Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
CASE20191028_013
| CORONARY - Adjunctive Procedures (thrombectomy, atherectomy, special balloons) | |
| Modifying Calcified Lesion with Orbital Atherectomy: Angioplasty Guided by Fractional Flow Reserve and Optical Coherent Tomography | |
| Afif Ashari1, Balachandran Kandasamy2 | |
| National Heart Institute, Malaysia1, Subang Jaya Medical Centre, Malaysia2, | |
|
[Clinical Information]
- Patient initials or identifier number:
BAM
-Relevant clinical history and physical exam:
81 year old lady presented with typical chest pain and breathlessness. ECG showed dynamic anterolateral and inferior T wave inversion. Troponin elevated and treated as NSTEMI. She has a background history of hypertension, and strong paternal family history of coronary artery disease. She is a non smoker and non alcohol drinker. She is physically active and independent of her daily activities. Clinical examination of the cardiovascular and respiratory system is unremarkable, no signs of failure
-Relevant test results prior to catheterization:
Blood investigations:
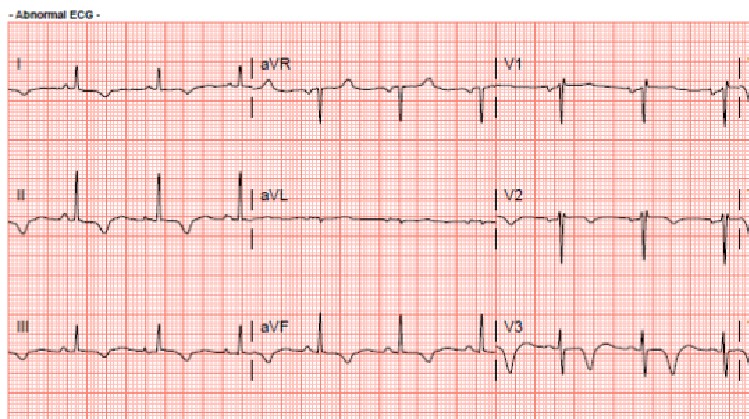 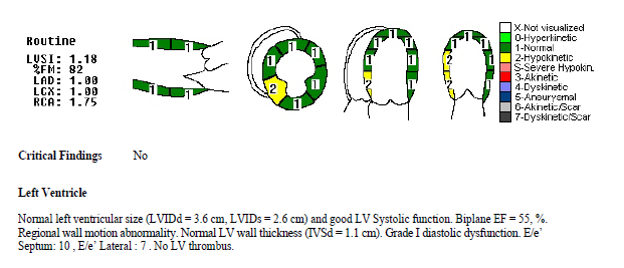 - Relevant catheterization findings:
Left main stem: Normal. Large, short vessel. Almost separate ostium of LAD and LCX
|
|
|
[Interventional Management]
- Procedural step:
Angioplasty to RCA
JR 3.5/6Fr (with sideholes), Heparin 5000 IU 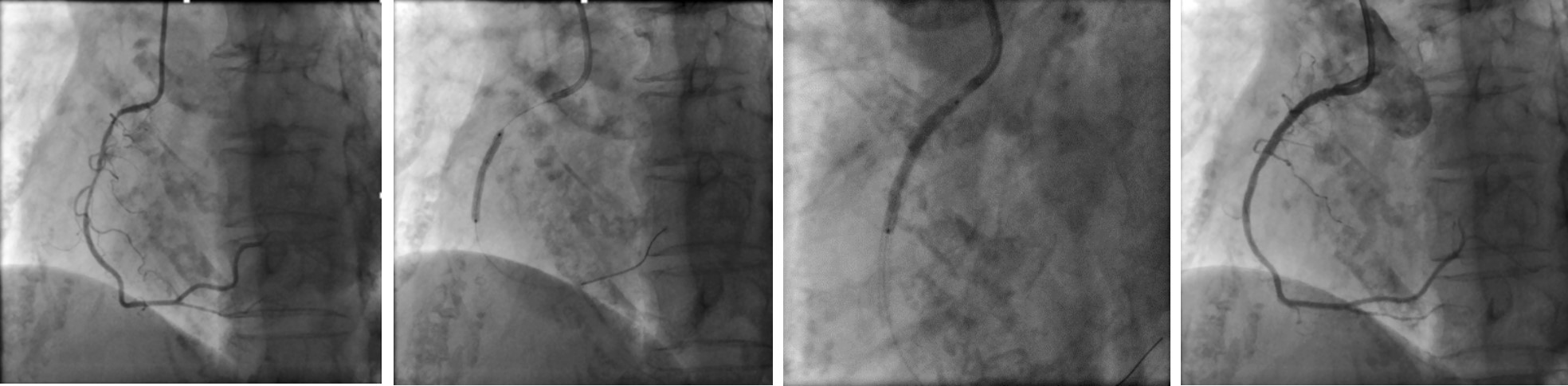 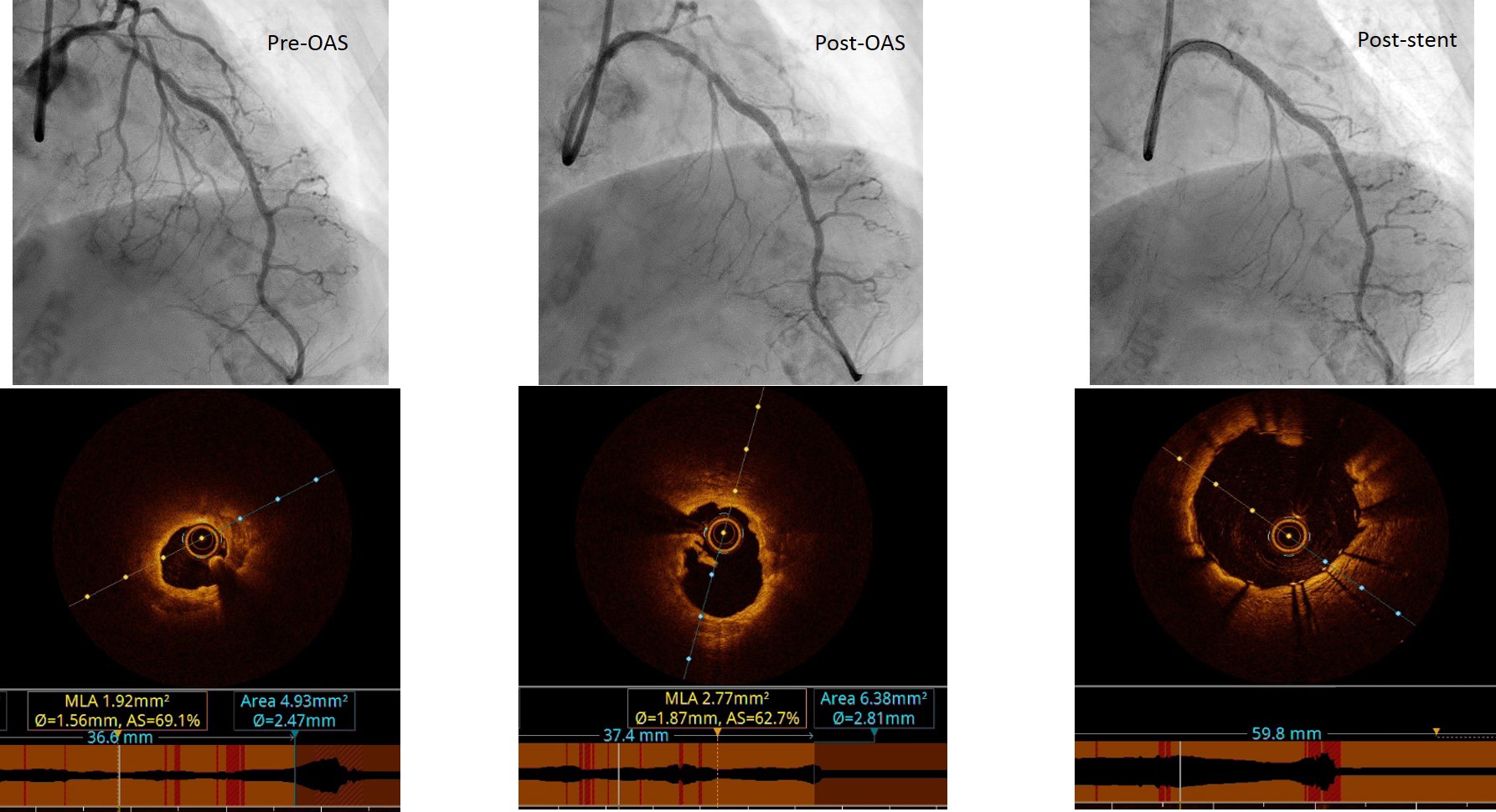 - Case Summary:
Importance of identifying calcified lesions and staging high risk procedures. In this case angioplasty done to RCA vessel first. After successful angioplasty of RCA, counseled patient and family for high risk orbital atherectomy angioplasty to LAD
Utility of intra-coronary functional assessment to confirm significant lesion. In this case FFR assessment confirmed significant lesion (FFR value 0.79 before adenosine). OCT pre-orbital atherectomy also showed significant stenosis with minimum luminal area of 2mm2 OCT is also useful to demonstrate adequate debulking of calcified lesion for better lesion preparation, and to optimize stent deployment (assess stent sizing, apposition, and expansion) |
|