Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
CASE20191117_003
| IMAGING AND PHYSIOLOGIC LESION ASSESSMENT - Vulnerable Plaque | |
| Very Late Stent Failure Is Not a Benign Clinical Entity! | |
| Ahmed Kasem1 | |
| King Abdulaziz University Hospital, Saudi Arabia1, | |
|
[Clinical Information]
- Patient initials or identifier number:
ak
-Relevant clinical history and physical exam:
50 y/o female patient. She had severe typical chest pain (40 min.prior to arrival). Risk factors: cigarette smoker, diabetes, hypertension. He is not compliant to his medication. physical exam: fully conscious, anxious due to chest pain. B/P 230/120 (iv tridil 50 µm/min) ¡¦ reduced to 143/73 then he was given IV thrombolytic (Metalase), in addition to other medications (morphine 3 mg, SL Nitrates 5mg, Aspirin 300mg, clopidogrel 600mg). 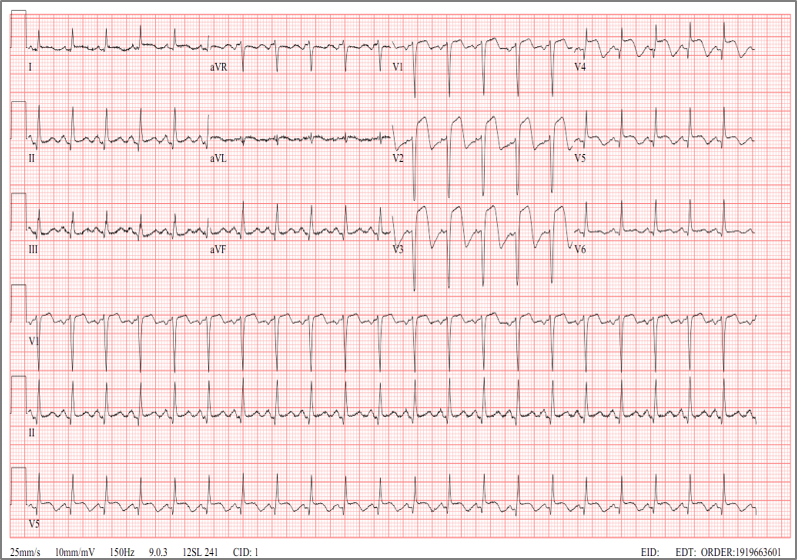  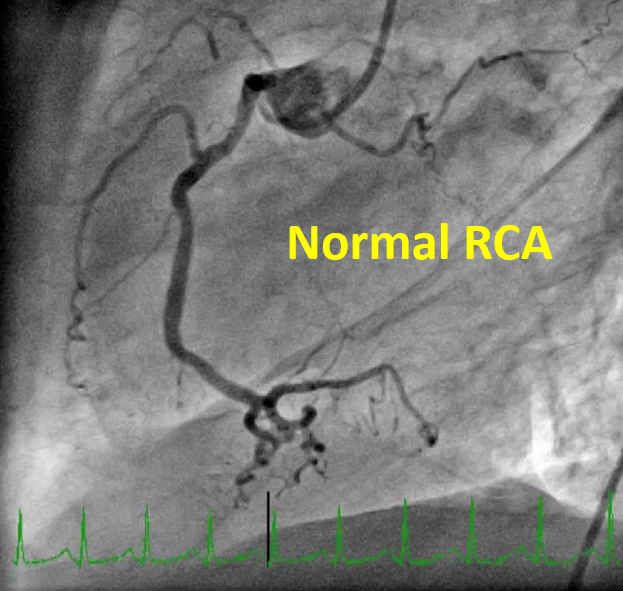 -Relevant test results prior to catheterization:
