Purpose: We compared in-hospital mortality and predictive performance of the TIMI risk score between invasive and conservative treatment strategies in Cambodian elderly STEMI patient.
Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
ABS20191107_0002
| Acute Coronary Syndromes (STEMI, NSTE-ACS) | |
| Effect of TIMI Risk Score and Invasive Strategy on In-Hospital Outcome in Elderly Patients with ST - Elevation Myocardial Infarction from a Cambodian Single Center ACS Registry | |
| Samrany San1, Sokha Chan1, Chour Sok1 | |
| Calmette Hospital, Cambodia1 | |
|
Background:
The incidence of ST elevation myocardial infarction in elderly individuals is high. The relationship between the predictive performance of the TIMI risk score for STEMI and treatment strategy has not been evaluated in the elderly patient.
|
|
|
Methods:
We analyzed data of consecutive elderly patients (> 65 years) with STEMI who were retrospective enrolled in the only Cambodian public PCI-capable hospital from January 2016 to December 2018. A multivariable logistic regression model, including TIMI risk score variables and treatment strategies, evaluated differences in in-hospital mortality between invasive and conservative strategies. The predictive performance of the TIMI risk score according to treatment strategies was evaluated in terms of discrimination and calibration. Mortality rate for TIMI scores in invasive and conservative strategies were compared. All the data were analyzed on SPSS 26.0.
|
|
|
Results:
Overall 436 patients were divided into two groups: 263 (60.3%) underwent coronary angiography and/or revascularization, 173 (39.7%) received conservative treatment. In the invasive group, percutaneous coronary intervention was performed in 98.9% (97% stent angioplasty and 1.9% balloon angioplasty) whereas 1.1% underwent coronary artery bypass grafting within the hospital stay. Invasive group were younger, had more comorbidities and shorter ischemic time. Crude in-hospital mortality was 8.7% in invasive group vs 17.9% in conservative group (OR 0.43; 95% CI 0.24-0.78, p=0.005). When adjusting for TIMI risk score variables, mortality remained higher in conservative group (OR 0.53; 95% CI 0.24-1.13, p=0.01). The TIMI risk score provided a good predictive discrimination and calibration in both group, invasive and conservative strategies (c-statistic=0.699 [95% CI: 0.582-0.817], goodness-of-fit p=0.32 and c-statistic=0.713 [95% CI: 0.601-0.825], goodness-of-fit p=0.268, respectively).
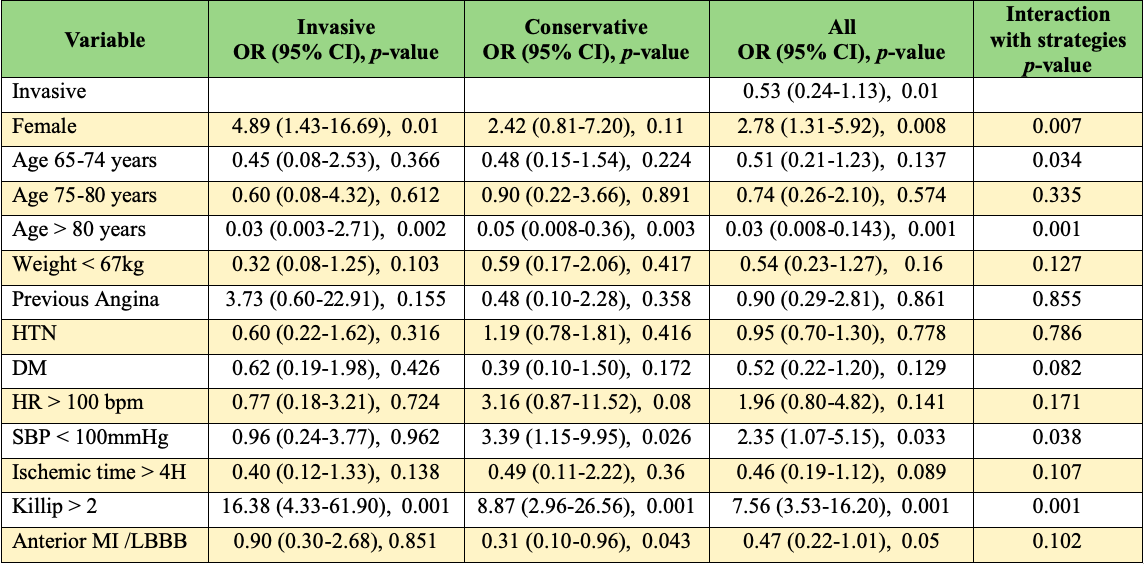 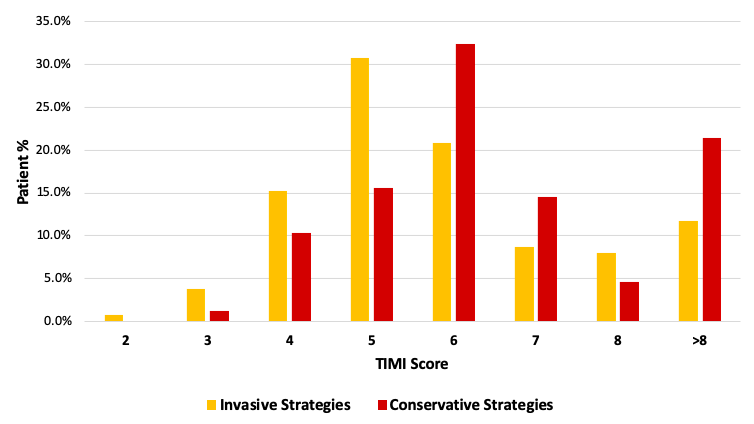 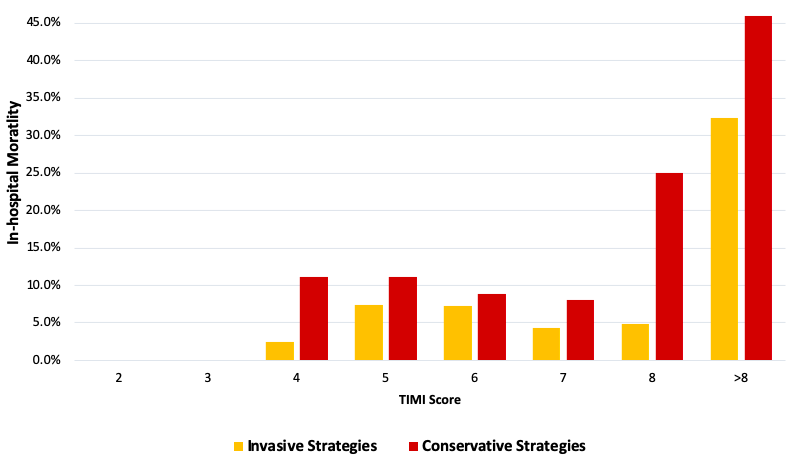 |
|
|
Conclusion:
According to this study, an invasive treatment strategy is superior to improve in-hospital outcome compared to a conservative treatment strategy in patients STEMI aged > 65 years. The TIMI risk score was effective in predicting in-hospital mortality.
|
|