Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. DonĄ¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
CASE20190904_001
| CORONARY - Acute Coronary Syndromes (STEMI, NSTE-ACS) | |
| How to Treat a 53-Year-Old Man with Tongue Cancer and Old Myocardial Infarction Who Is Now Presenting WellensĄ¯ Syndrome | |
| Feng-Ching Yang1 | |
| Taichung Tzu Chi Hospital, Taiwan1, | |
|
[Clinical Information]
- Patient initials or identifier number:
Mr.X
-Relevant clinical history and physical exam:
0ne week prior to visiting a doctor, a 53 year-old man suffered from serious chest tightness, dyspnea and diaphoresis for 10 minutes when he was doing heavy lifing. The pain radiated to his left shoulder and upper back. After he sat down and stopped working for some minutes, the symptoms were relieved spontaneously and he was able to continue doing his job. Although there was only one episode of chest pain without any recurrent symptoms, he visited a doctor one week later.
-Relevant test results prior to catheterization:
From the results of his examination, he had normal hemodynamic status without abnormal blood pressure or arrhythmia, his resting ECG showed sinus rhythm but anterior leads of STsegment form V1 to V4 had biphasic change and his R wave had a normal transition without Q wave. Besides the abnormal ECG findings , his cardiac enzymes were in normal range but LDL was 156 mg per dl. He was advised to receive a diagnostic angiography despite showing no symptoms.
 - Relevant catheterization findings:
After 2 days, the the anterior leads ST segment of his ECG returned to normal base line. I arranged a coronary angiogram for him. The angiogram showed his proximal LAD had moderate to severe in-stent re-stenosis with thrombosis formation. His left circumflex artery and right coronary artery were both normal.
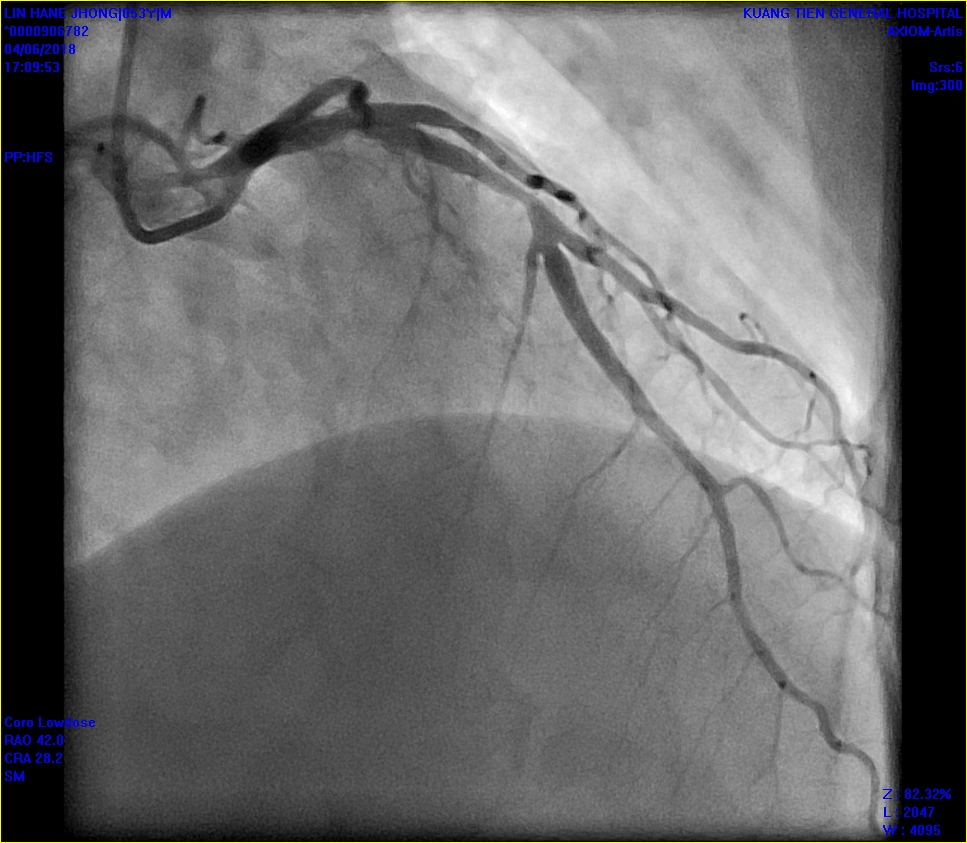 |
|
|
[Interventional Management]
- Procedural step:
From the IVUS examination, I found a ruptured plaque with a cavity and thrombosis at the distal stent portion. The previous stent was malpositioned with moderate to severe stenosis. After treating with non-compliant balloons, I deployed a bare metallic stent overlapping the distal portion of the previous stent to cover the ruptured plaque. His LVEF and cardiac enzymes were both in normal range pre and post-operation. The following day, he was discharged. He did not experience any symptoms such as angina or signs of heart failure the following year.
