Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
CASE20191021_006
| IMAGING AND PHYSIOLOGIC LESION ASSESSMENT - Imaging: Intravascular | |
| A Case of Coronary Rupture with Complete Stent Fracture | |
| Yusuke Hyodo1, Yoshihide Fujimoto2 | |
| Kimitsu Chuo Hospital, Japan1, International University of Health and Welfare Narita Hospital, Japan2, | |
|
[Clinical Information]
- Patient initials or identifier number:
00091033
-Relevant clinical history and physical exam:
A 71 years-old-man presented with chestpain during hemodialysis. He had diabetic nephropathy and underwent hemodialysis for 8 years. He had repeatedly undergone percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to the three vessels for ischemic heart disease from 7 years ago. Especially the right coronary artery (RCA) had required PCI 6 times for the in-stent restenosis (ISR) and the in-stent reocclusion.
-Relevant test results prior to catheterization:
Electrocardiogram and echocardiography didn¡¯t show specific findings. We diagnosed him with unstable angina. We performed emergent coronary angiography (CAG).
- Relevant catheterization findings:
CAG revealed the ISR lesion in mid portion of the left anterior descending artery (LAD) and the in-stent reocclusion in the RCA with stent fracture. There was a large gap in the RCA at the part of stent fracture.Because distal RCA blood flow was maintained through the collateral channel, we thought that the LAD lesion was culprit, and performed PCI to the LAD lesion followed by emergent CAG.
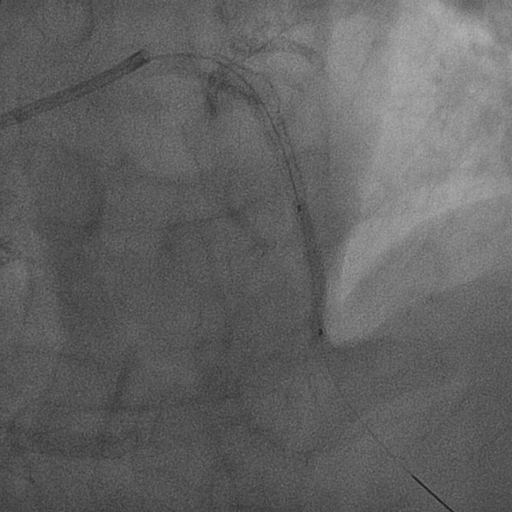 |
|
|
[Interventional Management]
- Procedural step:
One month later, we performed PCI to the RCA. We used X-treme XT-R¢ç wire (ASAHI INTECC, Tokyo, Japan) with Caravel¢ç micro catheter (ASAHI INTECC, Tokyo, Japan). The guidewire could proceed to the occlusion site but could not pass to the distal RCA. Then we tried retrograde approach PCI through the LAD septal branch channel, but micro catheter could not pass to the channel. We performed intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) to the proximal and mid portion of the RCA, and it showed the lack of vessel wall structure at the stent fracture site. We considered that it was difficult to pass guidewires due to discontinuity of the RCA. We finished the PCI procedure and have continued medical therapy. 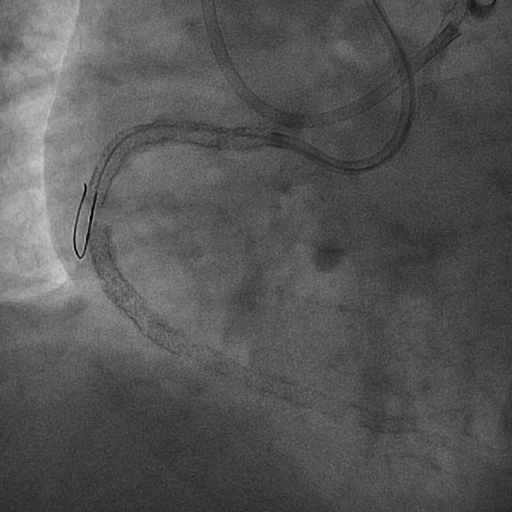 - Case Summary:
We experienced a case of coronary rupture due to stent fracture. We could see the lack of vessel structure by using IVUS. There was not any pericardial effusion or cardiac tamponade before and after PCI. Coronary rupture due to stent fracture might have occurred after the in-stent occlusion of RCA.
|
|