Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-180
Atrial Septal Defect With Desaturation in an Elderly Patient : Need to Closed
By Pranai Aroonsiriwattana, Mann Chandavimol
Presenter
Pranai Aroonsiriwattana
Authors
Pranai Aroonsiriwattana1, Mann Chandavimol1
Affiliation
Ramathibodi Hospital, Thailand1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-180
STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE - Congenital Heart Disease (ASD, PDA, PFO, VSD)
Atrial Septal Defect With Desaturation in an Elderly Patient : Need to Closed
Pranai Aroonsiriwattana1, Mann Chandavimol1
Ramathibodi Hospital, Thailand1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
BK
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
An 81-year-old female was presented with 2 weeks history of dyspnea. She had a history of pAF, which was being treated with NOACs. Physical examination revealed an irregular pulse rate 120 bpm and oxygen saturation 90%. Lung auscultation was clear. A cardiovascular examination showed no signs of heaving, trilling, or murmurs. The patient was given furosemide and amiodarone intravenously to control heart rate. Despite these treatments, the patient continued to dyspnea and persistent desaturation.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Chest X-rays revealed cardiomegaly and an enlargement of the pulmonary arteries. The ECG showed NSR with complete RBBB. CTA revealed no evidence of pulmonary embolism. TTE showed good left ventricular systolic function, dilated right ventricle, color doppler flow across the interatrial septum, and moderate TR. TEE revealed an ASD secundum with left to right shunt (size 2.5 x 1.8 cm) and an adequate rim for an ASD closure device, with the exception of the aortic rim which had preferential TR.
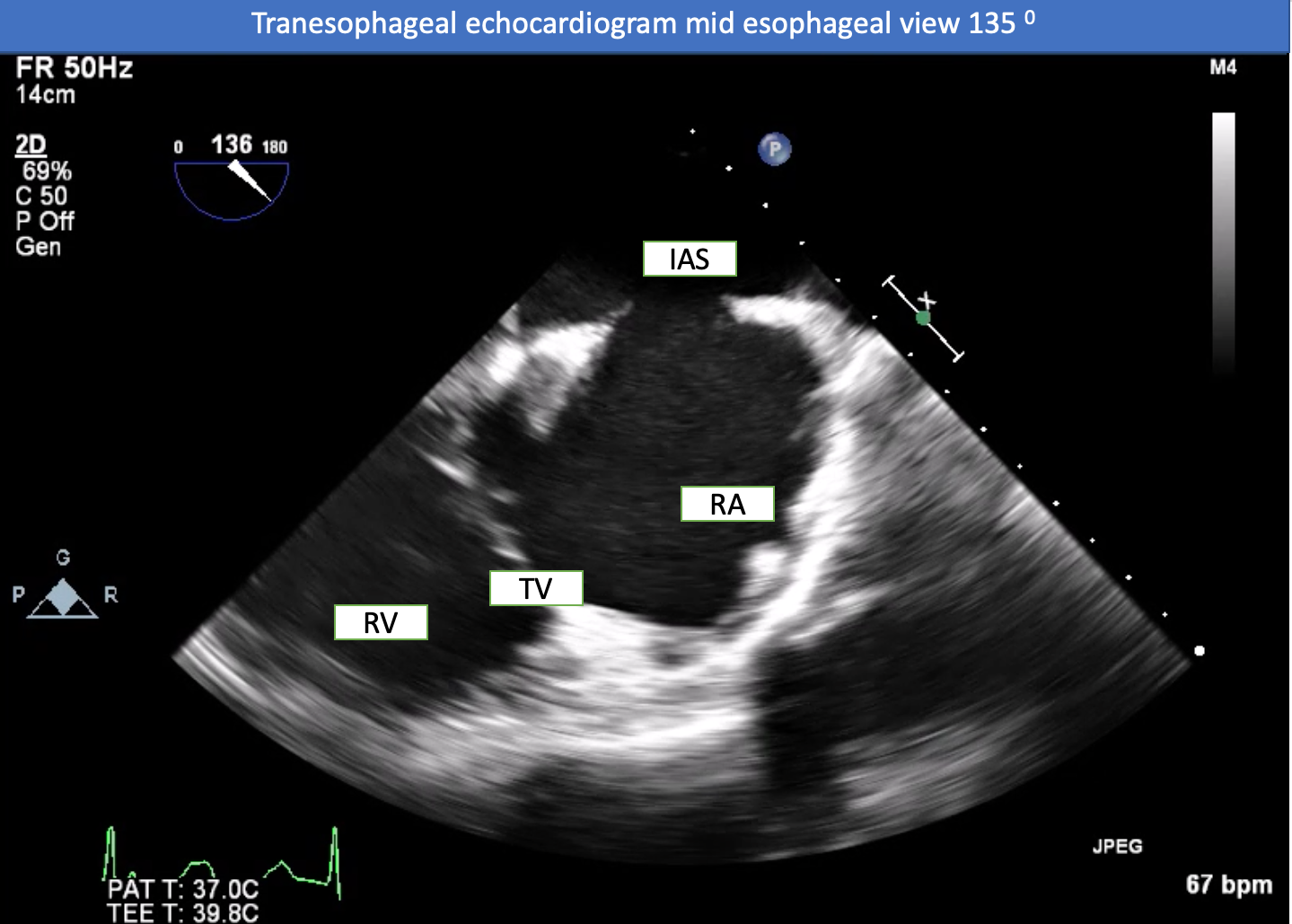
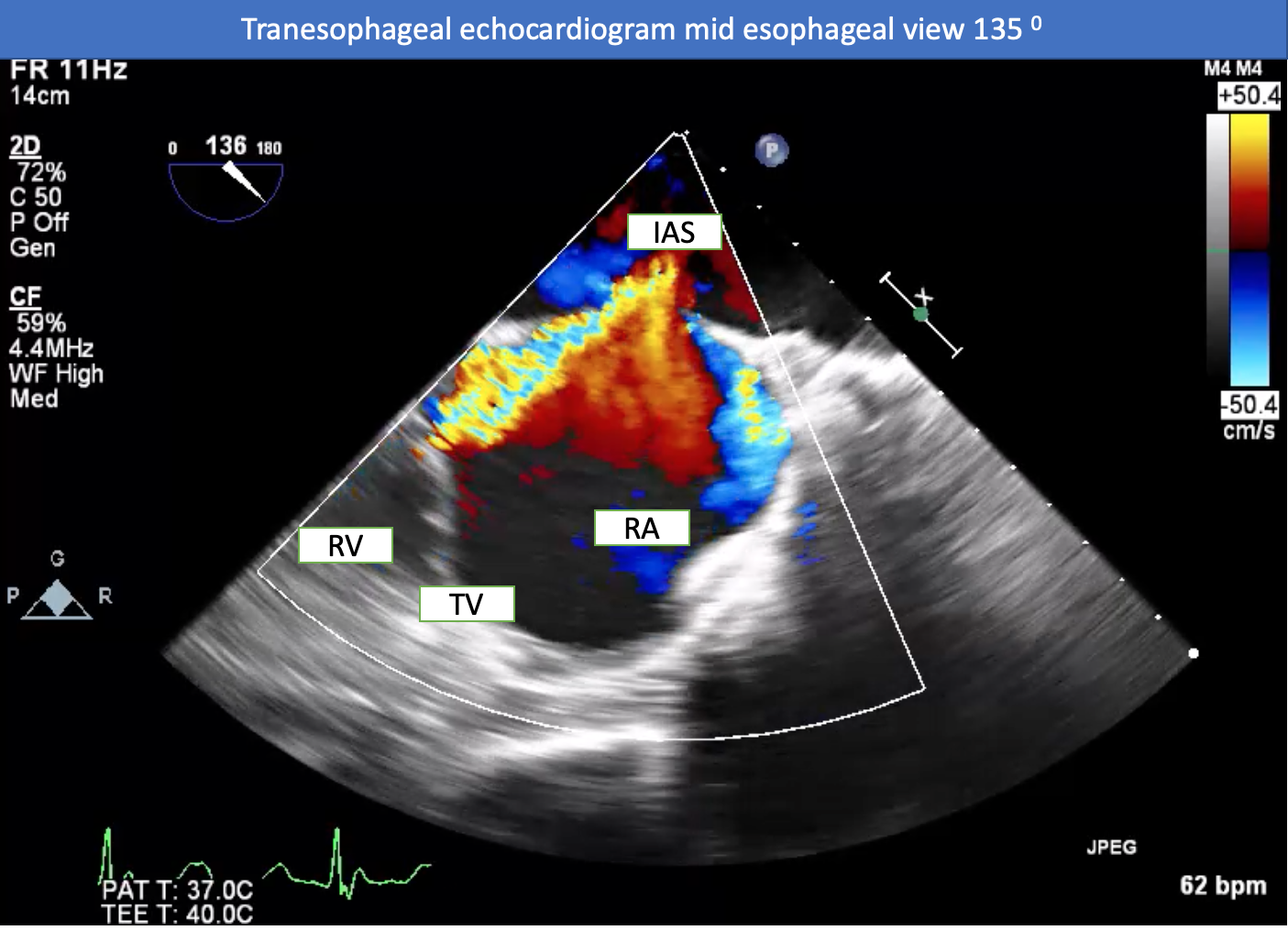


Relevant Catheterization Findings
Right and left heart catheterization was performed. The findings revealed an oxygen step up at the right atrial level, consistent with the prior ASD identified by echocardiography (Qp:Qs 2.51). The mean pulmonary pressure was 19 mmHg, the mean capillary wedge pressure was 6 mmHg, and the LVEDP was 6 mmHg. The oxygen saturation of pulmonary capillary wedge pressure was 95.3%, the left ventricular was 89.6%, and the aortic was 90.3%. The calculated pulmonary vascular resistance was 1.77 WU.
