Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
ABS20191027_0003
| Peripheral Vascular Disease and Intervention | |
| Predictive Value of Ankle Brachial Index in Patients with Combined Coronary and Cerebral Artery Atherosclerosis | |
| Ji Woong Roh1, Hee-Yeol Kim2 | |
| Yongin Severance Hospital, Korea (Republic of)1, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon St. Mary¡¯s Hospital, Korea (Republic of)2 | |
|
Background:
To evaluate the association between low ankle-brachial index (ABI) and clinical outcome in patients who are undergoing simultaneous coronary and cerebral artery angiography due to atherosclerosis detected on brain imaging studies.
|
|
|
Methods:
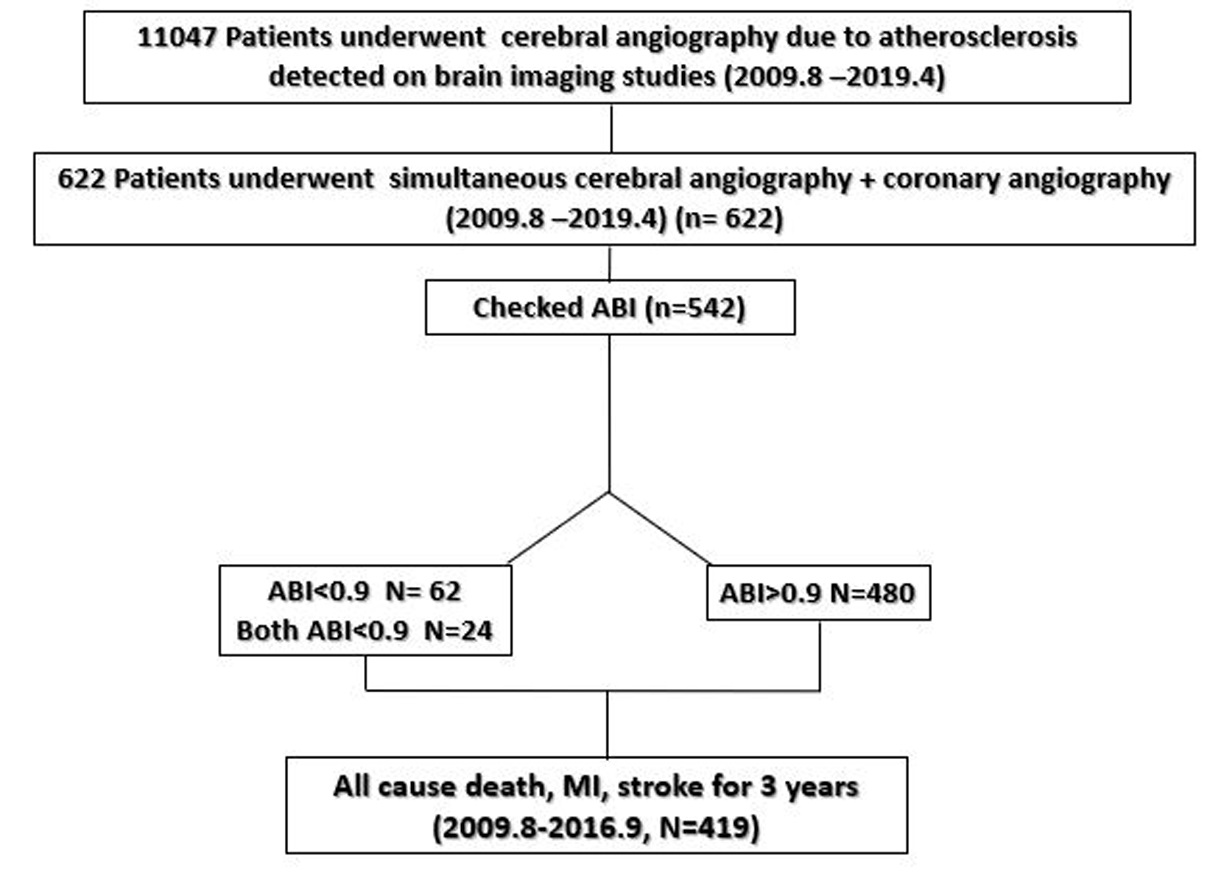
Between January 2009 and April 2019, 11047patients underwent cerebral angiography for atherosclerotic change seen in brain magnetic resonance angiography or computed tomography angiography at a single center. Of these, 543patients who underwent simultaneous coronary and cerebral angiography with ABI checked were enrolled. The primary outcome was major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular event (MACCE), defined as a composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, stroke over 3years.
