Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
CASE20191031_043
| CORONARY - Complications | |
| Sorting Out the Problem | |
| Chanikarn Kanaderm1 | |
| Central Chest Institute of Thailand, Thailand1, | |
|
[Clinical Information]
- Patient initials or identifier number:
Somsak
-Relevant clinical history and physical exam:
Thai 65-year-old male Type 2 DM,HT,DLP 1 months ago, present with inferoposterior MI Primary PCI to LCX with DES*1 Appoint to stage PCI to LAD and checked for distal LCX V/S Stable Alert and cooperative Lung Clear No Murmur -Relevant test results prior to catheterization:
Echo Good LV systolic function No significant VHD 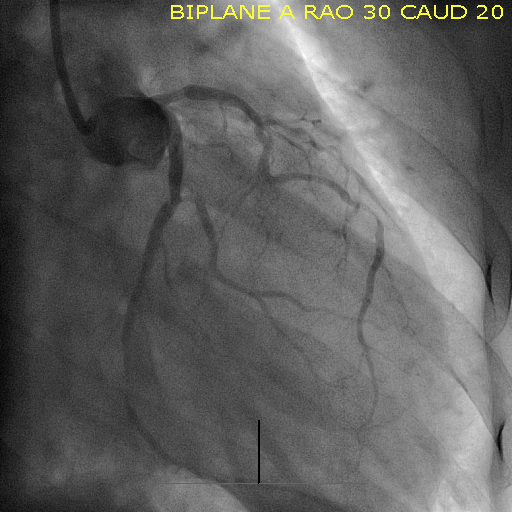 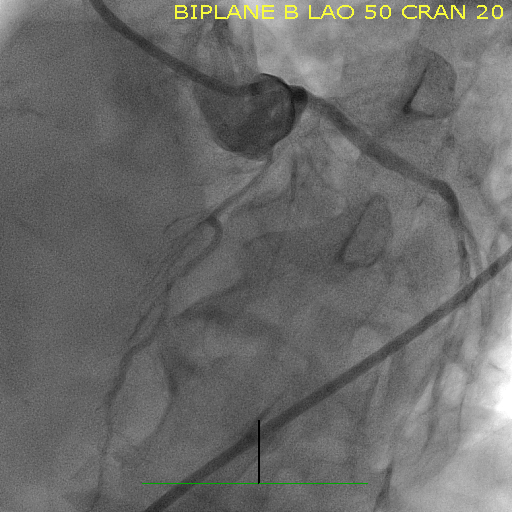 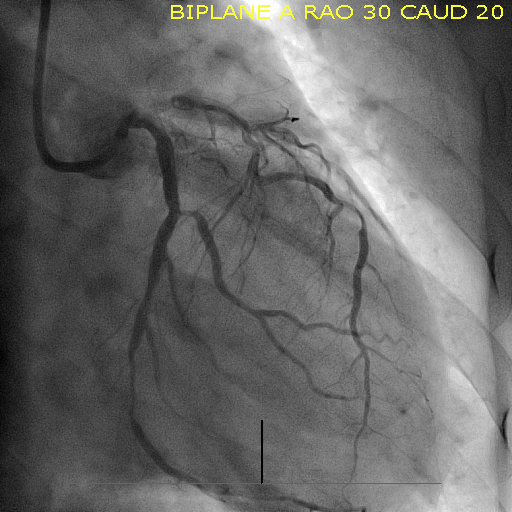 - Relevant catheterization findings:
LM Non significant lesion LAD Tortious and 80% mid LAD stenosis LCX Patent previous stent, 80% distal stent stenosis RCA diffuse non sig lesion |
|
|
[Interventional Management]
- Procedural step:
First procedureRight femoral artery approach.Short tip Judkins guiding and Sion guide wire taken.Start with PCI to mid LAD lesion.Wire to LCX and try to dilate distal to previous stent.Try to pass stent to distal LCX.However, couldn't cross the lesion and while pulling dislodged previous stent into the distal LM.Second procedureWire to true lumen of LCX stent.A small balloon tried to pass through the dislodged stent, however could not pass.A coronary snare taken and tried to engage the dislodged stent but not successful.
Another floppy wire taken and tried to intertwine distally, and successful remove dislodge stent with twist wire technique. Stent deployed from ostial LCX.Another stent deployed distally.Both stents post dilated.Final cine shows a good result.  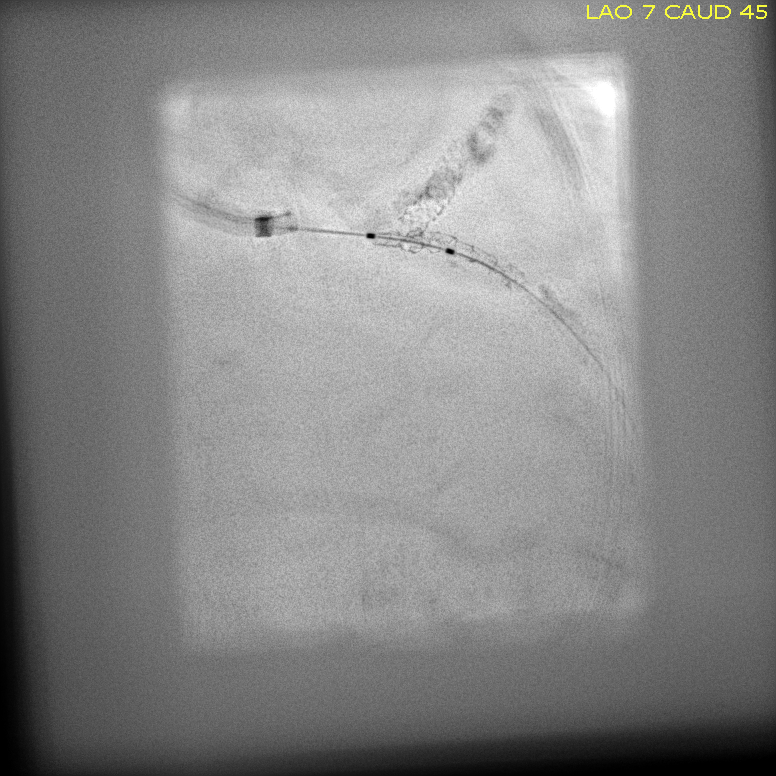  - Case Summary:
Stent loss during PCI occurs infrequently is more likely to occur in tortuous and calcified coronary arteries and can be successfully retrieved using a variety of retrieval techniques like low pressure balloon inflation technique, small balloon technique, double wire technique and loop snare technique. If stent is not retrieved it may be deployed or crushed and small branches can be left.
|
|