Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
CASE20191101_022
| ENDOVASCULAR - Peripheral Vascular Disease and Intervention | |
| First Case Report of Utilization of Aspirex¢ç Thrombectomy Device to Treat Massive Pulmonary Embolism in Taiwan | |
| Chung-Ho Hsu1, Chiung-Ray Lu1, Chun-Cheng Wang2 | |
| China Medical University Hospital, Taiwan1, Tzu Chi General Hospital, Taiwan2, | |
|
[Clinical Information]
- Patient initials or identifier number:
Chang
-Relevant clinical history and physical exam:
A 16-year-old man was sent to our ER due to dyspnea for 2 days. He ever suffered from hemoptysis 11 months ago. Chest CT disclosed peripheral right pulmonary embolism, but which was overlooked without anticoagulation therapy.
-Relevant test results prior to catheterization:
Worsened dyspnea was noted for 2 days. At ER, initial BP was 105/63 mmHg, pulse rate 113bpm, respiratory rate 31/min, sPO2 93% on O2 nasal cannula 6 liter/min. Chest CT showed bilateral massive pulmonary embolism with RV dilatation.
 - Relevant catheterization findings:
PA angiography showed bilateral PA trunk thrombosis.
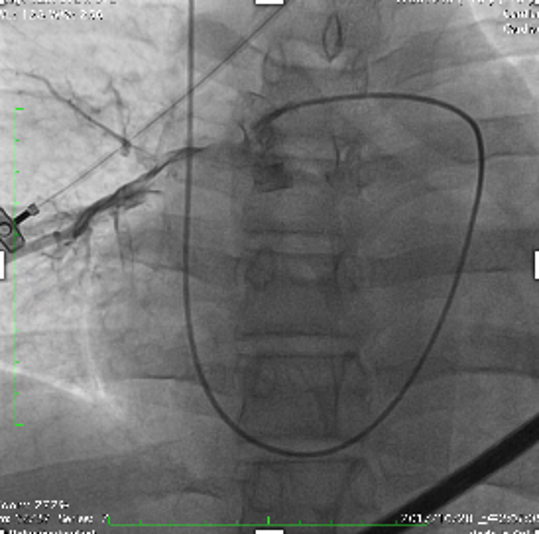 |
|
|
[Interventional Management]
- Procedural step:
Emergent EKOS directed thrombolysis was carried out at cath lab. However, hypotension with desaturation developed and ECMO was set at ICU. After one day of thrombolysis, right arm swelling with compartment syndrome was noted and CT showed right brachial artery bleeding hence urokinase was stopped. We use 10Fr Aspirex thrombectomy device to suction bilateral pulmonary embolism. PA pressure dropped from 60/30 mmHg to 37/10 mmHg after procedure. Patient was discharged two weeks later without other complications.
 - Case Summary:
For massive bilateral pulmonary embolism, EKOS facilitated thrombolysis is an effective new treatment modality. However, through rare, bleeding events can still be noted after EKOS use. Here we report our first case to use Aspirex thrombectomy device to treat massive bilateral pulmonary embolism in Taiwan, after right arm compartment syndrome due to brachial artery bleeding caused by EKOS facilitated thrombolysis.
|
|