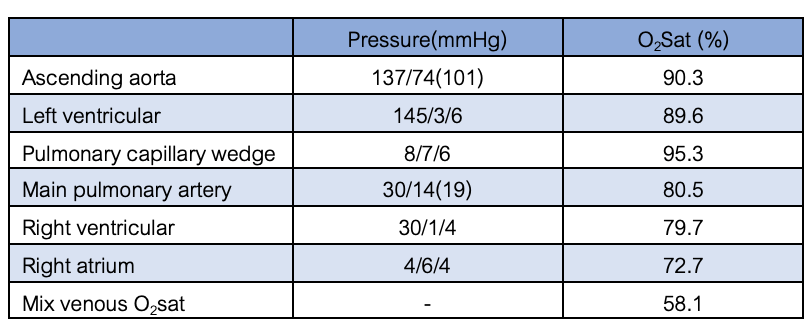

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
A transcatheter closure of the ASD was performed. A 6F multipurpose catheter with a 0.035" Terumo wire was used to cross the interatrial septum (IAS) and advance to the pulmonary vein. The 0.035" Terumo wire was exchanged for an Amplatz Superstiff wire, which was then placed into the pulmonary vein. A 7F femoral vein sheath was exchanged for a 10 Fr delivery sheath. A 24 mm sizing balloon was inflated at the interatrial septum for 5 minutes. A TEE revealed that there was no TR flow across the interatrial septum. The LVEDP did not increase and oxygen saturation from the LV increased from 89.6% to 95%. The 10 Fr delivery system was advanced over the wire into the pulmonary vein (PV). The Amplatz Superstiff wire was then removed together with the introducer catheter. The delivery sheath remained in the PV. A 28 mm septal occluder (Amplatz®) was prepped and loaded into the delivery sheath. The device was deployed across