Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
CASE20191028_002
| IMAGING AND PHYSIOLOGIC LESION ASSESSMENT - Vulnerable Plaque | |
| Angioscopy and Optical Coherence Tomography Revealed a Low Limb Vessel Stenosis Caused by Plaque Rupture | |
| Satoshi Suzuki1, Akinori Sumiyoshi2, Hirokazu Tanaka1, Kota Tanaka1, Masato Ishikawa1, Hiroyuki Nagai3, Satoshi Watanabe1, Mutsumi Iwamoto1, Atsunori Okamura4, Kenshi Fujii1 | |
| Sakurabashi Watanabe Hospital, Japan1, Sakurabashi Watanabe Advanced Health care Hospital, Japan2, Saint Joseph's Translational Research Institute, USA3, Sakurabashi Watanabe Advanced Healthcare Hospital, Japan4, | |
|
[Clinical Information]
- Patient initials or identifier number:
A K
-Relevant clinical history and physical exam:
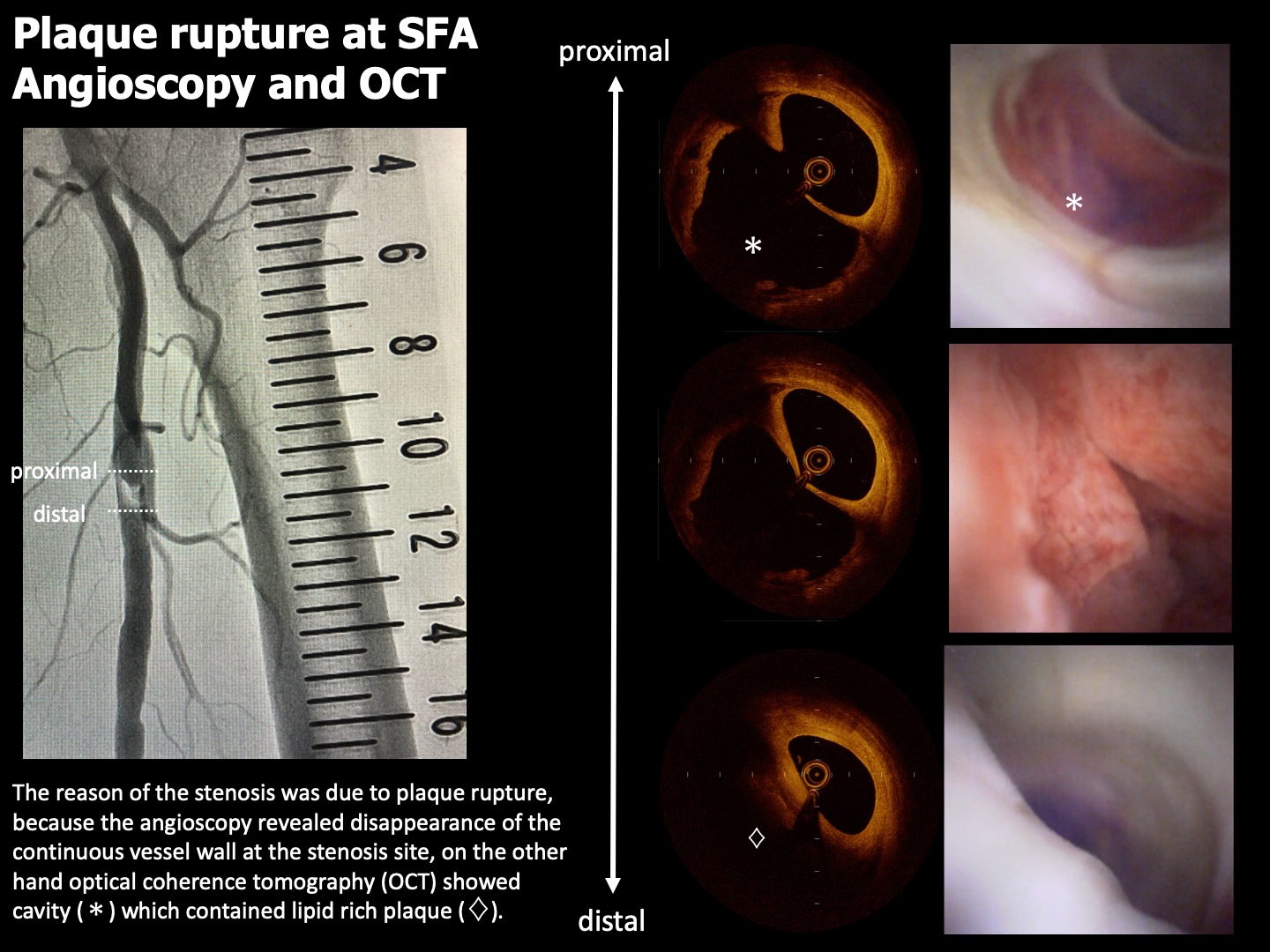
A 84-year old female was intermittent claudication for 1 month. She had hypertension as a risk factor. Left ankle brachial index (ABI) showed 0.82 and lower limb ultrasound revealed stenosis in the left superficial femoral artery (SFA).
-Relevant test results prior to catheterization:
The low limb angiography revealed the stenosis length of the left proximal SFA was approximately 2cm.
- Relevant catheterization findings:
The reason of the stenosis was due to plaque rupture, because the angioscopy revealed disappearance of the continuous vessel wall at the stenosis site, on the other hand optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed cavity which contained lipid rich plaque.
|
|
|
[Interventional Management]
- Procedural step:
The reason of the stenosis was due to plaque rupture, because the angioscopy revealed disappearance of the continuous vessel wall at the stenosis site, on the other hand optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed cavity which contained lipid rich plaque. After we performed plane old balloon angioplasty (POBA), angioscopy revealed hemorrhage which can cause stenosis or occlusion was not detected at the culprit lesion and acute gain was assured. Therefore, POBA and stent implantation was not performed. Drug coated balloon angioplasty was done to prevent neointimal hyperplasia proliferating at the culprit lesion.
 - Case Summary:
Angioscopy and OCT imaging revealed the cause of the stenosis at the left SFA was due to plaque rupture. These imaging modalities enabled us to develop the treatment which was only POBA therapy without stent implantation.
|
|