Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
CASE20191031_036
| STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE - Others (STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE) | |
| Post Myocardial Infarction Ventricular Septal Rupture with Heart Failure Treated Successfully by Device Closure | |
| Davinder Singh Chadha1, Keshavamurthy G2 | |
| Manipal Hospital, India1, Ahrr, India2, | |
|
[Clinical Information]
- Patient initials or identifier number:
VDVL
-Relevant clinical history and physical exam:
A 69-year-old gentleman, tobacco chewer, presented with anginal chest pain of 8 hours duration. Clinically he had tachycardia. Other vitals and systems- unremarkable. ECG showed ST elevation in leads II, III and AVF. 2D Echocardiography showed RWMA in inferior wall with LVEF 55%. He was immediately taken up for Primary Angioplasty. CAG showed TVD. PAMI + DES to RCA was done. Subsequently staged PCI to LAD and LCX were done. After 2 months he presented with sudden onset heart failure and PSM.
   -Relevant test results prior to catheterization:
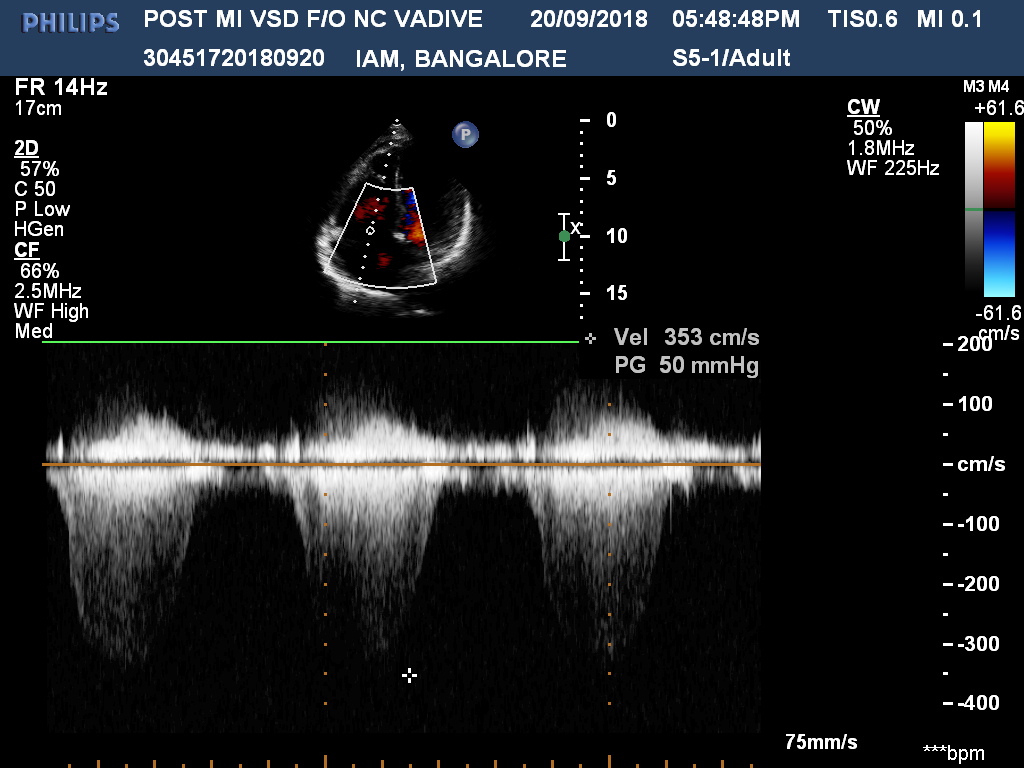
Echocardiography showed 14 mm ventricular septal rupture in apical inferior septum with left to right shunt. PA pressure was 60 mmHg.
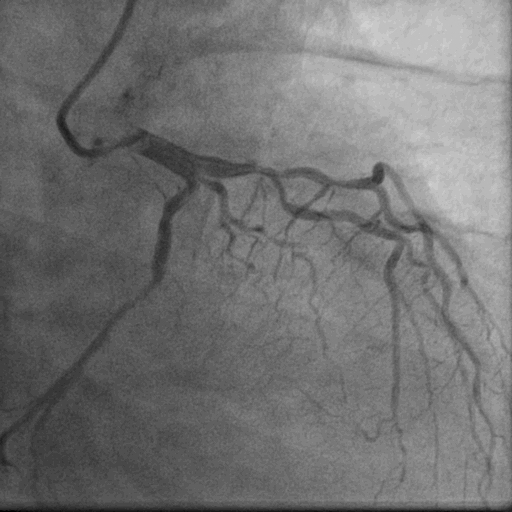
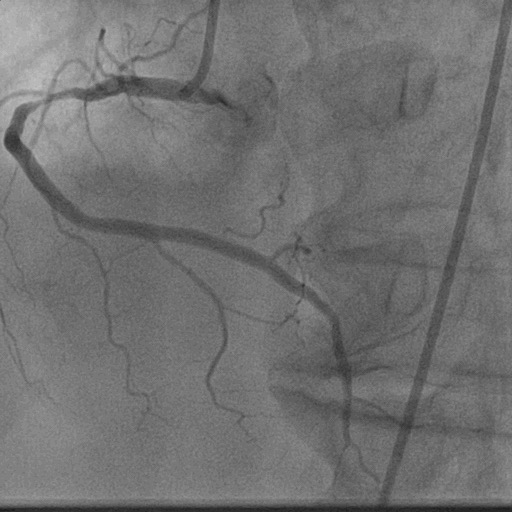
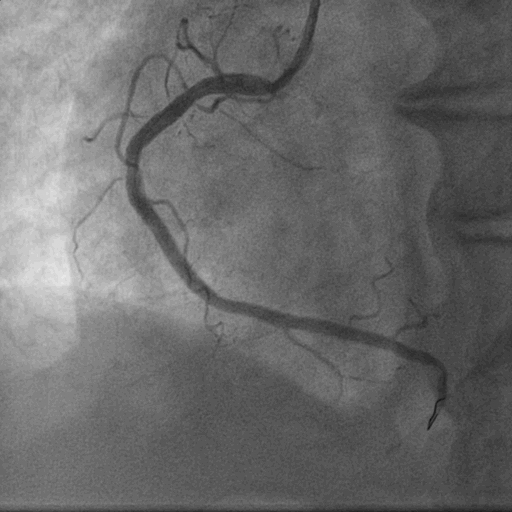
 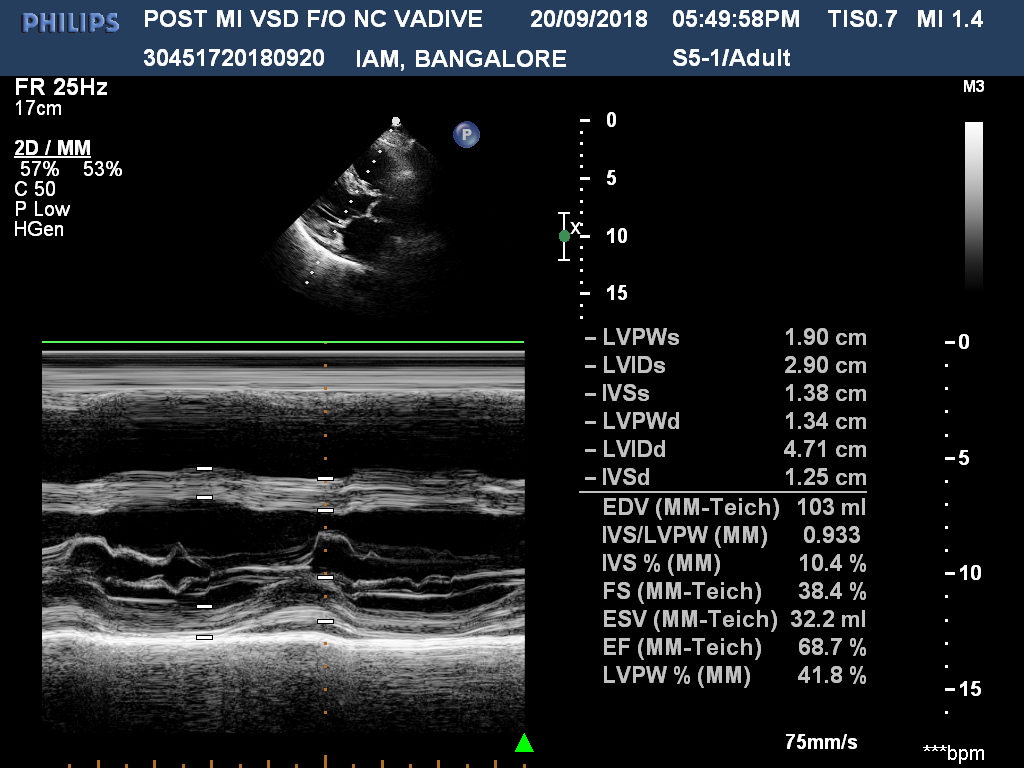 - Relevant catheterization findings:
