Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP & AP VALVES 2020 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don¡¯t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
* The E-Science Station is well-optimized for PC.
We highly recommend you use a desktop computer or laptop to browse E-posters.
ABS20191006_0001
| Acute Coronary Syndromes (STEMI, NSTE-ACS) | |
| Plasma Big Endothelin-1 Level as a Prognostic Indicator of Long-Term Outcomes Among Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention | |
| Yan Chen1, Lin Jiang1, Ping Jiang1, Xueyan Zhao1, Runlin Gao1, Yuejin Yang1, Bo Xu1, Jinqing Yuan1 | |
| Fuwai Hospital, China1 | |
|
Background:
Whether high plasma big endothelin-1 (ET-1) level confers an increased risk of long-term adverse outcomes after acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in the modern era of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and medication remains uncertain. And some studies found only a moderate discrimination ability of the SYNTAX score for long-term mortality prediction in those patients. We sought to investigate the clinical impact of plasma big ET-1 level in AMI patients who underwent PCI, as well as the prognostic value of plasma big ET-1 beyond the SYNTAX score.
|
|
|
Methods:
A total of 1,494 ¡±all-comer¡± patients in Fuwai hospital who underwent PCI for AMI were consecutively enrolled From January 2013 to December 2013. Patients were divided into two sub-groups based on an optimal cut-off value of plasma big ET-1 predicting 2-year all-cause mortality. Multivariable Cox regression analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis were conducted. Concordance index (C-index), continuous net reclassification improvement (NRI), and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) were calculated to assess the added prognostic value of plasma big ET-1.
|
|
|
Results:
During 2-year follow-up, the high big ET-1 group was associated with a significantly higher rate of all-cause death (5.6% vs 0.5%, p < 0.001) and major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (MACCE, 19.4% vs 12.6%, p = 0.003) compared to the low big ET-1 group. A big ET-1 cut-off value of 0.39 pmol/L had an area under curve of 0.846 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.782 to 0.910),with 71.4% sensitivity and 82.8% specificity for the prediction of death. In multivariate analysis, high big ET-1 level was an independent predictor of 2-year all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR] 3.59, 95% CI 1.13 to 11.47, p =0.031), along with age, drug-eluting stent implantation and left main lesion.
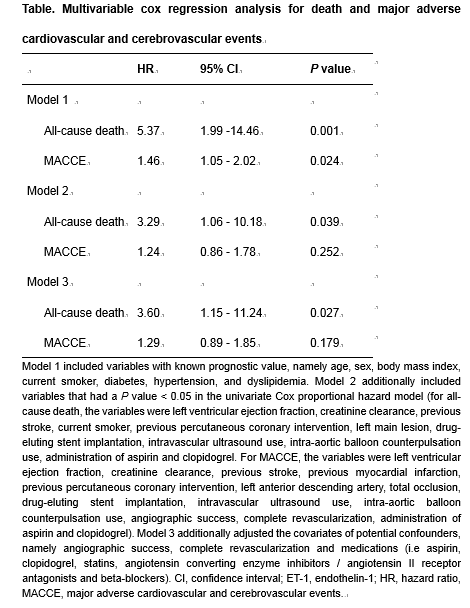 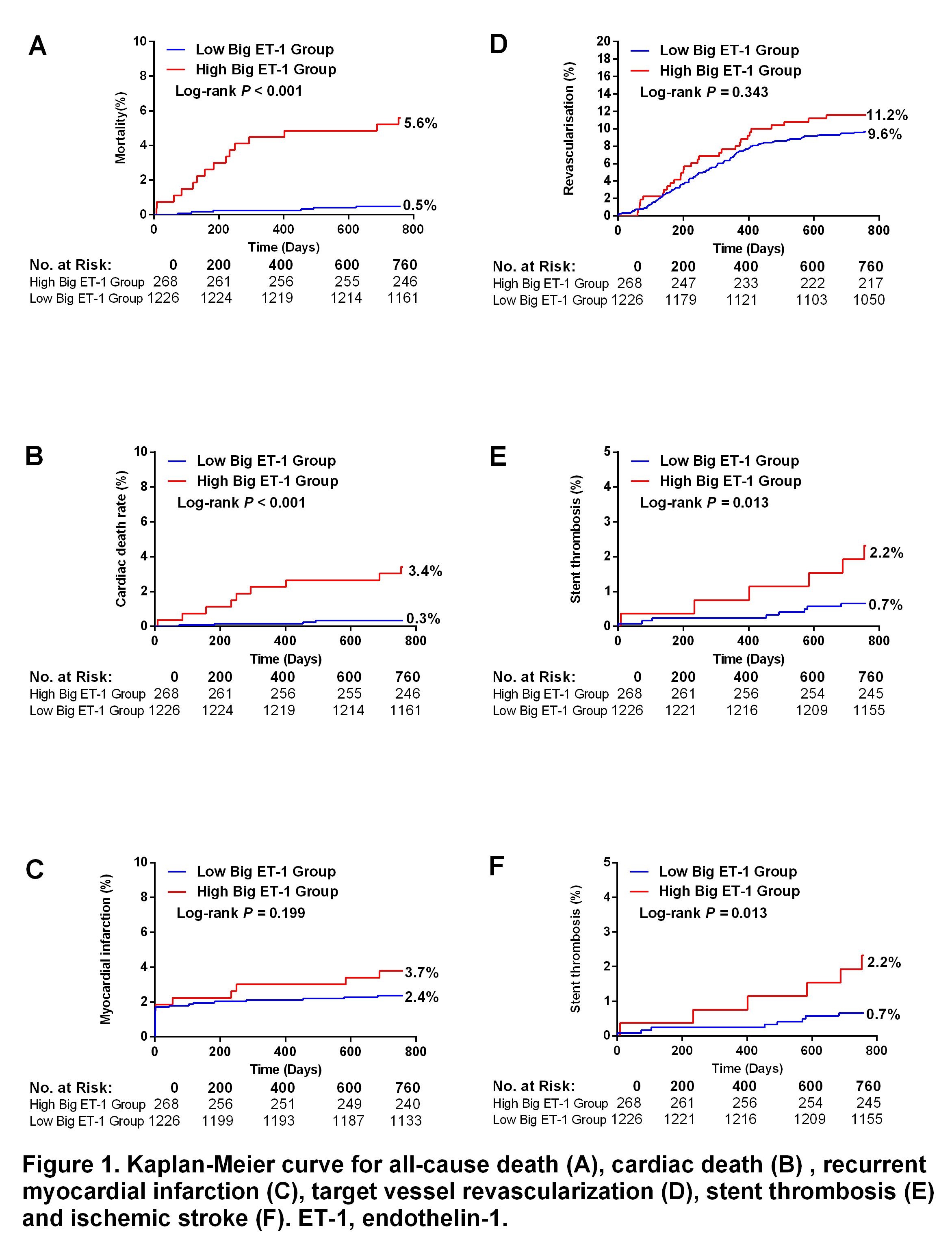 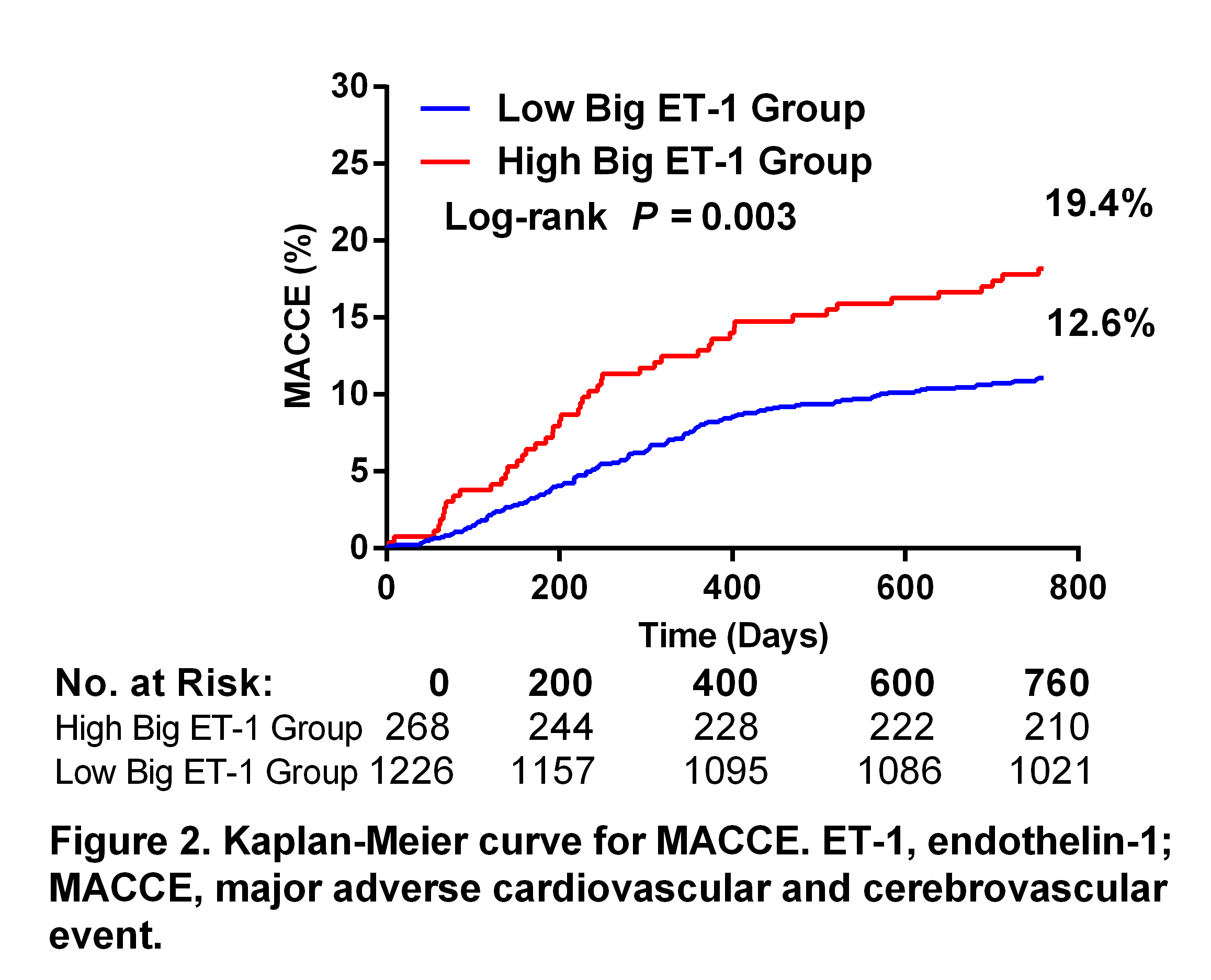 |
|
|
Conclusion:
The admission plasma big ET-1 level was independently associated with 2-year mortality, which may aid in the risk stratification of patients undergoing PCI for AMI.
|
|