Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
ABS20191015_0001
| Drug-Eluting Balloons | |
| The Outcome of Cutting Balloon Combined with Drug-Eluting Balloon Angioplasty for Treatment of In-Stent Restenosis | |
| Wei-Chieh Lee1, You-Cheng Zheng2, Hsiu-Yu Fang2 | |
| Chi Mei Medical Center, Taiwan1, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan2 | |
|
Background:
Drug-eluting balloon (DEB) had emerged as an alternative therapeutic choice for in-stent restenosis (ISR) lesions. Cutting balloon angioplasty (CBA) was a strategy applied to treat tight stenotic lesions or ISR lesions. However, few studies focused on whether CBA plus DEBcould achieve a better result in lowering the incidence of recurrent ISR. The study aims to evaluate the efficacy of CBA plus DEB for ISR lesions.
|
|
|
Methods:
Between August 2011 and December 2017, 681 patients were diagnosed with ISR in our hospital and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with DEBs was performed for a total of 936 coronary ISR lesions. 90patients who underwent PCI with further CBA plus DEB were divided into CBA plus DEB group. 591 patients who underwent PCI with DEB only were divided into only DEB group. Clinical outcomes included target lesion revascularization, target vessel revascularization, recurrent myocardial infarction, cardiovascular mortality, and all-cause mortality were compared between two groups.
|
|
|
Results:
Baseline characteristics including clinical conditions showed no significant difference between two groups. The kinds of previous stents, lesion