After 3 weeks of anti-failure therapy, he was taken up for percutaneous device closure of ventricular septal rupture (VSR). PA pressure was 55/30 mmHg. Step up in oxygen saturation was noted in RV apex. Qp/Qs was 2:1. Left Ventricular angiography in LAO Cranial 400- 300 showed Ventricular Septal Rupture near apex with left right shunt.
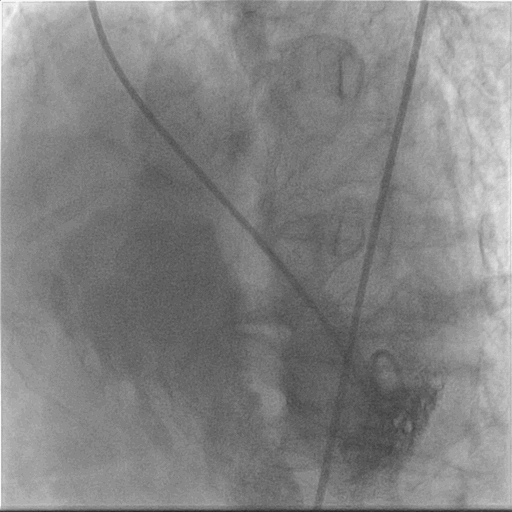 |
|
|
[Interventional Management]
- Procedural step:
The procedure was meticulously planned including access, hardware, possible complications and solutions. Surgical team was kept stand by. It was decided to establish arteriovenous loop from right femoral artery to right internal jugular vein (RIJV) so that it becomes easier to negotiate apical VSR while bringing delivery sheath from RIJV. Accesses were: right femoral artery (RFA) -6F, right femoral vein (RFV)- 6F. right internal jugular vein (RIJV) – 6F.
- Case Summary:
Ventricularseptal rupture (VSR) is a rare but life-threatening complication of acute myocardialinfarction. Wherever feasible, complete revascularisation andstabilization should be done before attempting closure of VSR to allow themargins of VSR to heal and become firm. In this patient we performedmultivessel PCI (TVD) and stabilized heart failure before device closure. Oneneeds to oversize the device by at least 4-6 mm unlike congenitalVSD. Ideally Post MI VSR device to be used which has wider LV discand longer waist. One need not chase small residual shunts. Theyare hemodynamically insignificant and usually close over a period oftime. |
|