the ASD. The seating of the device was tested to ensure stable positioning. The device remained in place after detachment. Real-time 3D TEE confirmed good positioning of the device with no significant shunt flow across the occluded ASD.
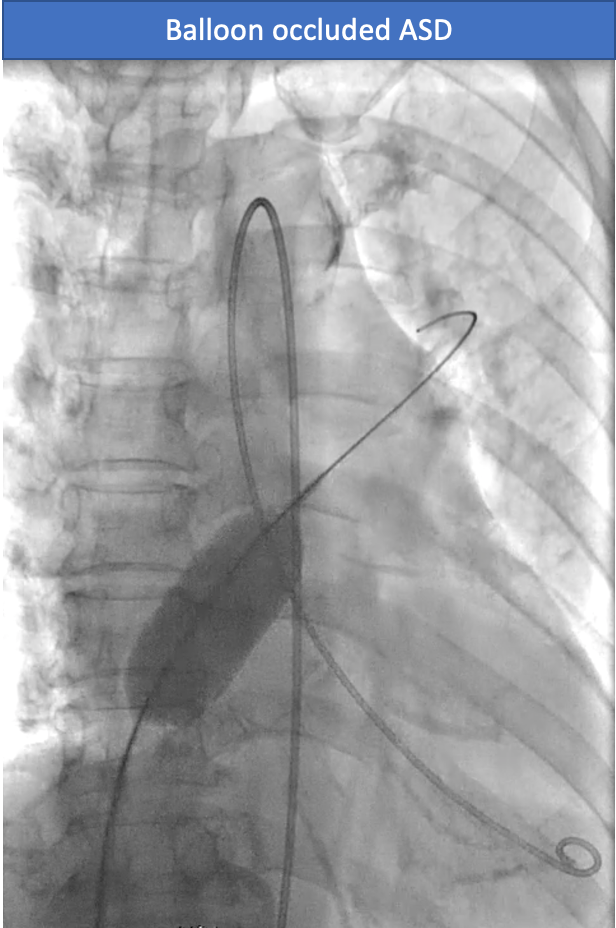
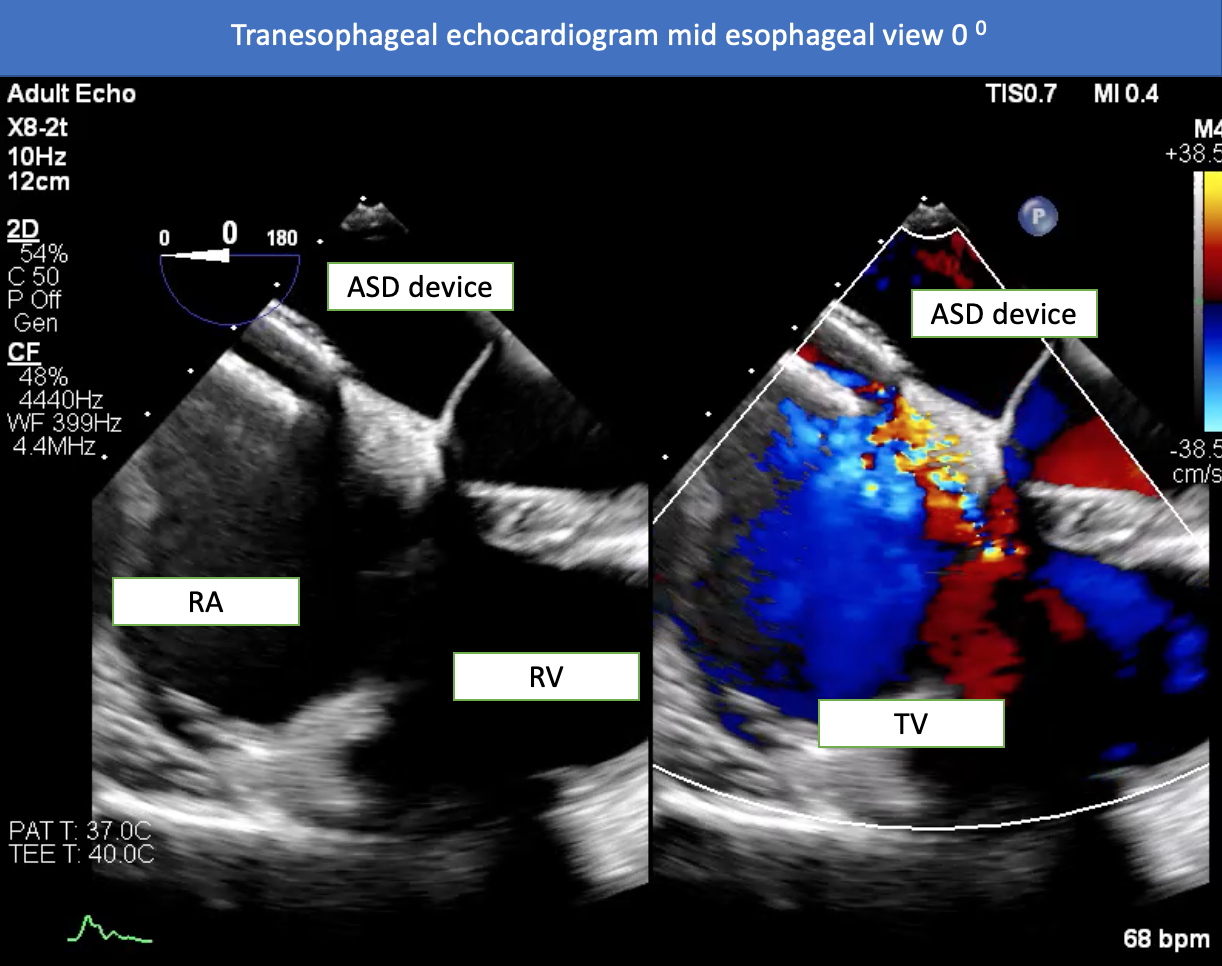


Case Summary
Adults with atrial septal defects (ASD) and systemic desaturation is uncommon, but when present, transesophageal echocardiograms are a useful tool to enhance the clinical and hemodynamic data for patient care, based on the etiology. Eisenmenger's syndrome in a person with ASD is unusual, but in adult ASD patients with cyanosis, there are three major causes: ASD with preferential tricuspid regurgitation (TR), ASD with reduced right ventricular compliance or abnormalities in right ventricular filling, and ASD with thrombus in situ. In this patient, the ASD was found to be associated with preferential TR, and was closed using a percutaneous ASD device closure and showed good results.