type, the prevalence of ostial lesion and left main lesion, pre-PCI and post-PCI stenotic percentage showed no significant difference between two groups. Only post-PCI reference luminal diameter (RLD) and the size of DEB were larger in CBA plus DEB group. During in-hospital and one-year follow-up period, clinical outcomes did not differ between two groups.
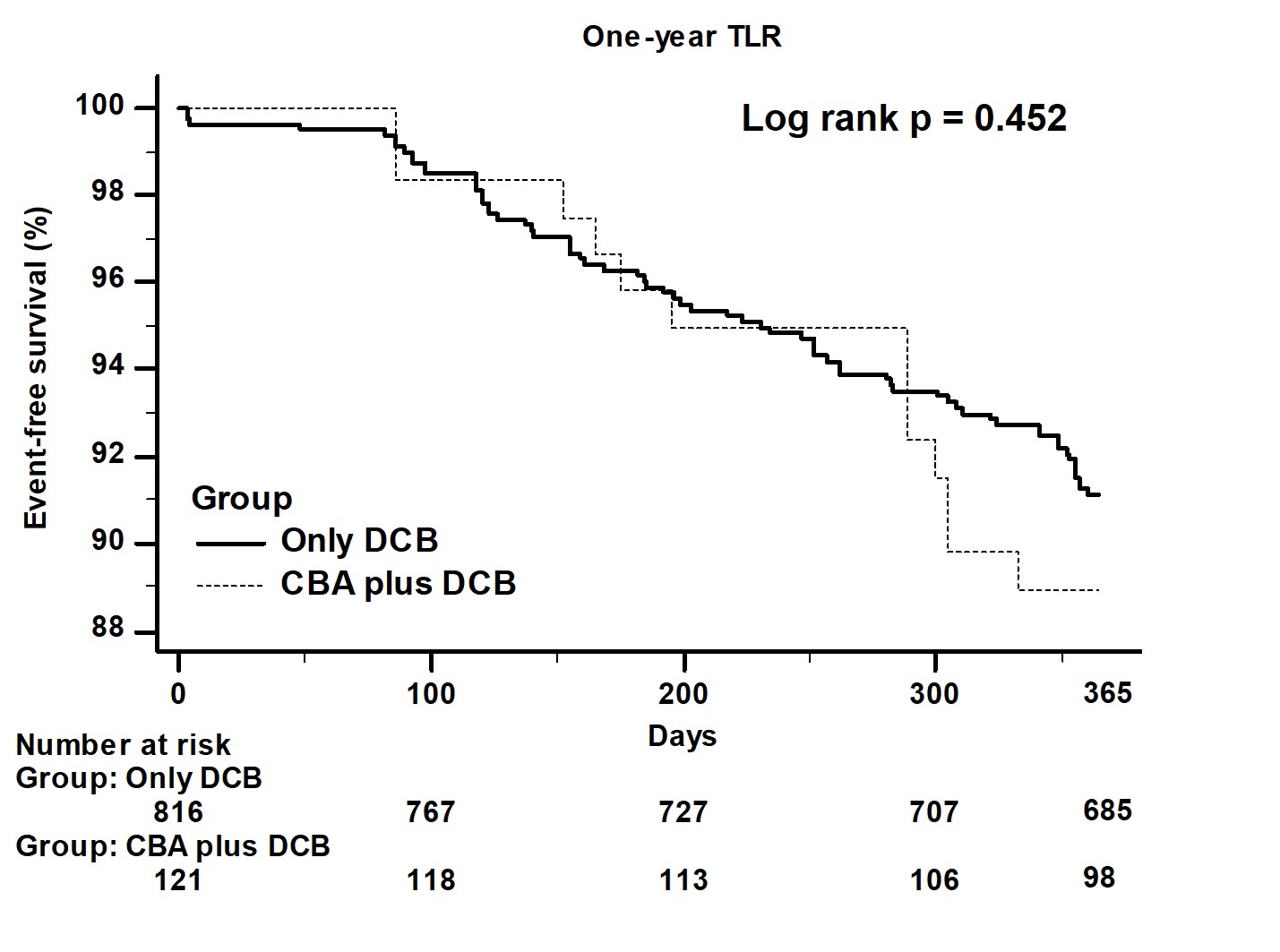 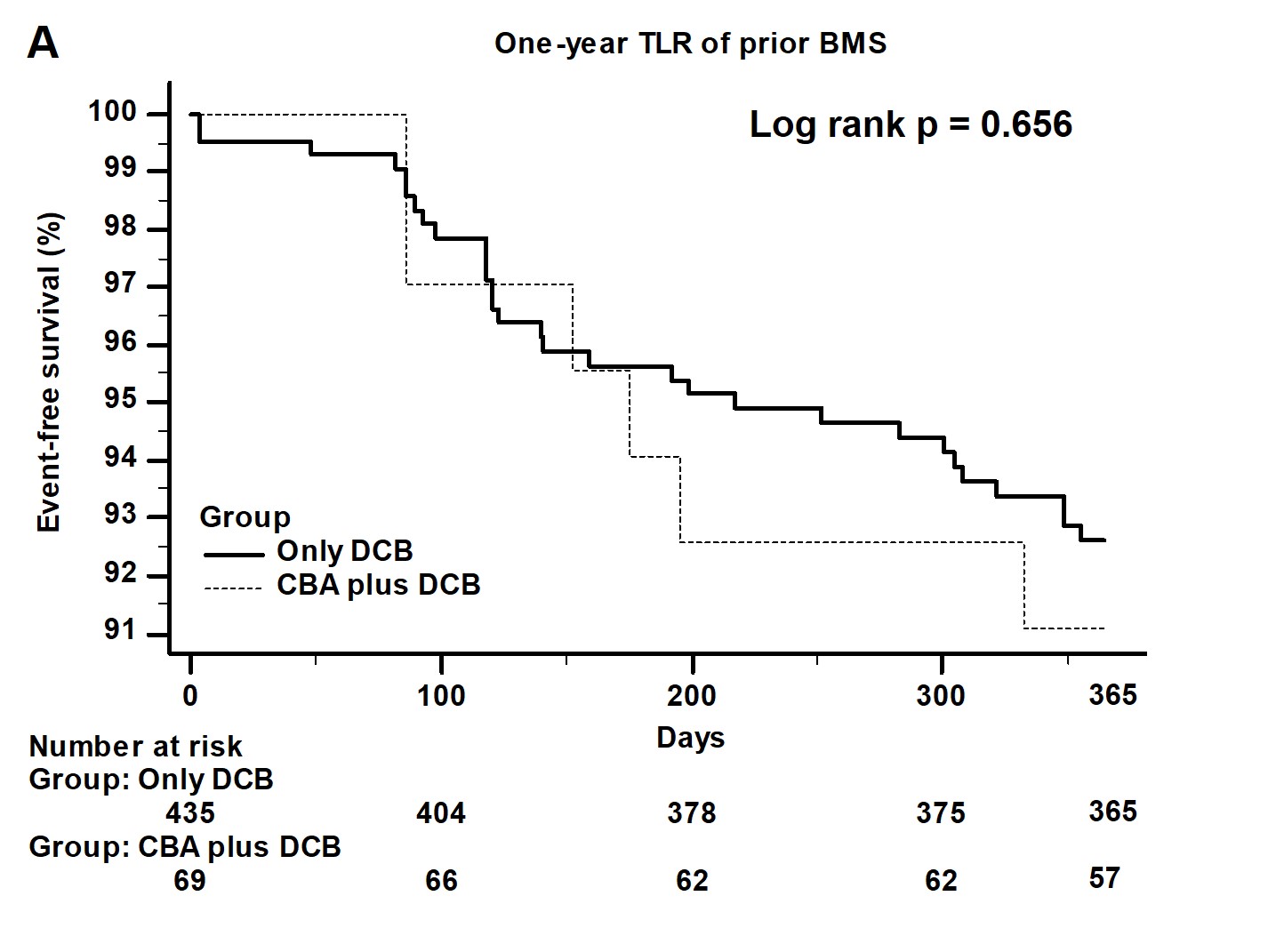 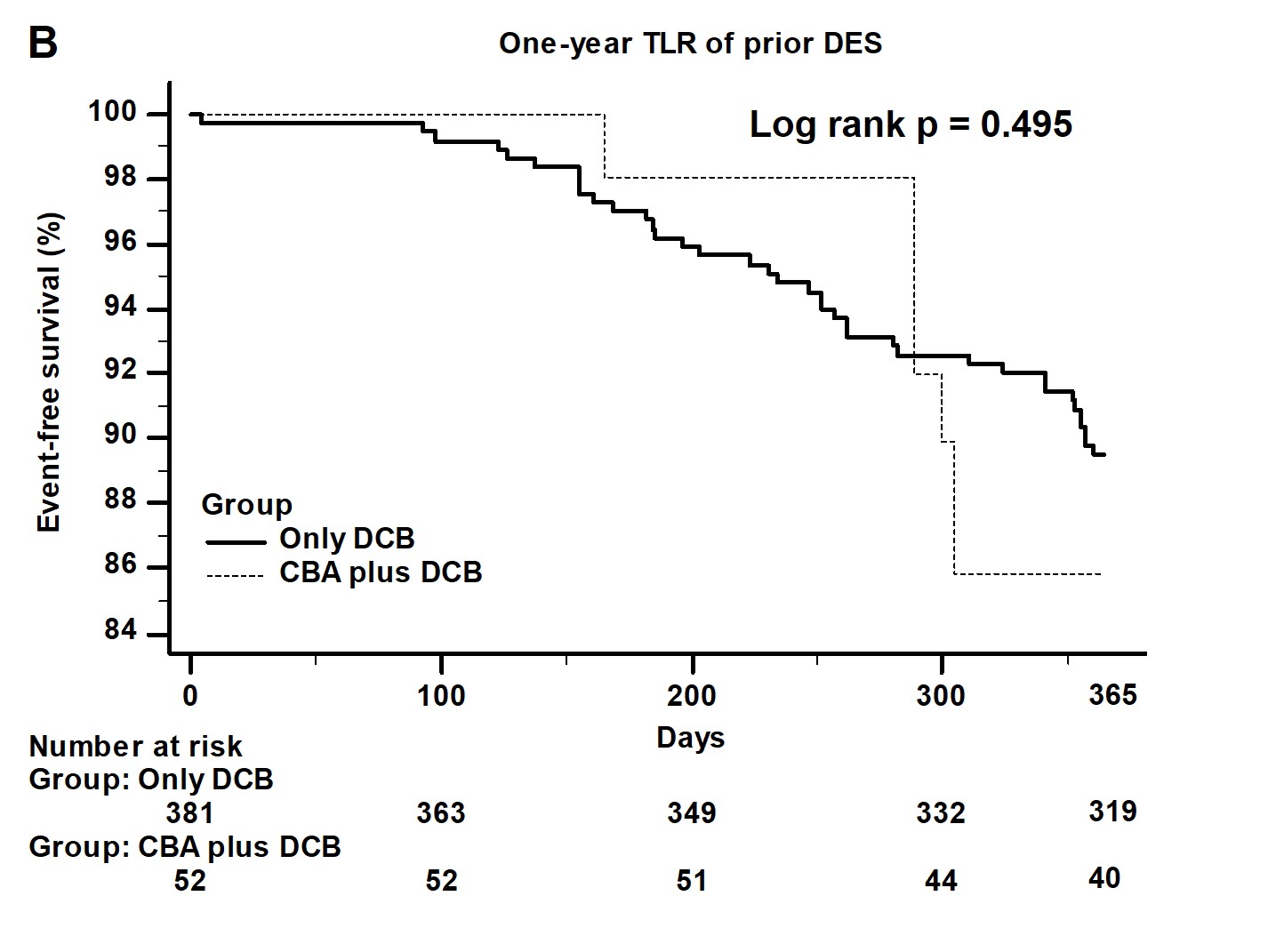 |
|
|
Conclusion:
For ISR lesion, the use of CBA plus DEB did not improve the clinical outcomes and did not decrease the incidence of recurrent target lesion restenosis. The use of CBA could let we choose larger size of DEB and did not bring more complications when comparing with the use of DEB only.
|
|