CK-MB 84, Troponin 200 ECG: showed Anterior Wall STEMI. Echo: akinesia of anterior wall and antero-septal wall 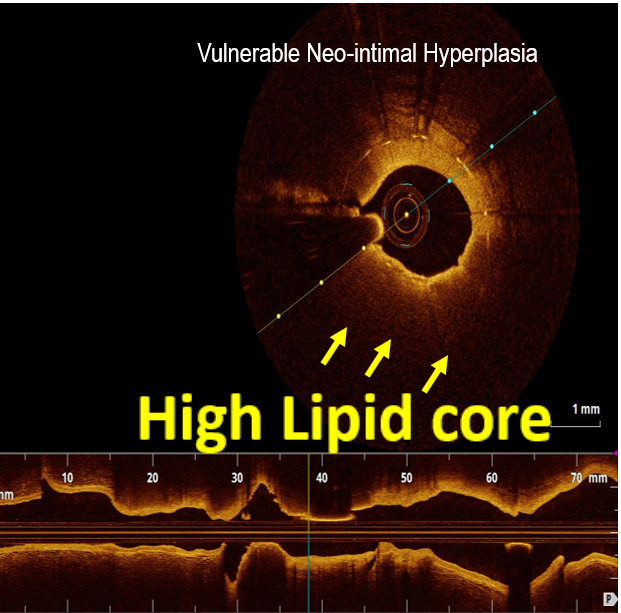 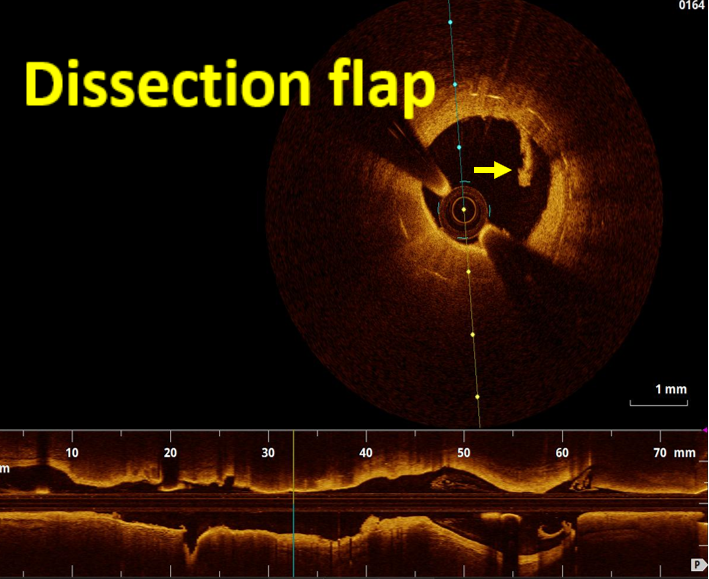 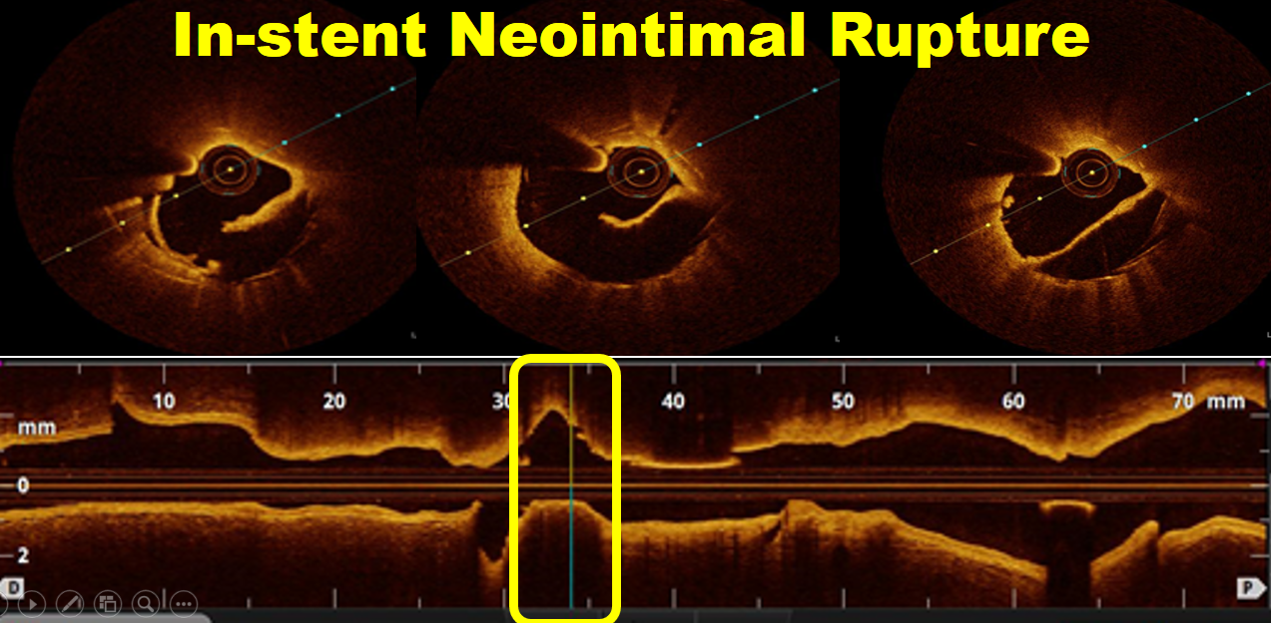 - Relevant catheterization findings:
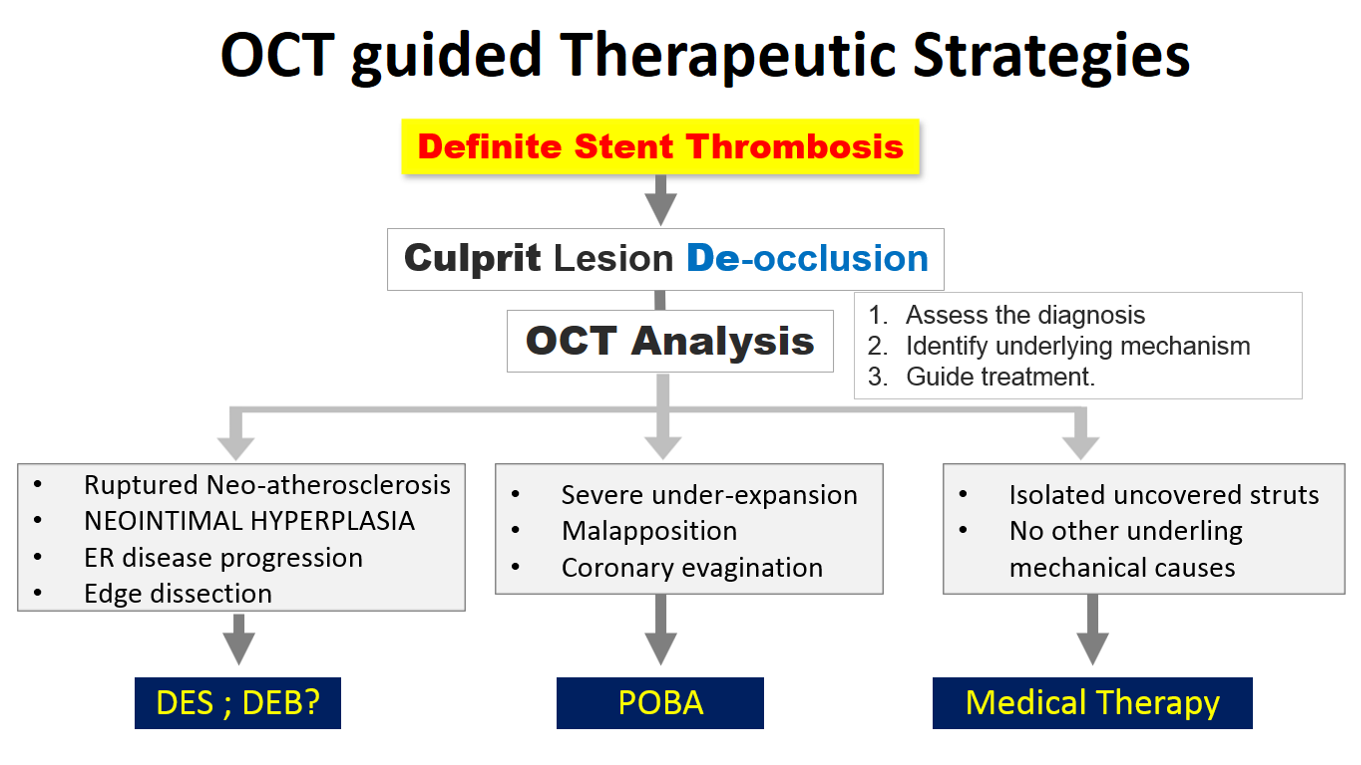
LAD Successfully recanalized after IV thrombolysis, there is borderline underling In-stent restenosis in mid LAD. left circumflex and RCA are normal.OCT was done to assess the diagnosis, identify underling mechanism, and guide the treatment.
