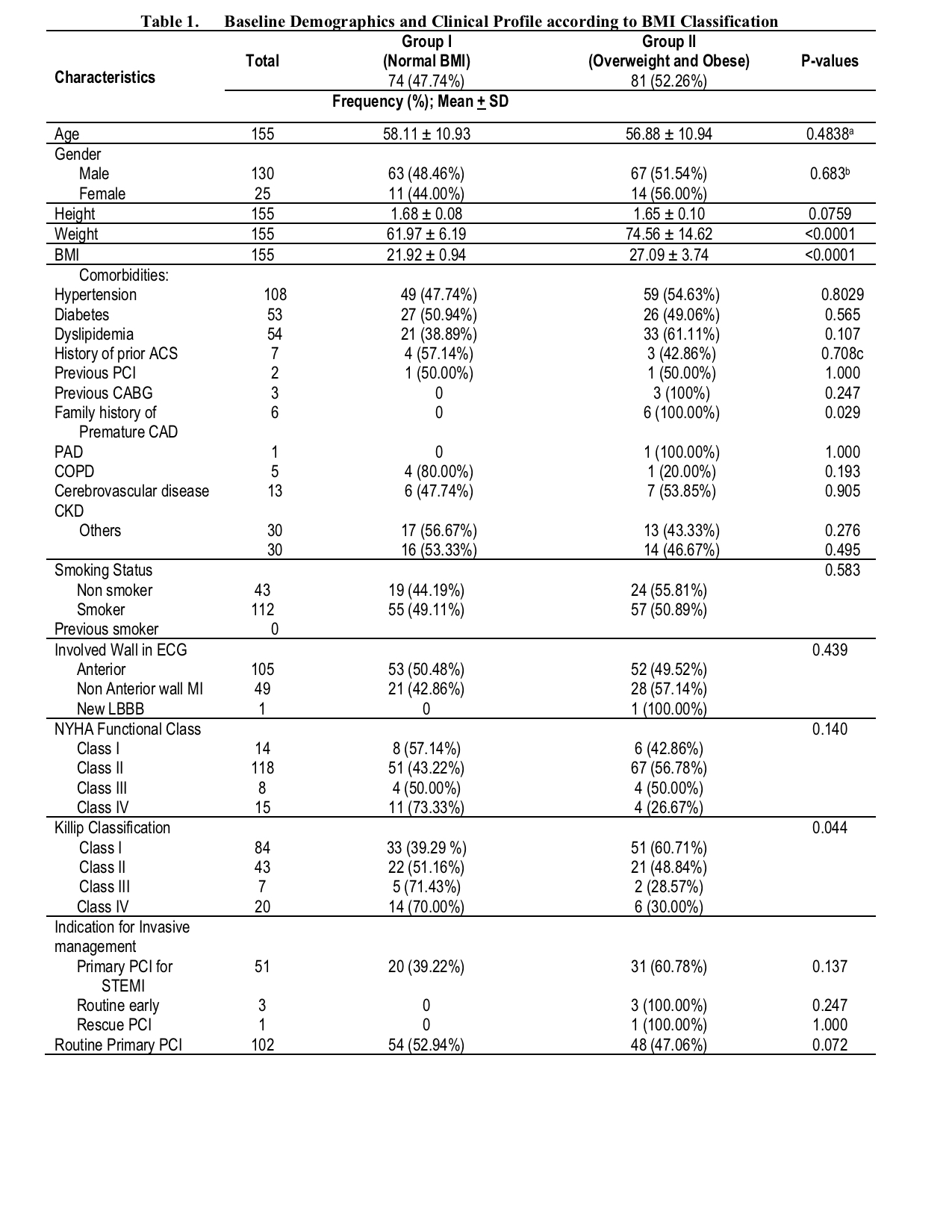
Between March 1, 2020 to March 30, 2022, a total of 155 patients underwent cardiac catheterization and percutaneous coronary intervention for STEMI. Among these, 25 were women and 130 were men with mean age of 56.88 ± 10.94 years old among the overweight and obese group, and 58.11± 10.93 among the normal BMI group. 47.74% of the population had normal BMI (BMI <= 22.9), while 81 or 52.26% were identified as Overweight and Obese based on BMI using the Asia Pacific criteria. Obese and overweight patients have higher frequencies of hypertension, hyperlipidemia. Normal BMI patients presented with more severe heart failure, higher New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional Class and Killip Classification. Frequency of those with prolonged hospital stay is higher among those with normal BMI. The odds of in-hospital, 1 month, and 6months mortality among overweight and obese individuals are lower but are not statistically significant also when adjusted for the following confounders: hypertension, diabetes, covid status, smoking status, HDL, LDL and HBA1c levels.