 |
|
|
Results:
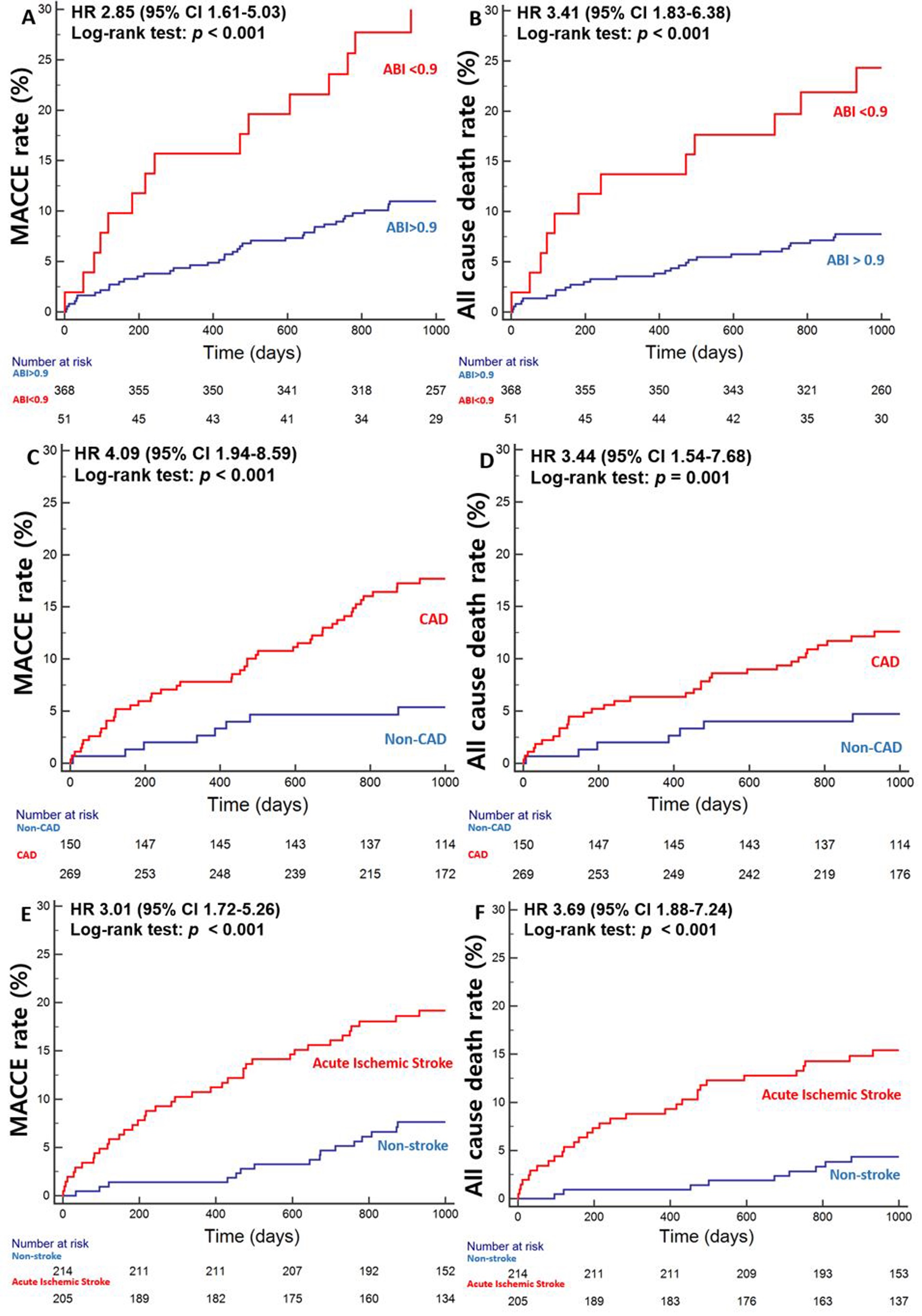
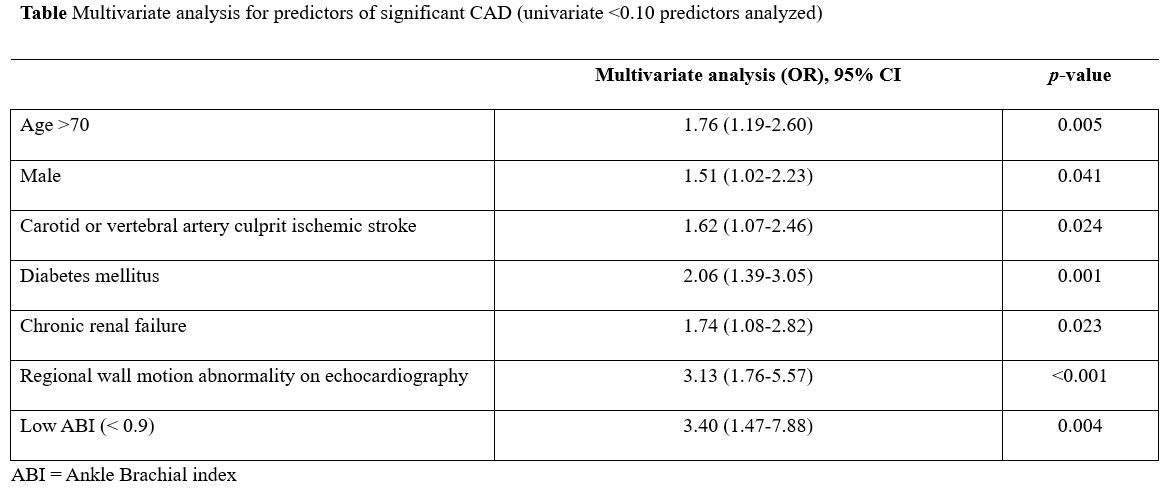
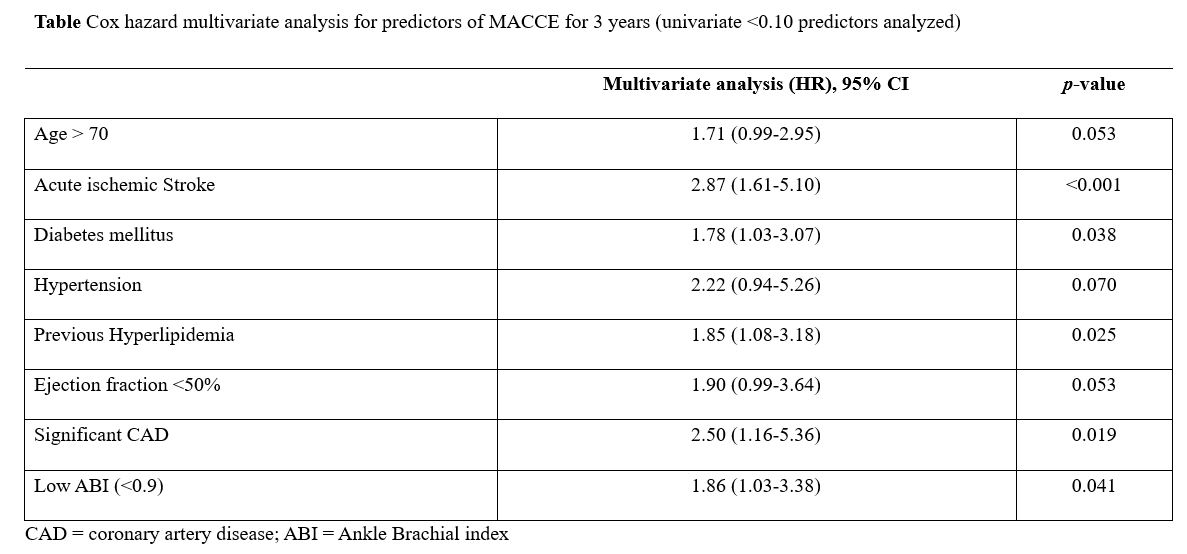
Of the 542 patients, 480 (88.6%) had normal ABI (>0.9) and 62 (11.4%) had low ABI (<0.9). Low ABI (odds ratio [OR], 3.40;95% confidence index [CI], 1.47-7.88; p=0.004) was the most important predictor for significant coronary artery disease (CAD). The incidence of MACCE (hazard ratio [HR], 2.85; 95% CI, 1.61-5.03; p<0.001) and all-cause death (HR,3.41;95% CI, 1.83-6.38; p<0.001) were significantly higher in the low ABI group. MACCE was independently associated with acute ischemic stroke (HR, 2.87; 95% CI,1.61-5.10; p<0.001), diabetes mellitus (HR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.03-3.07;p=0.038), previous hyperlipidemia (HR,1.85; 95% CI, 1.08-3.18; p=0.025),significant CAD (HR, 2.50; 95% CI, 1.16-5.36; p=0.019), and low ABI (HR, 1.86;95% CI, 1.03-3.38; p=0.041).
   |
|
|
Conclusion:
The presence of low ABI was associated with significant CAD and worse clinical outcomes during follow-up. ABI measurement should be considered in patients with cerebral artery atherosclerosis on brain imaging. Especially, patients with low ABI (<0.9) need accurate CAD assessment with coronary angiography.
|
|