   |
|
|
[Interventional Management]
- Procedural step:
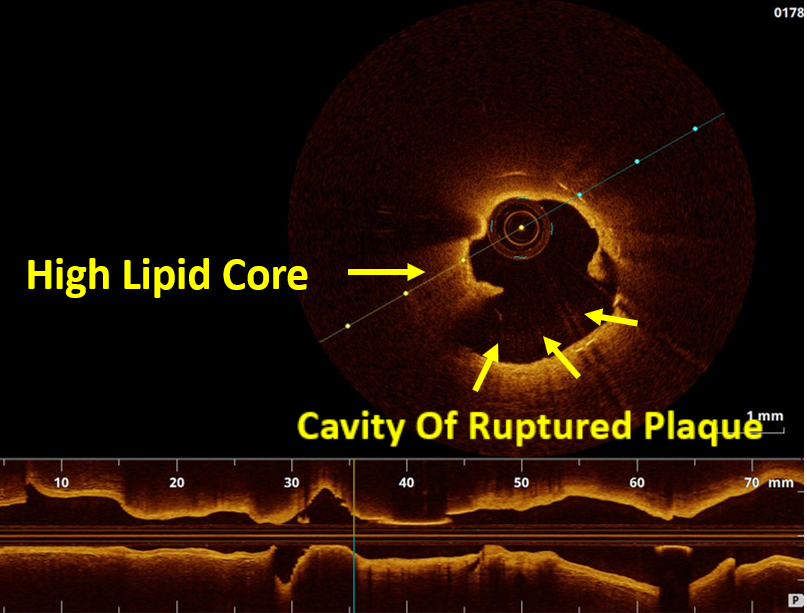
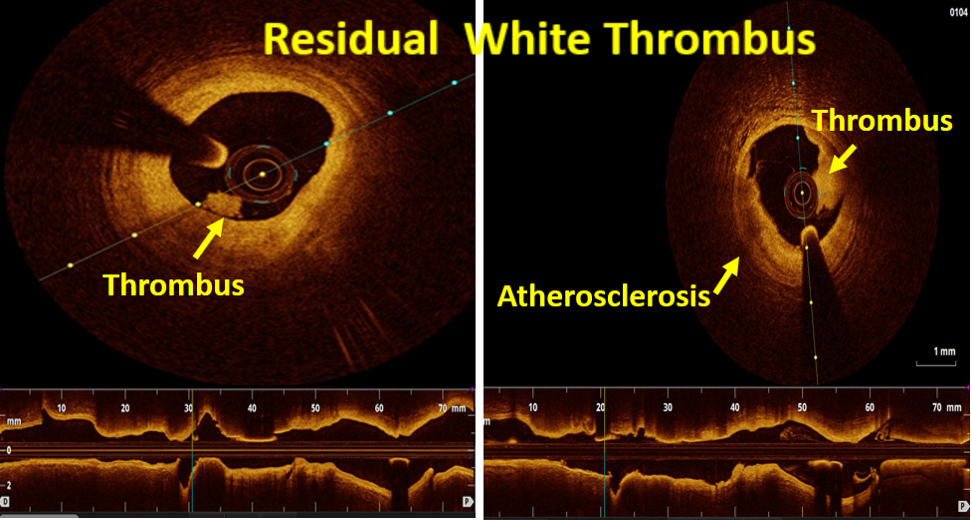
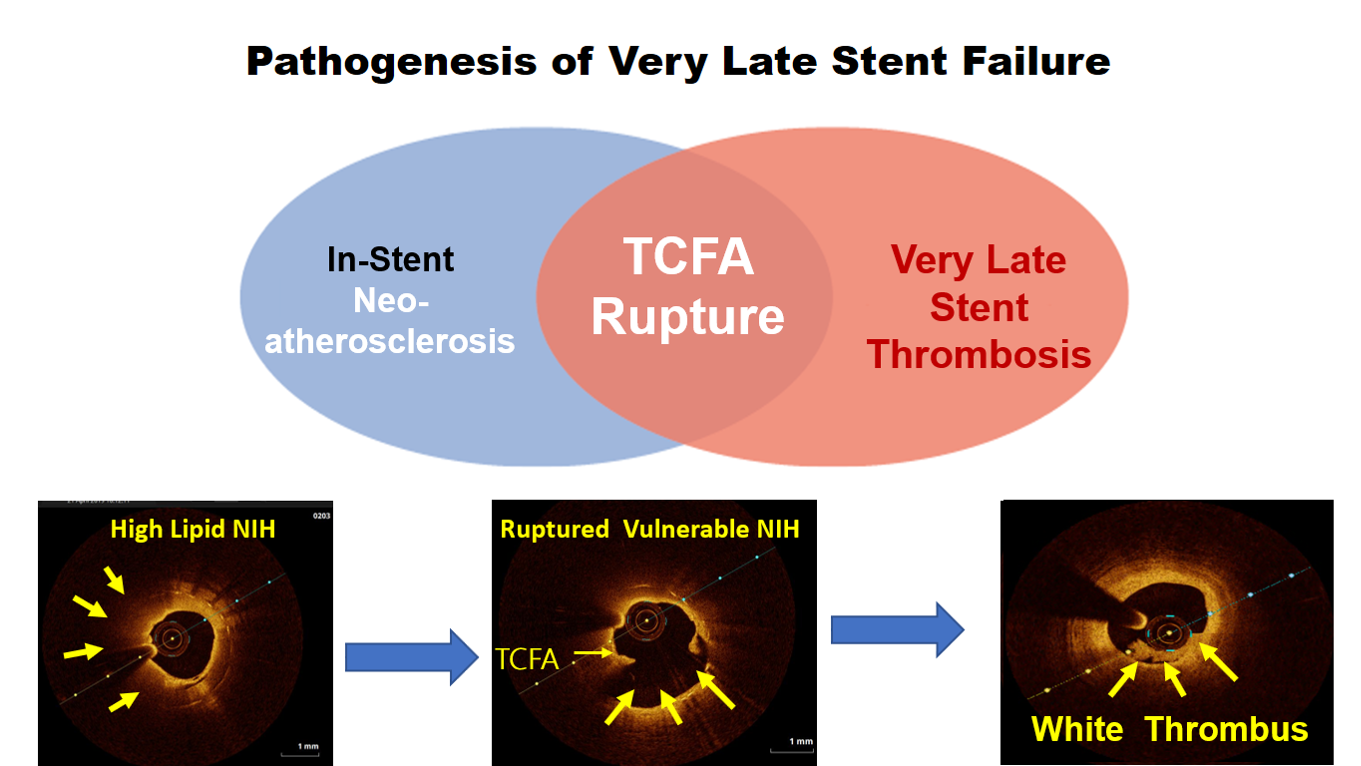
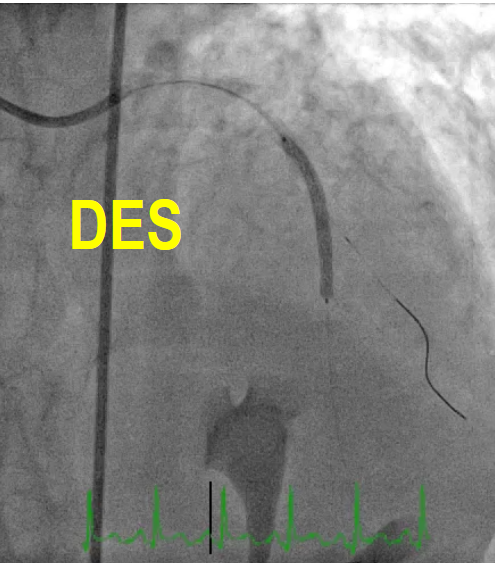
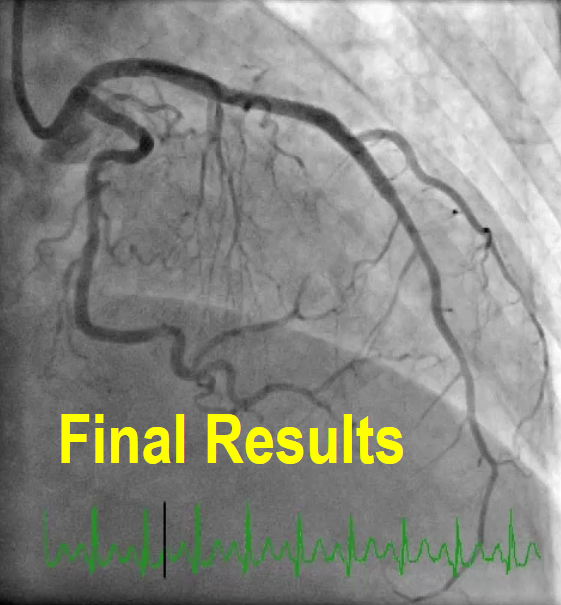
OCT imaging clearly identifying the underlying mechanism of very late stent thrombosis which is a vulnerable in-stent neointimal hyperplasia, with high lipid core, dissection flap, thin cap fibro atheroma and large cavity of ruptured vulnerable in-stent neoatherosclerotic plaque with residual white thrombus, and accordingly, balloon predilatation and DES (Hetero-Stent) to mid-LAD In-Stent Restenosis with wire protection in diagonal branch, OCT repeated again after stent deployment showed well apposition stent. excellent final results.
   - Case Summary:
Neoatherosclerosis is a masquerading mechanism of very late stent thrombosis which not only contribute in very late luminal narrowing(in-stent restenosis) but also it can cause very late stent thrombosis through the vulnerable in-stent plaque ruptures and thrombus occlusion.OCT is currently the best available imaging tools not only to explore the underling mechanism of very late stent failure (like Neoatherosclerosis) but also to guide the appropriate treatment strategy for in-stent restenosis and thrombosis.New stent technology or targeted anti-atherosclerotic drug therapy may be needed to prevent very late stent failure
|
|