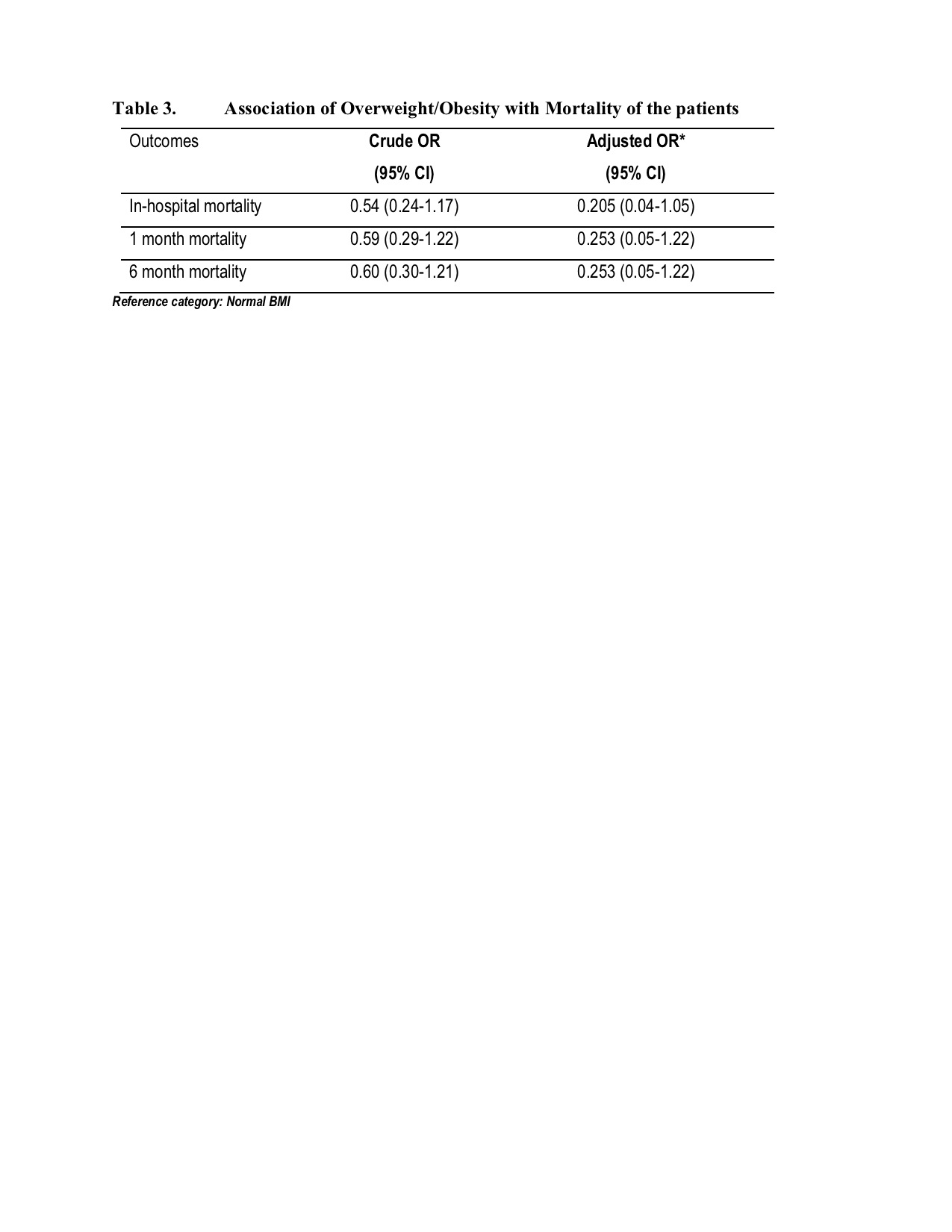



Conclusion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first local study to evaluate the impact of body mass index as well as the applicability of Obesity Paradox in STEMI patients post percutaneous coronary intervention among Filipino population. In conclusion, our study showed that obese and overweight patients has increased risk of prolonged length of hospitalization but no significant difference in in-hospital, 1 month, and 6 months all- cause mortality of STEMI patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention.