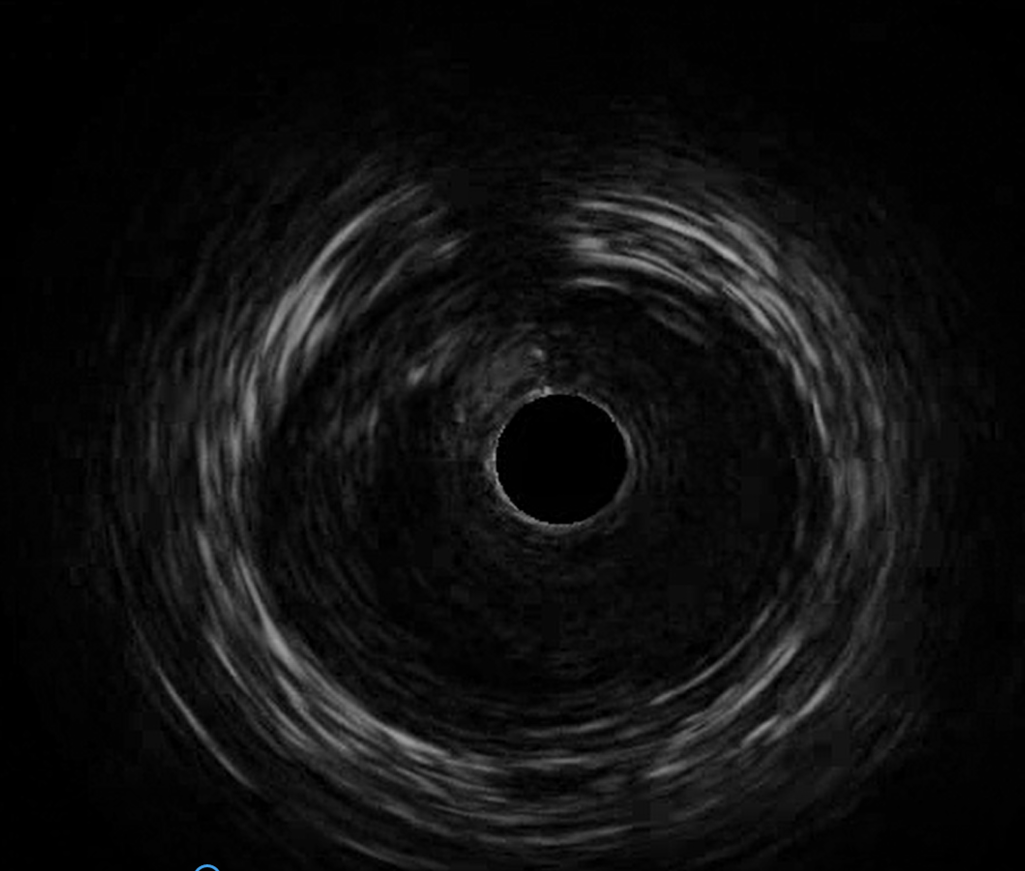 - Case Summary:
WellensĄ¯ syndrome, as described by HJ Wellens and Zwaan in 1982, implied the patient had severe stenosis in LAD. The disease is easy to misdiagnosis because patients are symptom-free while visiting a doctor. There is no standard guideline treatments, but a stress test is considered to be contraindicative because there is a possiblity of a plaque rupture and a risk of malignant arrhythmia when they are uder stress. OCT or OFDI is the standard diagnostic tool for an in-stent restenosis with thrombosis formation although IVUS can also provide some useful information.
|
|