Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
ABS20191031_0001
| Peripheral Vascular Disease and Intervention | |
| Suboptimal Compliance to Best Medical Practice in Patients with Vascular Disease in a Specialist Practice | |
| Ryan Teh1, Warren David Raymond2, Kishore Sieunarine3 | |
| Fiona Stanley Hospital, Australia1, The University of Western Australia, Australia2, Royal Perth Hospital, Australia3 | |
|
Background:
The risk of athersclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is increased in patients with peripheral vascular disease (PVD), abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), and carotid artery disease (CAD). In Australia, it is recognised that many of these events are attributable to comorbid hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes ; and the National Vascular Disease Prevention Alliance (NVDPA), recognises the need for all high risk adults to follow the current Dietary Guidelines for Australian Adults, cease smoking, reduce alcohol intake and undertake behavioural changes for better lifestyle practices.
|
|
|
Methods:
This is a cross-sectional study of patients with established PVD, carotid artery and AAA disease seen in the setting of a private specialist clinic between October 2015 to September 2019 (n=1689). These patients were attending the clinic for the first time, referred by their primary healthcare providers for PAD, AAA and carotid occlusive disease.
|
|
|
Results:
A total of 1,689 participants with a primary diagnosis of PVD, CAD and AAA, who attended private outpatient vascular clinics between October 2015 and September 2019, were identified.
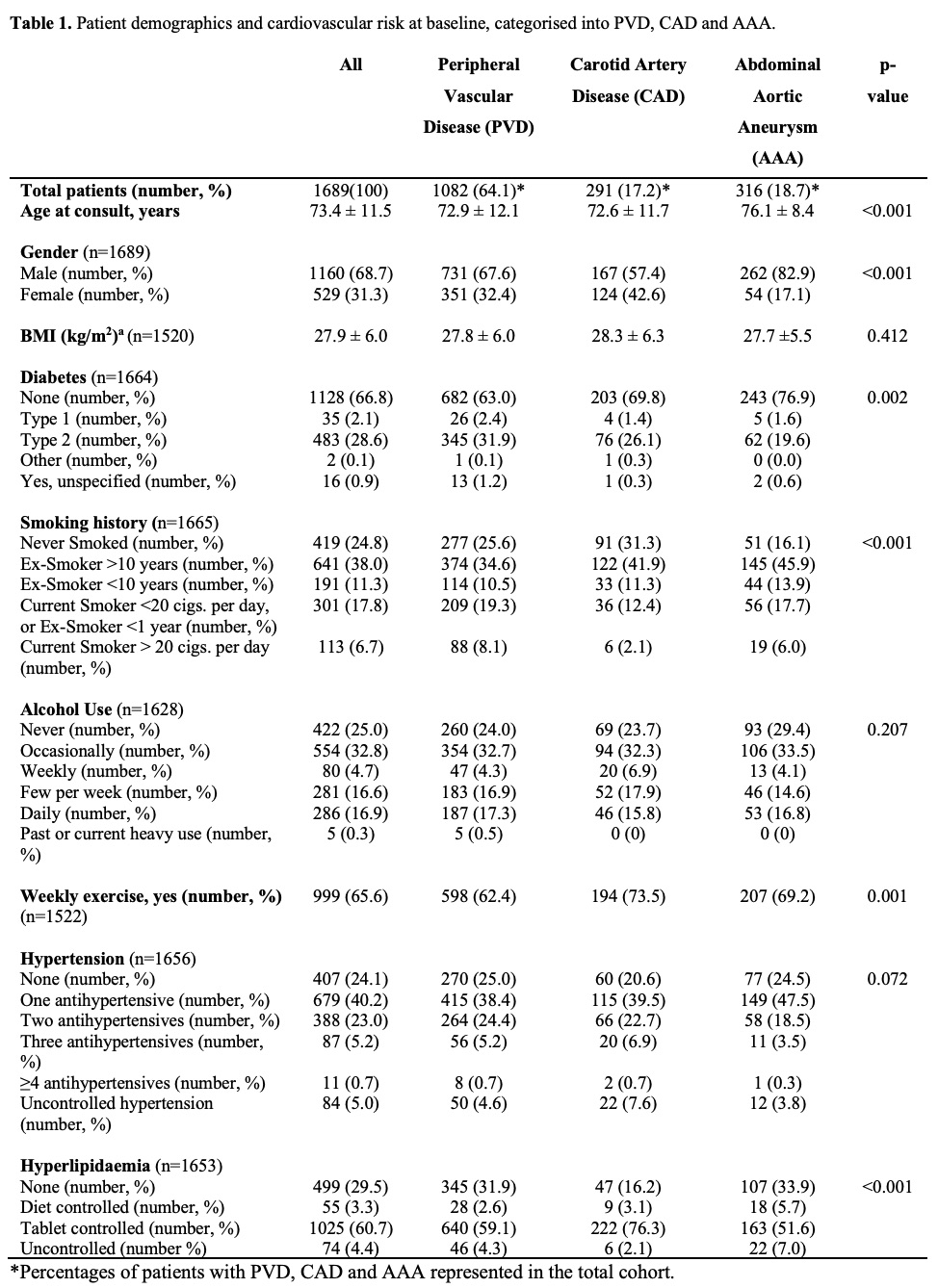 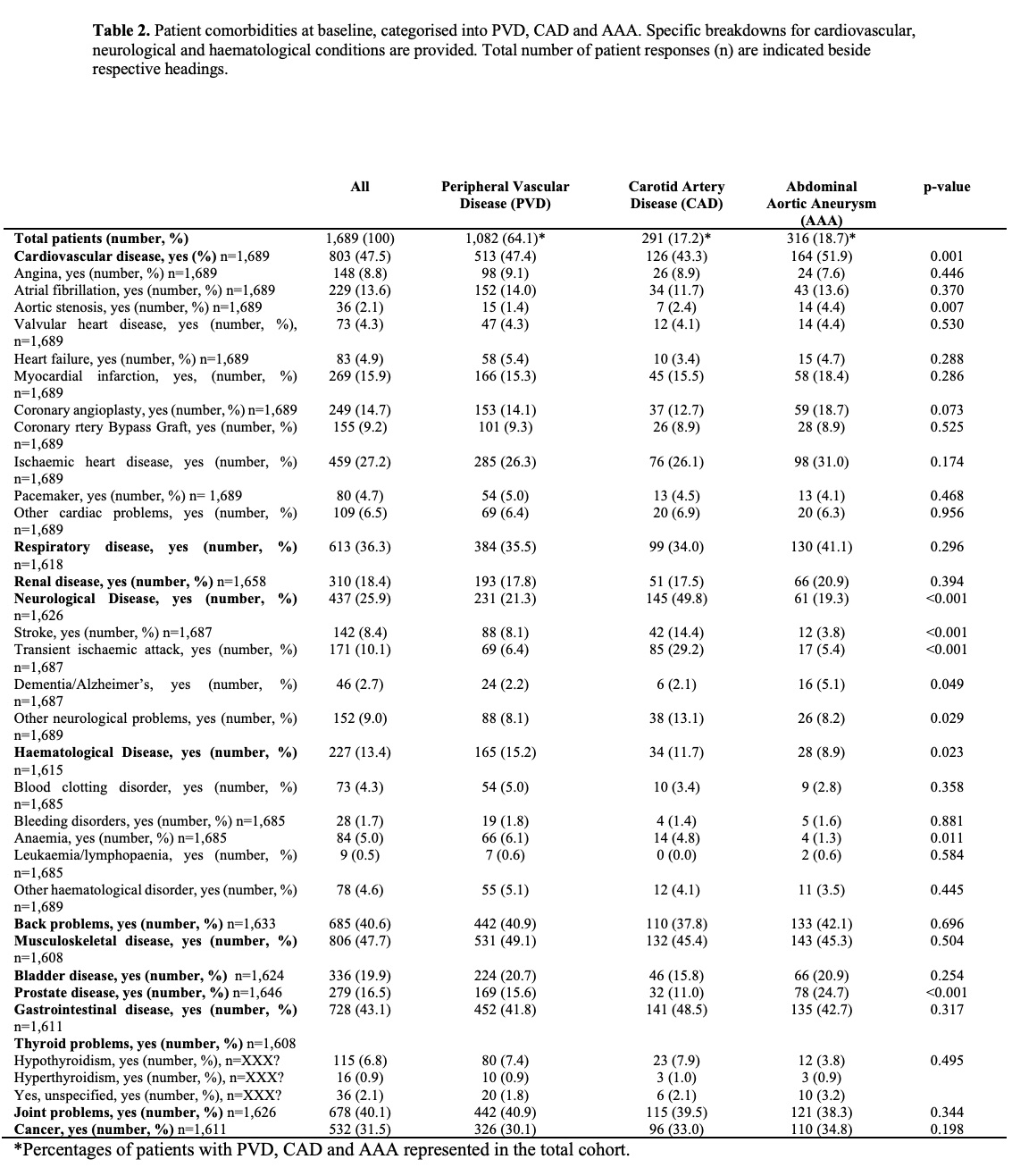 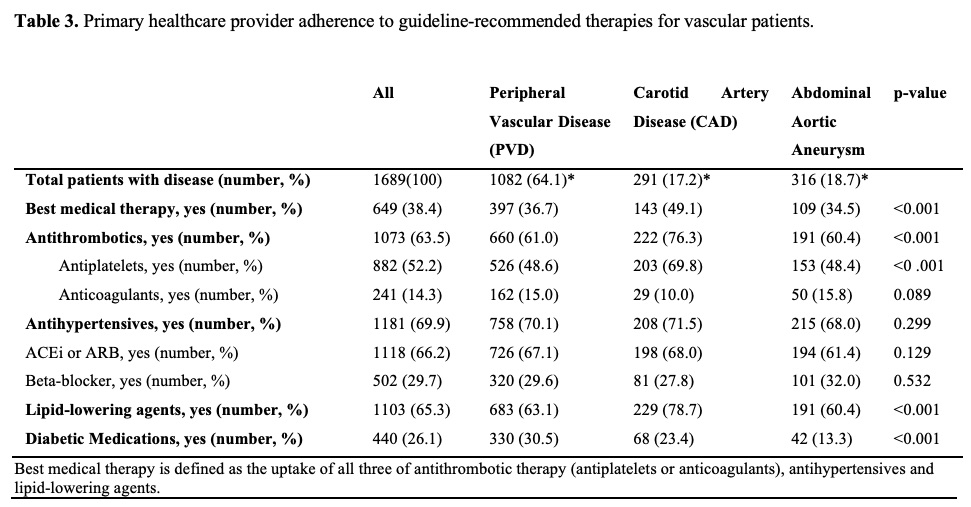 |
|
|
Conclusion:
In this study, patients referred to the vascular surgery outpatient clinic should have been on life-long 'best medical therapy'. However, there was suboptimal uptake of antithrombotics, antihypertensives and lipid-lowering agents identified. Reasons for deprescribing medications have been attributed to adverse drug reactions, polypharmacy and palliative care strategies. Our current data does not allow for investigation into maintenance and deprescribing practices of guideline-recommended therapies, however future studies intend to address this gap.
|
|